What does a positive Babinski sign mean?
In adults or children over 2 years old, a positive Babinski sign happens when the big toe bends up and back to the top of the foot and the other toes fan out. This can mean that you may have an underlying nervous system or brain condition that's causing your reflexes to react abnormally.
Is Babinski positive or negative?
The Babinski reflex is known by a number of other names: the plantar response (because the sole is the plantar surface of the foot), the toe or big toe sign or phenomenon, the Babinski phenomenon or sign. (It is wrong to say that the Babinski reflex is positive or negative; it is present or absent).
When does the Babinski reflex disappear?
The Babinski sign is common in newborns and typically disappears by 9–12 months. Some older babies still display the reflex at 24 months, but beyond this age, it is usually associated with developmental problems.
What does Babinski reflex mean in medical dictionary?
Response, Babinski: A neurologic reflex that constitutes an important medical examination based, believe it or not, upon what the big toe does when the sole of the foot is stroked. If the big toe goes up, that may mean trouble. The Babinski response is obtained by stimulating the external portion (the outside) of the sole.
Why does Babinski sign happen?
The sign is generally attributed to a lesion of the pyramidal tract. It is of interest to look back on the diagnosis of pyramidal lesions before Remak and Babinski.
What is Babinski's sign and what does it indicate?
In adults or children over 2 years old, a positive Babinski sign happens when the big toe bends up and back to the top of the foot and the other toes fan out. This can mean that you may have an underlying nervous system or brain condition that's causing your reflexes to react abnormally.
What does abnormal Babinski mean?
Signs of Abnormal Babinski Reflex When the bottom of the foot in stimulated in an older child or adult, the toes should curl downward. If the big toe extends upward and the toes flare out as they do for infants and children under two, this may indicate a concerning medical condition.
Where does the Babinski sign indicate damage?
While a response similar to the sign exists when the plantar reflex is elicited in infants, Presence of Babinski's sign in adults can be indicative of a lesion or damage in the corticospinal tract, and identification of the sign remains one of the least-invasive methods for supporting an Upper Motor Neuron damage ...
What does it mean when a child has a Babinski reflex?
When the Babinski reflex is present in a child older than 2 years or in an adult, it is often a sign of a central nervous system disorder. The central nervous system (CNS) includes the brain and spinal cord.
When does babinski reflex disappears?
Babinski reflex is normal in children up to 2 years old. Babinski reflex disappears as the child gets older. It may disappear as early as 12 months.
What nerves are involved in the ascending sensory stimulation?
The descending fibers of the cortical spinal tract normally keep the ascending sensory stimulation from spreading to other nerve roots. When there is damage to the cortical spinal tract, nociceptive input spreads beyond S1 anterior horn cells. This leads to the L5/L4 anterior horn cells firing, which results in the contraction of toe extensors (extensor hallucis longus, extensor digitorum longus) via the deep peroneal nerve.
What is the Babinski reflex test?
The Babinski reflex test is done as part of the routine neurological exam and is utilized to determine the integrity of the cortical spinal tract. The presence of a Babinski sign suggests damage to the cortical spinal tract. Because the cortical spinal tract fiber tracts run from the brain, through the brainstem and into the spinal cord, lesions of the central nervous system (CNS) often affect the integrity of the cortical spinal tract. Thus, the presence or absence of the Babinski reflex can provide very useful information on the presence or absence of pathology affecting the central nervous system. Babinski reflex is especially important in the setting where there is suspicion of spinal cord injury or stroke, as it may be an early indicator of the presence of these emergency conditions 12).
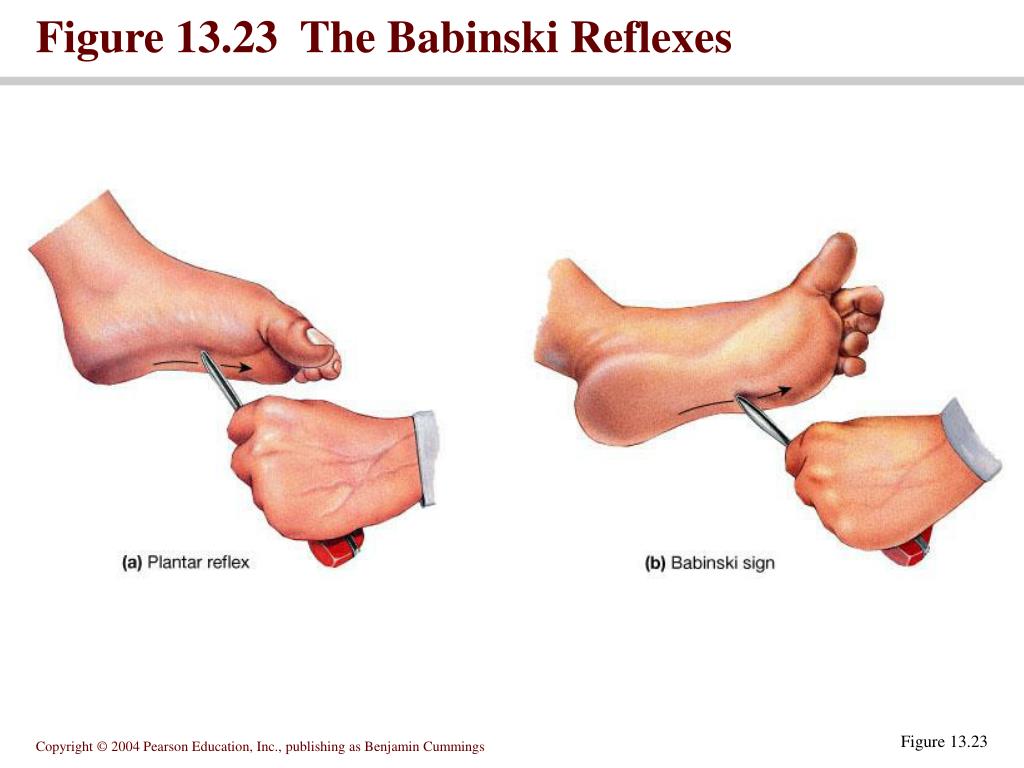
What is the Babinski sign?
Positive Babinski sign occurs when stimulation of lateral plantar aspect of the foot leads to extension (dorsiflexion or upward movement) of the big toe (hallux). Also, there may be fanning of the other toes. This suggests that there is been spread of the sensory input beyond the S1 myotome to L4 and L5.
What is the lateral plantar aspect of the foot?
Stimulation of the lateral plantar aspect of the foot (S1 dermatome) normally leads to plantar flexion of the toes (due to stimulation of the S1 myotome). The response results from nociceptive fibers in the S1 dermatome detecting the stimulation. Nociceptive input travels up the tibial and sciatic nerve to the S1 region of the spine and synapse with anterior horn cells. The motor response which leads to the plantar flexion is mediated through the S1 root and tibial nerve. The toes curl down and inward. Sometimes there is no response to stimulation. This is called a neutral response. This response does not rule out pathology.
What happens when you stroke your foot?
The Babinski reflex occurs after the sole of the foot has been firmly stroked. The big toe then moves upward or toward the top surface of the foot. The other toes fan out .
Brief history
The Babinski reflex was described by the French neurologist Joseph Françoise Félix Babinski in the late 19th century. This author was the first to report this phenomenon at a meeting of the Société de biologie in 1896.
How is the Babinski reflex provoked?
Doctors can elicit the Babinski reflex on a physical exam. To do this, the lateral part of the foot is rubbed with a flat instrument. This is specially designed not to cause pain, discomfort or injury to the skin.
Variants of the Babinski reflex
The Babinski reflex can be tested in different ways. The usual way is the one explained in the previous point, since it seems to be the most reliable.
Causes of the Babinski reflex
The plantar reflex has been understood to involve more movements than just the toes. In most mammals, the extremities automatically retract on a painful stimulus. This defensive reflex is controlled by polysynaptic pathways in the spinal cord.
Neurological immaturity
Most newborns and young children are not neurologically mature, thus showing the Babinski reflex. Unlike the older ones, in babies the flexion is much faster. The toes rise as the ankle, knee, and hip flex.
Reflex responses in the skin
However, the neurophysiology of the Babinski reflex is still not fully understood. From electromyographic studies, it is known that each area of skin appears to have a specific reflex response to noxious stimuli. The purpose of the reflex is to cause the skin to withdraw from such a stimulus.
Big toe reflex
Another normal individual reflex is the big toe reflex. Stimulation of the receptive field of the ball of the foot causes extension of the toe, in addition to flexion of the ankle, knee and hip joints.