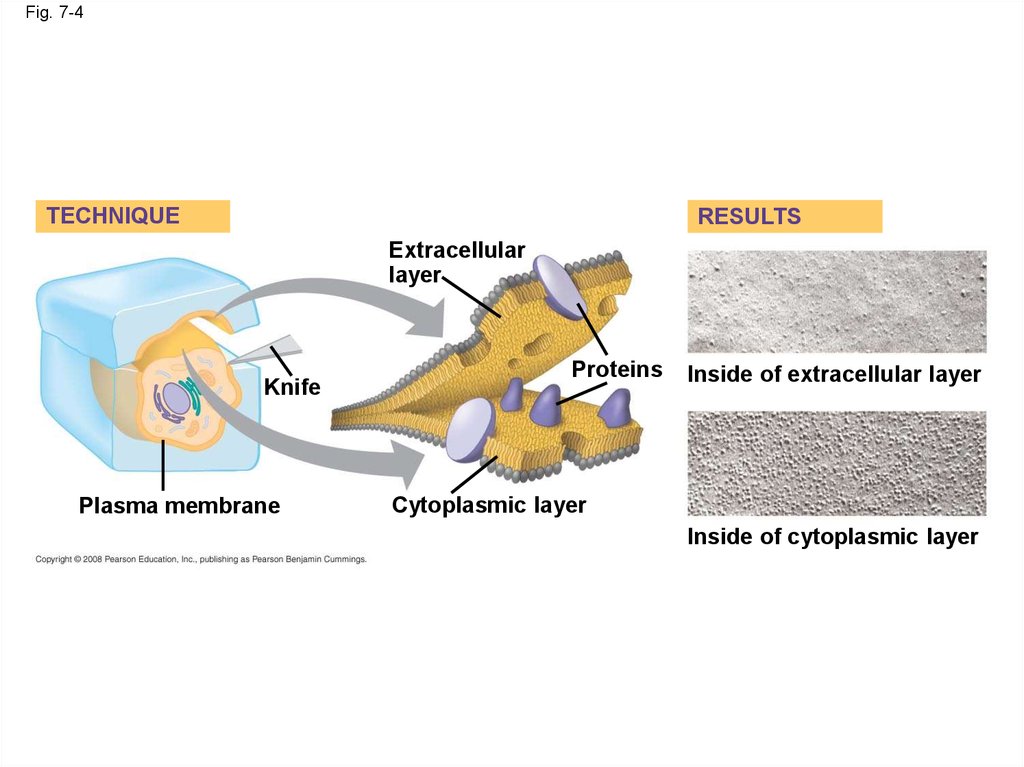
What is the outer membrane function?
The outer membrane has several important functions. It acts as a permeability barrier to solutes; it hinders the entry of some antibiotics and protects the cell wall peptidoglycan from lysozyme, which can degrade peptidoglycan, leading to cell lysis. The outer membrane is a highly organized structure with an asymmetrical lipid bilayer.
What are the six functions of membrane proteins?
What are the 6 functional classes of membrane proteins? Terms in this set (6) transport proteins. provide a means of regulating the movement of substances across the plasma membrane. cell surface receptors. bind specific molecules that are called ligands. identity markers. enzymes. anchoring sites. cell-adhesion proteins.
What functions does the cell membrane perform?
What are the 7 functions of the plasma membrane?
- A Physical Barrier. …
- Selective Permeability. …
- Endocytosis and Exocytosis. …
- Cell Signaling. …
- Phospholipids. …
- Proteins. …
- Carbohydrates. …
- Fluid Mosaic Model.
What are the functions of membrane receptors?
Publication types
- Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't
- Research Support, U.S. Gov't, Non-P.H.S.
- Research Support, U.S. Gov't, P.H.S.
- Review

What is the purpose of the inner membrane of the mitochondria?
Consequently, the inner mitochondrial membrane is the functional barrier to the passage of small molecules between the cytosol and the matrix and maintains the proton gradient that drives oxidative phosphorylation.
What is the function of the inner and outer membrane?
The outer membrane has many protein-based pores that are big enough to allow the passage of ions and molecules as large as a small protein. In contrast, the inner membrane has much more restricted permeability, much like the plasma membrane of a cell.
What is the inner membrane system?
The endomembrane system separates the cell into different compartments, or organelles, such as the nucleus, the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), the Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes (see Table 2.2). The endomembrane system is derived from the ER and flows to the Golgi apparatus, from which lysosomes bud.
What is the function of inner membrane in chloroplast?
The inner membrane of the chloroplast forms a border to the stroma. It regulates the passage of materials in and out of the chloroplast. In addition to regulation activity, fatty acids, lipids, and carotenoids are synthesized in the inner chloroplast membrane.
What is the difference between inner membrane and Intermembrane?
The intermembrane space located between outer and inner membrane contains proteins have a critical role in mitochondrial energetics and apoptosis (process of programmed cell death). Unlike the outer membrane, the inner membrane is highly impermeable to the ions and molecules.
Where is the inner membrane space?
The intermembrane space (IMS) is the space occurring between or involving two or more membranes. In cell biology, it is most commonly described as the region between the inner membrane and the outer membrane of a mitochondrion or a chloroplast.
What is the inner membrane of mitochondria called?
cristaeExplanation: Inner membrane foldings of mitochondria are called cristae. They increase the surface area.
What is the function of the outer membrane?
The outer membrane has several important functions. It acts as a permeability barrier to solutes; it hinders the entry of some antibiotics and protects the cell wall peptidoglycan from lysozyme, which can degrade peptidoglycan, leading to cell lysis.
What is the function of the outer membrane?
The outer membrane has several important functions. It acts as a permeability barrier to solutes; it hinders the entry of some antibiotics and protects the cell wall peptidoglycan from lysozyme, which can degrade peptidoglycan, leading to cell lysis.
What is the specific function of outer membrane?
The outer membrane protects Gram-negative bacteria against a harsh environment. At the same time, the embedded proteins fulfil a number of tasks that are crucial to the bacterial cell, such as solute and protein translocation, as well as signal transduction.
What is the outer membrane of the cell?
The outer membrane is an integral component of the cell envelope of Gram-negative bacteria, where it is thought to act as a selective permeability barrier mainly. It is composed of (lipo)proteins, phospholipids, and lipopolysaccharides (LPSs).
What is the outer membrane called?
the plasma membraneThe cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is found in all cells and separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable.
How the outer mitochondrial membrane is different from inner mitochondrial membrane?
Outer membrane is different from inner membrane of mitochondria in several aspects. For example outer membrane is permeable for ions and small unch...
What is the role of the inner mitochondrial membrane?
The inner mitochondrial membrane is the site of electron transport chain reactions and the synthesis of ATP. The protein and enzyme complexes invol...
What does the inner mitochondrial membrane do in ATP synthase?
Electron transport chain generate a proton concentration gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane. This proton gradient drives ATP synthesi...
Mitochondria Membranes
A mitochondrion is a double membrane containing organelle each having distinct functions. The outer membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer similar to any eukaryotic membrane and contains around 5% mitochondrial proteins with an abundance of porin proteins.
Inner Mitochondria Membranes
The inner membrane is home to numerous proteins and enzyme complexes especially related to cellular respiration and protein transportation. Proteins and enzymes of the inner membrane of mitochondria can be categorized by the functions they perform:
Processes of Inner Mitochondria Membranes
Inner membranes of the mitochondria are sites where the last phase of cellular respiration occurs. All the protein and enzyme complexes involved in this step are embedded in the inner membrane. Aerobic cellular respiration occurs in three steps:
What is the inner mitochondrial membrane made of?
The mitochondrial inner membrane is made primarily of a phospholipid bilayer, just like the cell membrane. Embedded in this bilayer are various proteins that serve to carry out the electron transport chain.
Which membrane carries out electron transport?
The mitochondrial inner membrane carries out electron transport with the products of the citric acid cycle. It channels H+ ions into the inter-membrane space with a negative electric current generated by electron transport.
What is the role of the mitochondria in aerobic respiration?
The mitochondrial inner membrane is the site of the electron transport chain, an important step in aerobic respiration. Between the inner membrane and outer membrane is the inter-membrane space. There, H+ ions build up to create a proton potential that helps power the ATP energy formation. ATP is the energy currency of the cell.
What is the mitochondria?
The mitochondria is known as the powerhouse of the cell and exists in all eukaryotic cells, able to extract a significant amount of energy from each glucose molecule. The mitochondrion has an outer membrane and an inner membrane. The mitochondrial inner membrane is the site of the electron transport chain, ...
Which membrane is involved in aerobic respiration?
The inner membrane of the mitochondrion is involved in the final step in aerobic respiration. Discover the intricacies of this membrane and how it is the key to unlocking the full energy potential of food. Create an account.
Which products are sent to the electron transport chain?
The Electron Transport Chain. The products of the citric acid cycle are sent to the electron transport chain. These products are NADH and FADH2. They contribute electrons to the electron transport chain, where they create a negative current along the inner membrane.