
What is the purpose of tubular reabsorption? Tubular reabsorption is the process that moves solutes and water out of the filtrate and back into your bloodstream.
What are the three processes of urine formation?
Urine is formed in the kidney’s nephrons by a combination of following three processes:
- Filtration
- Tubular Secretion
- Reabsorption
What happens in the nephron During secretion or reabsorption?
In renal physiology, reabsorption or tubular reabsorption is the process by which the nephron removes water and solutes from the tubular fluid (pre-urine) and returns them to the circulating blood. What is the difference between selective reabsorption and tubular secretion? Selective reabsorbtion occurs in the PCT.
What is tubular secretion and where does it occur?
What is tubular secretion and where does it occur? Tubular secretion is the transfer of materials from peritubular capillaries to the renal tubular lumen and occurs mainly by active transport and passive diffusion. What is absorbed and secreted in the nephron? Each nephron begins with a filtration component that filters the blood entering the kidney.
What are the steps in urine formation?
The Three Processes of Urine Formation
- Filtration. Stage 1: filtration. The kidney is the body's blood filtering system. ...
- Reabsorption. Stage 2: reabsorption. The filtrate enters the kidney in the proximal tubule. ...
- Secretion. Stage 3: secretion. The filtrate then passes through a really neat structure called the Loop of Henle where it gains and loses water and salt.
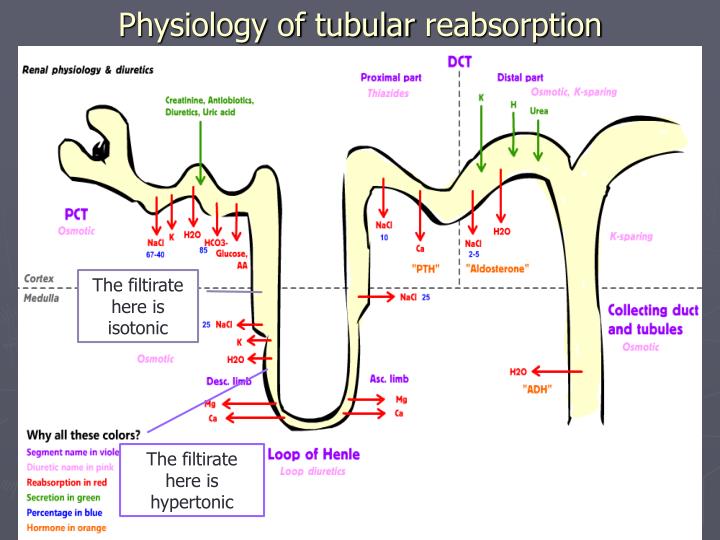
What is the purpose of tubular reabsorption quizlet?
what is the purpose of tubular reabsorption? Tubular reabsorption allows the body to reclaim any needed materials from the kidneys after glomerular filtration. Glomerular filtration is the process of forcing water, salts, urea and glucose from the blood through a membrane via pressure.
What is the purpose of the reabsorption process?
Reabsorption allows many useful solutes (primarily glucose and amino acids), salts and water that have passed through Bowman's capsule, to return to the circulation.
What happens in tubular reabsorption quizlet?
Tubular reabsorption is the process by which the body reclaims substances within the filtrate that it wants to keep. Most reabsorption is an active process using membrane carriers. Substances that are typically reabsorbed include amino acids, glucose, and ions.
Why is reabsorption in the kidneys important?
Reabsorption Moves Nutrients and Water Back into the Bloodstream. The glomerulus filters water and small solutes out of the bloodstream. The resulting filtrate contains waste, but also other substances the body needs: essential ions, glucose, amino acids, and smaller proteins.
What is tubular reabsorption and secretion in the kidney?
Glomerular filtration produces ultrafiltrate of plasma, i.e. without proteins. Some substances are reabsorbed almost entirely and returned to circulation while others are secreted to remove substances from the peritubular capillary blood.
Where does tubular reabsorption occur?
Tubular reabsorption is the second major step in urine formation. Most of the reabsorption of solutes necessary for normal body function, such as amino acids, glucose, and salts, takes place in the proximal part of the tubule.
What describes the process of reabsorption in the kidneys quizlet?
Describe the process of reabsorption. Reabsorption is the removal of water and solutes from the filtrate. It takes place after the filtrate has left the renal corpuscle, in the PCT. It is a selective process, involving simple diffusion and carrier proteins.
What occurs during tubular secretion?
Tubular secretion involves the removal of toxic substances from the blood capillaries and tissue and their active secretion into the nephron. Metabolic wastes such as urea, uric acid, ammonia and hydrogen ions are secreted into the fluid within the nephron.
What does reabsorption mean in kidney?
Being absorbed againReabsorption: Being absorbed again. For example, the kidney selectively reabsorbs substances it has already secreted into the renal tubules, such as glucose, protein, and sodium. These reabsorbed substances are returned to the blood.
What describes the process of reabsorption in the kidneys quizlet?
Describe the process of reabsorption. Reabsorption is the removal of water and solutes from the filtrate. It takes place after the filtrate has left the renal corpuscle, in the PCT. It is a selective process, involving simple diffusion and carrier proteins.
What happens in the nephron during reabsorption?
Tubule reabsorption is the process by which molecules from the glomerular filtrate are returned back to the plasma. This occurs along the entire nephron unit.
Where does reabsorption occur in the kidney?
Most of the reabsorption of solutes necessary for normal body function, such as amino acids, glucose, and salts, takes place in the proximal part of the tubule. This reabsorption may be active, as in the case of glucose, amino acids, and peptides, whereas water, chloride, and other ions are passively reabsorbed.
What is the process of reabsorption?
Reabsorption is a finely tuned process that is altered to maintain homeostasis of blood volume, blood pressure, plasma osmolarity, and blood pH. Reabsorbed fluids, ions, and molecules are returned to the bloodstream through the peri-tubular capillaries, and are not excreted as urine.
What is reabsorption in the kidney?
Reabsorption in the nephron may be either a passive or active process, and the specific permeability of the each part of the nephron varies considerably in terms of the amount and type of substance reabsorbed. The mechanisms of reabsorption into the peri-tubular capillaries include: 1 Passive diffusion—passing through plasma membranes of the kidney epithelial cells by concentration gradients. 2 Active transport—membrane-bound ATPase pumps (such as NA + /K + ATPase pumps) with carrier proteins that carry substances across the plasma membranes of the kidney epithelial cells by consuming ATP. 3 Cotransport—this process is particularly important for the reabsorption of water. Water can follow other molecules that are actively transported, particularly glucose and sodium ions in the nephron.
What is the process by which solutes and water are removed from the tubular fluid and transported into the blood?
Tubular reabsorption is the process by which solutes and water are removed from the tubular fluid and transported into the blood.
What is the function of the kidney?
Proper function of the kidney requires that it receives and adequately filters blood. Reabsorption includes passive diffusion, active transport, and cotransport. Water is mostly reabsorbed by the cotransport of glucose and sodium.
Where do substances pass through the renal epithelial cells?
These processes involve the substance passing though the luminal barrier and the basolateral membrane, two plasma membranes of the kidney epithelial cells, and into the peri-tubular capillaries on the other side. Some substances can also pass through tiny spaces in between the renal epithelial cells, called tight junctions.
Is reabsorption passive or active?
Namely filtration, reabsorption, secretion, and excretion. Reabsorption in the nephron may be either a passive or active process, and the specific permeability of the each part of the nephron varies considerably in terms of the amount and type of substance reabsorbed.
Is the final osmolarity of urine dependent on the final collecting tubules and duct?
The final osmolarity of urine is therefore dependent on whether or not the final collecting tubules and ducts are permeable to water or not, which is regulated by homeostasis.
