Apart from the transmission of the medulla oblongata
Medulla oblongata
The medulla oblongata is a long stem-like structure located in the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic functions ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure …
Where would the foramen magnum most likely be located?
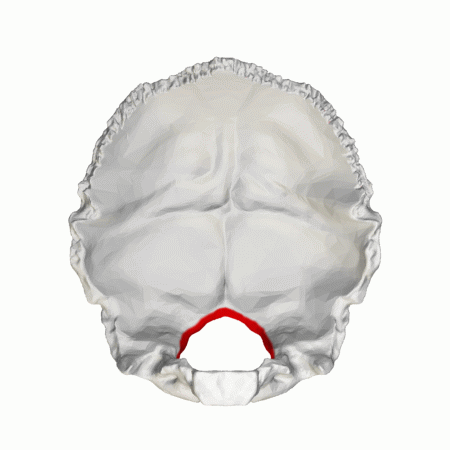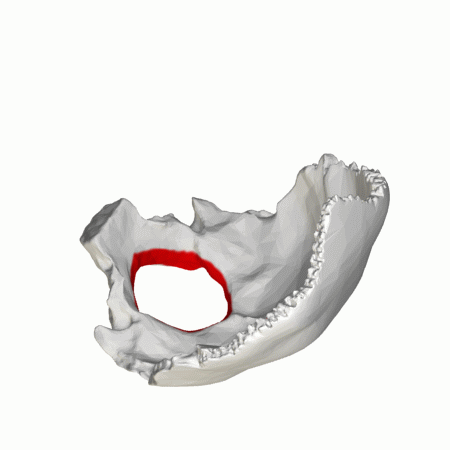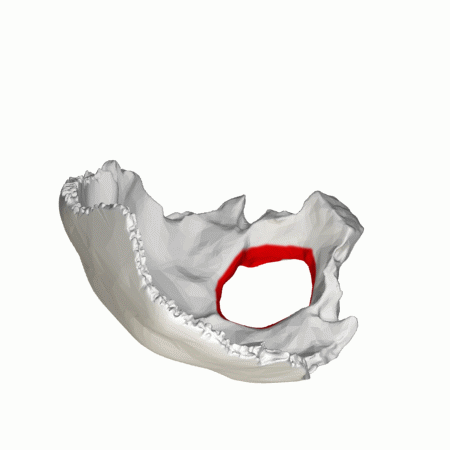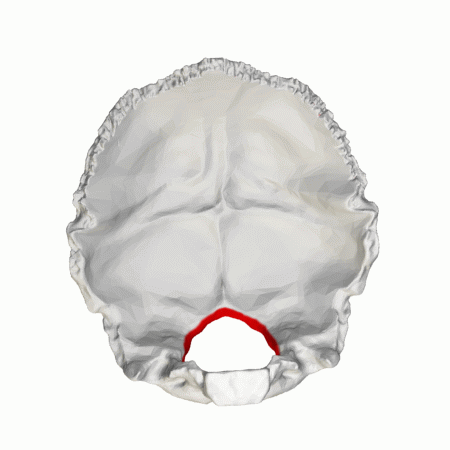
The foramen magnum is situated in the occipital bone, and forms around the base of the brainstem (the medulla oblongata), separating the brain above from the spinal cord below. The foramen magnum in apes and humans is formed by the fusion of the four individual parts of the occipital (pars squama, left and right pars lateralis, and pars basilaris).
What structure passes through the foramen magnum?
- Foramen Magnum :- spinal cord, anterior spinal artery, posterior spinal artery, vertebral artery, sympathetic plexus, three meninges.
- Jugular Foramen :- internal jugular vein, Inferior petrosal sinus, 9th 10th 11th cranial nerve
- Foramen Ovale :- Lesser petrosal nerve, mandibular nerve, accessory meningeal artery, emissory veins.
What bone would you find the foramen magnum?
The foramen magnum is the largest foramen of the skull. It is located in the most inferior portion of the cranial fossa as a part of the occipital bone. Its contents include the medulla oblongata, meninges, spinal root of cranial nerve XI, vertebral arteries, anterior and posterior spinal arteries, the tectorial membrane, and alar ligaments.
What does the foramen magnum pass through?
It transmits several structures that are listed below (from superior to inferior):
- Lacrimal nerve (branch of the ophthalmic nerve, the first division of the trigeminal nerve)
- Frontal nerve (branch of the ophthalmic nerve, the first division of the trigeminal nerve)
- Superior ophthalmic vein
- Trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- Superior division of the Oculomotor nerve (CN III)
See more

What does the foramen magnum protect?
TerminologyEnglish: Foramen magnum Latin: Foramen magnum, Foramen magnum ossis occipitalisDefinitionLarge oval-shaped opening in the occipital boneFunctionsPassage of the spinal cord and meninges; vertebral arteries; anterior and posterior spinal arteries; dural veins; spinal roots of the accessory nerve
What is in foramen magnum?
human skull The foramen magnum, the opening through which the brain and the spinal cord make connection, is in the lowest part of the fossa. Between its forward margin and the base of the dorsum sellae is a broad, smooth, bony surface called the clivus (Latin for “hill”).…
Why is the foramen magnum an important landmark?
The foramen magnum as a transition area between skull and spine plays an important role as a landmark, because of its close relationship to vital structures such as the brain and spinal cord.
What vessels pass through foramen magnum?
Apart from the transmission of the medulla oblongata and its membranes, the foramen magnum transmits the vertebral arteries, the anterior and posterior spinal arteries, the tectorial membranes and alar ligaments.
Which describes the foramen magnum quizlet?
Describe the location of the foramen magnum and its function? The foramen magnum is the opening in the skull, which the spinal chord passes through.
Why is the foramen magnum located where it is in humans?
The anterior position of the human foramen magnum is often explained as an adaptation for maintaining balance of the head atop the cervical vertebral column during bipedalism and the assumption of orthograde trunk postures.
How does the foramen magnum relate to movement?
If the foramen magnum indicates the position of the spine in relation to the head, and therefore whether the creature was bipedal or moved about some other way, then the position of the opening might indicate when our ancestors developed the upright, bipedal posture so often taken to be the hallmark of humanity.
What is the hole in the skull called?
Foramen magnum: You can't miss this one! The name in Latin means “great hole” and it has to be relatively large to allow the lower end of the brainstem and the upper end of the spinal cord to pass through. Importantly, the foramen magnum also allows the vertebral arteries to enter the skull.
Do veins pass through the foramen magnum?
While smaller foramina allow nerves and veins to cross through bone tissue, the foramen magnum is large enough to convey larger structures such as the medulla oblongata, brain membranes (meninges), blood vessels, nerves, and ligaments.
How do you memorize the foramen of the skull?
A mnemonic phrase that I've used to help remind us of the anatomical locations and names of the paired foramina in the cranial floor is this: Old Rotund Owls Spin Lazily Across Jugs.
What passes through each foramen?
In anatomy, a foramen is any opening. Foramina inside the body of humans and other animals typically allow muscles, nerves, arteries, veins, or other structures to connect one part of the body with another. The human skull has numerous foramina through which cranial nerves, arteries, veins, and other structures pass.
How big is the foramen magnum?
Morphometry of the foramen magnum [20,22] Adult females have a reported mean transverse diameter ranging from 25.45 to 31.34 mm,[21,23] whereas adult males have a reported mean transverse diameter ranging from 26.92 to 38.0 mm.
What passes through the foramen spinosum?
The foramen spinosum permits the passage of the middle meningeal artery, middle meningeal vein, and the meningeal branch of the mandibular nerve.
What passes through the optic canal?
The optic canal transmits the optic nerve, ophthalmic artery, and sympathetic nerve fibers.
What passes through the vertebral foramen?
function in vertebral column arch surround an opening, the vertebral foramen, through which the spinal cord passes.
What is the hole in the skull called?
On the bottom of your skull, there is a distinctive hole. The technical name for the opening is the foramen magnum – the “great hole” that the spinal cord and other critical soft tissues run through.
Where is the foramen magnum located?
The foramen magnum is the largest foramen of the skull. It is located in the most inferior portion of the cranial fossa as a part of the occipital bone. Its contents include the medulla oblongata, meninges, spinal root of cranial nerve XI, vertebral arteries, anterior and posterior spinal arteries, the tectorial membrane, and alar ligaments.
What are the two points of the foramen magnum?
On the foramen magnum, there are two craniometric points: the basion, the median point of the front edge of the hole, and the opisthion, posterior correspondence.
What is the anatomical variance of the foramen magnum?
The anatomical variance of the foramen magnum may have some impact on certain surgical procedures such as vertebral artery and posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysm repairs, foramen magnum meningioma resections, and foramen magnum decompression among others. In an ovoid type foramen magnum, it is difficult for a surgeon to adequately expose the anterior portion of the foramen. Additionally, the occipital condyle and jugular tubercle are the main bony prominence obstructing the anterolateral portion of the foramen magnum. Extension of the occipital condyles into the foramen magnum may indicate the need for more extensive bony removal in certain procedures. [7]
What are the sclerotomes of the occipital bone?
These sclerotomes derive membrane and cartilage, the developmental origin of the occipital bone. Four primary cartilaginous centers, the anterior basioccipital (basilar), the lateral exoccipitals (condylars), and the posterior supraoccipital (squamous), in addition to a fifth membranous element, referred to as the interparietal combine around the foramen magnum to form the occipital bone. The mendosal suture runs horizontally between the developing inferior supraoccipital and superior interparietal bones. [2]
What bone do fetuses fuse?
Fetuses at 9 weeks gestation have an ossification center around the hypoglossal canal in each exoccipital part and a single median ossification center in the basioccipital cartilage.[3] At 12 weeks gestation, a pair of ossification centers in the supraoccipital cartilage fuse together to form the supraoccipital bone. Rostral to the supraoccipital bone, the second pair of ossification centers in the membranous portion fuse to form the interparietal bone.[4] The intraparietal portion ossifies intramembranous while the rest of the occipital bone ossifies endochondrally utilizing cartilage as a precursor.[1] The supra occipital and interparietal bones then fuse midline, but at this point in development are still separated laterally by the mendosal suture. At 14 weeks, ossification of the basioccipital occurs and advances laterally into the ventral portion of the condylars, while concurrently the ventral portions advance into the dorsal portions. Also, during the 14th week, the fusion of the supraoccipital and interparietal bones progress almost to completion. The full union of these segments does not occur until between 2 and 4 years of age.[3] By the 16th week of fetal development, all intramembranous ossification centers are generally fused forming a lattice of trabeculae overlaying the external surface of the occipital squama.[4] The exoccipitals remain separated from both the basioccipital and the supraoccipital segments by synchondroses and will not fuse until between 2 and 4 years of age. [3]
Why is the foramen important?
The position of the foramen is essential for posture in orthostatism, as it allows a correct relationship between the skull and the cervical spine.In fossil hominins, the position of the foramen is indicative of the bipedalism of our ancestors.
What is the process of developing bones in the skull?
All the bones of the skull develop from paraxial mesoderm and neural crest cells. During gastrulation in the third week, mesenchymal cells migrate through the primitive streak to form the mesoderm. At the end of the third week, the paraxial mesoderm is segmented into somites that differentiate to become sclerotomes.[1] During the fourth week, the occipital sclerotomes concentrate around the notochord under the influence of signals from the rhombencephalon.
What is the position of the foramen magnum?
Accordingly the position and orientation of the foramen magnum is considered to be a reliable reflection of mode of locomotion in fossil hominins. The foramen magnum position has been cited as evidence of bipedal locomotion (a hominin characteristics), so fossil hominins are classified based on evidence of an anteriorly placed foramen magnum, ...
Where is the foramen magnum located?
The foramen magnum is situated in the occipital bone, and forms around the base of the brainstem (the medulla oblongata), separating the brain above from the spinal cord below.
Which position of the foramen magnum helps to balance the mass of the head above the vertebrae?
In orthograde (upright), bipedal humans have a cranium that rests atop the vertebral column: the anterior position of the foramen magnum helps to balance the mass of the head above the vertebrae, and its inferior orientation reflects the anatomical relationship between the cranium and vertebral column. In pronograde (with a body more parallel ...
Which ape has the most posteriorly positioned foramen magnum?
In addition to being more posteriorly positioned, the foramen magnum in apes is more vertically oriented (opening backwards and downwards, rather than directly downwards). Pongo have the most anteriorly situated foramen magnum of the apes, but the most vertically oriented. During growth of the occipital bone, human have proportionately less ...
What is a Foramen?
The Latin word foramen means an aperture or opening. Most foramina are found in the facial bones and cranial bones.
What is the cranial foramen?
Cranial Foramen. A cranial foramen allows important nervous and circulatory tissue to travel throughout the head and neck region. The following headings list the singular or paired name, location, and the structures that pass through each aperture.
What is the single foramen cecum?
Single foramen cecum; shared between the frontal crest of the temporal bone and the ethmoid bone, between the cranium and nasal cavity; emissary veins.
Where is the Paired Foramen lacerum located?
Paired foramen lacerum; the end of the shared carotid canal that begins at the carotid f. (temporal bone); located next to the sella turcica; nerve and artery of the pyterygoid canal, internal carotid artery, and emissary vein.
What is the procedure called when the parietal foramina is enlarged?
Alternatively, parietal foramina can be so enlarged that, when found in ancient remains, archeologists think that the person has undergone an early surgical procedure called trepanning or trepanation.
What is the result of mirrored notches in multiple bone articulations that, when put together, form a?
Some foramina are the result of mirrored notches in multiple bone articulations that, when put together, form a circular hole; in this case, the information is repeated.
Which ventricle is linked by the paired foramen of Luschka?
The paired foramen of Luschka links the fourth ventricle to the cerebellopontine cistern.