Is visceral pericardium the same as epicardium?
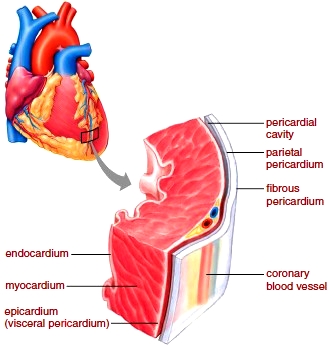
The word "pericardium" means around the heart. The outer layer of the pericardium is called the parietal pericardium. The inner part of the pericardium that closely envelops the heart is, as stated, the epicardium; it is also called the visceral pericardium.
What is the inner most layer of the heart?
The layers of the heart are as follows: Endocardium, the innermost layer of the heart. The myocardium composes the majority of the heart wall (tan), while endocardium composes the inner lining and valves. In this lesson, investigate the layers of the heart wall to better understand how they function and contribute to the circulatory system.
What is the function of pericardial space?
Functions of the pericardium are: (1) to prevent the displacement of the heart during gravitational acceleration or deceleration, (2) to provide a physical barrier that protects the heart against infection and inflammation from the lungs and pleural space, and (3) to provide pain receptors and mechanoreceptors that can.
What is the function of the pericardium?
The pericardium
- Fixes the heart in the mediastinum and limits motion . ...
- Prevents overfilling of the heart It's a relatively in-extendable fibrous layer and it stops the heart from increasing in size too much
- Lubrication A thin fluid, serous between the two layers reduces friction
See more
/heart_interior-570555cf3df78c7d9e908901.jpg)
How does the epicardium protect the heart?
The epicardium is a thin layer of elastic connective tissue and fat that serves as an additional layer of protection from trauma or friction for the heart under the pericardium. This layer contains the coronary blood vessels, which oxygenate the tissues of the heart with a blood supply from the coronary arteries.
What are the three layers of the heart and what is their purpose?
The epicardium is the outer layer that contains blood vessels. The myocardium is the middle layer that is composed of contractile tissues. The endocardium is the innermost layer and composes the valves, inner lining of the chambers, and contains vessels and nerves.
What is the function of the myocardium in the heart?
Cardiac muscle tissue, or myocardium, is a specialized type of muscle tissue that forms the heart. This muscle tissue, which contracts and releases involuntarily, is responsible for keeping the heart pumping blood around the body.
What is the epicardium also known as?
The inner part of the pericardium that closely envelops the heart is, as stated, the epicardium; it is also called the visceral pericardium.
What is epicardium made of?
The epicardium, or the innermost layer of the pericardium, is the outermost layer of the heart itself. It is composed of mesothelial cells, fat, and connective tissue. It is adjacent to the myocardium, the middle muscular layer. The innermost layer is referred to as the endocardium.
What is the protective layer of the heart?
Pericardium: The heart is covered by a double membranous protective layer known as the pericardium. The space that is present between the two pericardial membranes is filled with a fluid called pericardial fluid. It prevents the heart from mechanical injury and shocks and also helps to reduce friction.
What is endocardium of the heart?
The endocardium is the innermost layer of the heart and lines the chambers and extends over projecting structures such as the valves, chordae tendineae, and papillary muscles.
What are the 4 layers of the heart?
The wall of the heart separates into the following layers: epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium. These three layers of the heart are embryologically equivalent to the three layers of blood vessels: tunica adventitia, tunica media, and tunica intima, respectively.
What are the 3 layers of the heart muscle?
The outer layer of the heart wall is the epicardium, the middle layer is the myocardium, and the inner layer is the endocardium.
Is epicardium a layer of the heart?
The walls of the heart are composed of three layers: Epicardium - the outer layer. Myocardium - the middle, muscular layer. Endocardium - the inner layer.
Is the epicardium muscle?
The epicardium is a layer of epithelial cells that wrap the whole heart. This layer mainly contributes to generate smooth muscle cells and cardiac fibroblasts (Lie-Venema et al., 2007).
What is the root of epicardium?
The word [epicardium] is composed by the prefix [epi-], meaning "outer" or "above"; the root term [-card-], meaning "heart"; and the suffix [-ium], meaning "layer" or "membrane".
What are the 3 layers of the heart?
The wall of the heart separates into the following layers: epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium. These three layers of the heart are embryologically equivalent to the three layers of blood vessels: tunica adventitia, tunica media, and tunica intima, respectively.
What are the 3 layers of the heart muscle?
Three distinct layers comprise the heart walls, from inner to outer: Endocardium. Myocardium. Epicardium (inner layer of the pericardium)
What are the 3 layers of pericardium?
The pericardium is the fibrous sac that surrounds the heart. It can be divided into three layers, the fibrous pericardium, the parietal pericardium, and the visceral pericardium. The parietal and visceral pericardia together form the serous pericardium.
Which of the three layers is most important in causing contractions of the heart?
myocardiumThe myocardium is functionally the main constituent of the heart and the thickest layer of all three heart layers. It is a muscle layer that enables heart contractions.
What is the epicardium?
The epicardium refers to the outermost protective layer of the heart. The epicardium is composed of mesothelium, a cell type that covers and protec...
Where is the epicardium located?
The epicardium is located adjacent to the myocardium and surrounds the heart.
What is the function of the epicardium?
There are many functions of the epicardium aside from its main protective role as the outer surface of the heart. It is the innermost layer of the...
What is the difference between the epicardium and the pericardium?
The epicardium is part of the pericardium. It is the innermost layer and is referred to as the visceral layer of the serous pericardium. The main d...
What are the most important facts to know about the epicardium?
The epicardium, or the innermost layer of the pericardium, is the outermost layer of the heart itself. It is composed of mesothelial cells, fat, an...
What is the layer of connective tissue that binds the epicardium to the myocardium and cushions?
Below the mesothelial cells is a layer of adipose and connective tissue that binds the epicardium to the myocardium and cushions the heart. Nerves and blood vessels that supply the heart are found in the epicardium.
What is the myocardium made of?
Histologically, the myocardium is comprised of cardiomyocytes. Cardiomyocytes have a single nucleus in the center of the cell, which helps to distinguish them from skeletal muscle cells that have multiple nuclei dispersed in the periphery of the cell. Cardiomyocytes are very rich in glycogen deposits and mitochondria.
What is the outermost layer of the heart?
The epicardium is the outermost layer of the heart. It is actually the visceral layer of the serous pericardium, which adheres to the myocardium of the heart. Histologically, it is made of mesothelial cells, the same as the parietal pericardium.
Why is the myocardium thicker in the atria than in the ventricles?
This is due to the greater hydrostatic pressure that the ventricles must overcome when pumping the blood into the systemic vessels.
How long does it take for endocarditis to go away?
Infectious endocarditis is treated by intravenous antibiotics for 2 to 6 weeks. If the disease has significantly damaged the heart valves, it is indicated to perform a valve replacement or repair surgery.
What are the layers of the heart?
Histologically, the heart is made of three layers of tissue: epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium. Key facts about the layers of the heart. Epicardium. Visceral layer of serous pericardium. Comprised of mesothelial cells and fat and connective tissues. Myo cardium.
What causes endocarditis?
Usually, it has an infectious etiology. It mostly affects already damaged heart valves and in most cases, is caused by the bacteria Streptococcus viridans. In the case of a healthy heart, the pathogenic bacteria is Streptococcus aureus. No matter what bacteria is the cause, pathogenesis is the same. Once the bacteria carried by the bloodstream reaches the heart valves, they invade the endocardium. Then they cause the destruction of heart tissue, which leads to the formation of friable vegetations composed of necrotic debris (destructed heart cells), thrombi, and microorganisms. Parts of the vegetation can be loosened by the bloodstream and disseminated throughout the body, forming secondary deposits of infection. If the causing bacteria is very virulent, the endocarditis has a fulminant course and often a fatal outcome. On the other hand, when the bacteria are not so virulent they can persist for some time in the heart causing valves deformities.
What is the role of the pericardium in the heart?
The pericardium anchors and protects your heart and allows it to move easily within your chest. When fluid or other substances build up in the pericardium, they can put pressure on your heart and affect its ability to pump blood.
Why is the pericardium important?
The pericardium has a few important roles: It keeps your heart fixed in place within your chest cavity. It prevents your heart from stretching too much and overfilling with blood. It lubricates your heart to prevent friction with the tissues around it as it beats. It protects your heart from any infections that might spread from nearby organs like ...
What causes a tamponade in the heart?
Cardiac tamponade is a condition that’s caused by a buildup of fluid, blood, gas, or a tumor in your pericardial cavity. This buildup places pressure on your heart, which prevents it from filling and emptying properly.
What is the term for the buildup of fluid between the heart and the pericardium?
Pericardial effusion is the buildup of too much fluid between the pericardium and your heart. This can happen from damage or disease in the pericardium. Fluid can also build up if there’s bleeding in your pericardium after an injury.
What is the inner layer of the heart?
Serous pericardium is the inner layer. It’s further divided into two more layers: the visceral and parietal layers. The serous pericardium helps to lubricate your heart.
How rare is a pericardial cyst?
Pericardial cyst. A pericardial cyst is a noncancerous, fluid-filled growth in the pericardium. This type of cyst is very rare, affecting only 1 in 100,000 people. Most people who have pericardial cysts are born with them, but they often aren’t diagnosed until they reach their 20s or 30s.
What are the symptoms of pericardial effusion?
Symptoms of pericardial effusion include: chest pressure or pain. shortness of breath. difficulty breathing when you lie down. nausea. a feeling of fullness in your chest. trouble swallowing.
What is the epicardium made of?
The epicardium is composed primarily of loose connective tissue, including elastic fibers and adipose tissue. The epicardium functions to protect the inner heart layers and also assists in the production of pericardial fluid. This fluid fills the pericardial cavity and helps to reduce friction between pericardial membranes.
What is the outer protective layer of the heart?
Epicardium: the outer protective layer of the heart.
Which layer of the heart is covered by the heart valves?
This layer lines the inner heart chambers, covers heart valves, and is continuous with the endothelium of large blood vessels. The endocardium of heart atria consists of smooth muscle, as well as elastic fibers. An infection of the endocardium can lead to a condition known as endocarditis.
Which layer of the heart is the thickest?
The myocardium is the thickest layer of the heart wall, with its thickness varying in different parts of the heart. The myocardium of the left ventricle is the thickest, as this ventricle is responsible for generating the power needed to pump oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
What are the layers of the heart wall?
It is the cardiac muscle that enables the heart to contract and allows for the synchronization of the heartbeat. The heart wall is divided into three layers: epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium.
What is the heart?
The heart is an extraordinary organ. It is about the size of a clenched fist, weighs about 10.5 ounces and is shaped like a cone. Along with the circulatory system, the heart works to supply blood and oxygen to all parts of the body. The heart is located in the chest cavity just posterior to the breastbone, between the lungs, ...
Which layer of the heart is in direct contact with the myocardium?
Also found in this heart layer are the coronary blood vessels, which supply the heart wall with blood. The inner layer of the epicardium is in direct contact with the myocardium.
