Important Points
- The main point is that the quantity theory of money states that the quantity of money will determine the value of money.
- So, to stop inflation, economies need to check the supply of money.
- This theory assumes that the output of goods and velocity remain constant.
Why quantity theory of money is wrong?
Why quantity theory of money is wrong? First, the contention that money stock increases induce direct and proportional changes in the price level is empirically questionable (De Grauwe and Polan 2005). Secondly, there is the direction of causation. Why velocity is constant in quantity theory of money?
What is the definition of Quantity Theory?
quantity theory n (Economics) economics a theory stating that the general price level varies directly with the quantity of money in circulation and the velocity with which it is circulated, and inversely with the volume of production expressed by the total number of money transactions
What are the functions of money economics?
- Money as a medium of exchange enables a person to buy or sell at different points of time.
- It has separated the acts of sale and purchase.
- A buyer can buy goods through money, and the seller can sell goods for money.
- Thus, buyers and sellers of goods/ services can solve their purposes with the help of money by using it as a medium of exchange.
What is the quantity theory of inflation?
The quantity theory of money reveals a very important truth. That is, if a state expands its money supply to cover its spending, the end result will be rapid inflation. Examples: During the First World War, Germany printed large sums of money (by expanding money) to cover its war expenses.

What is meant by quantity theory of money?
Definition: Quantity theory of money states that money supply and price level in an economy are in direct proportion to one another. When there is a change in the supply of money, there is a proportional change in the price level and vice-versa.
What is the formula for quantity theory of money?
We can apply this to the quantity equation: money supply × velocity of money = price level × real GDP. growth rate of the money supply + growth rate of the velocity of money = inflation rate + growth rate of output.
Why is quantity theory of money important?
Important Points The main point is that the quantity theory of money states that the quantity of money will determine the value of money. So, to stop inflation, economies need to check the supply of money. This theory assumes that the output of goods and velocity remain constant.
What is an example of the quantity theory of money?
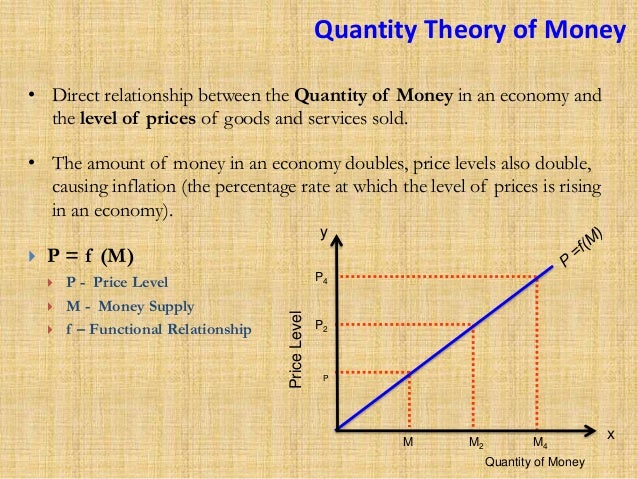
For example, if the Federal Reserve (Fed) or European Central Bank (ECB) doubled the supply of money in the economy, the long-run prices in the economy would tend to increase dramatically. This is because more money circulating in an economy would equal more demand and spending by consumers, driving prices up.
What are the three theories of money?
These are credit creation theory, fractional reserve theory and debt intermediation theory.
What is the conclusion of the quantity theory of money?
The quantity theory of money explains that the money supply of a nation has a direct proportional relationship with the price level. The important conclusion we can draw from this is: other things remaining the same, if the quantity of money is doubled, prices will double also.
Who proposed quantity theory of money?
John Maynard Keynes was a British economist who developed this theory in the 1930s as part of his research trying to understand, first and foremost, the causes of the Great Depression.
What are the assumptions of quantity theory of money?
Assumptions of the Theory :- Demand for money remains constant. Trade and business activities remains constant. Supply of credit money remains constant. Velocity of money should not change.
What is the quantity equation?
Quantity equation is an identity which was defined by Irving fisher, and is usually used to understand the relation between the money and total expenditure. The quantity equation is represented as MV = PT and relates the price levels and the quantity and availability of money.
How the quantity of money is measured?
The money supply is the total quantity of money in the economy at any given time. Economists measure the money supply because it's directly connected to the activity taking place all around us in the economy. M1 is the narrowest definition of money.
What is M1 M2 M3 money supply?
M1, M2 and M3 are measurements of the United States money supply, known as the money aggregates. M1 includes money in circulation plus checkable deposits in banks. M2 includes M1 plus savings deposits (less than $100,000) and money market mutual funds. M3 includes M2 plus large time deposits in banks.
What is inflation rate formula?
Written out, the formula to calculate inflation rate is: ((Current CPI – Past CPI) ÷ Current CPI) x 100 = Inflation Rate. or. ((B – A)/A) x 100 = Inflation Rate.
What is the quantity theory of money?
The Quantity Theory of Money refers to the idea that the quantity of money. Cash In finance and accounting, cash refers to money (currency) that is readily available for use. It may be kept in physical form, digital form, available (money supply) grows at the same rate as price levels do in the long run. When interest rates.
How to understand the quantity theory of money?
To better understand the Quantity Theory of Money, we can use the Exchange Equation. The equation enables economists to model the relationship between money supply and price levels. The exchange equation is:
What is the Q of GDP?
Q – refers to the quantity of goods and services offered in the economy. Shortcomings of GDP Gross Domestic Product (GDP) refers to the total economic output achieved by a country over a period of time. While GDP is generally a good. of a country.
What does V mean in economics?
V – refers to the Velocity of Money, which measures how much a single dollar of money supply spend contributes to GDP
What is the theory of inflation?
The theory provides a quick overview of monetarist theory, which states that changes in the current money supply cause fluctuations in overall economic output; excessive growth in money supply causes hikes in inflation.
What happens when Q and V are constant?
Holding Q and V constant, we can see that increases in the money supply will cause price levels to increase, thus causing inflation. The assumption that Q and V are constant holds in the long run as these factors cannot be influenced by changes in the economy’s money supply.
What is available money supply?
available (money supply) grows at the same rate as price levels do in the long run. When interest rates. Interest Rate An interest rate refers to the amount charged by a lender to a borrower for any form of debt given, generally expressed as a percentage of the principal.
What is the quantity theory of money?
The quantity theory of money describes the relationship between the supply of money and the price of goods in the economy and states that percentage change in the money supply will be resulting in an equivalent level of inflation or deflation. An increase in prices will be termed as inflation while a decrease in the price of goods is deflation.
What are the limitations of Quantity Theory of Money?
Limitations of Quantity Theory of Money. Some of the limitations are as follows: Its simplicity is one of its limitations. People know that it is an obvious fact that if the money supply will increase the price will decrease. It does not state the cause and effect of the increasing supply. This equation assumes that velocity and output ...
What is the difference between inflation and deflation?
An increase in prices will be termed as inflation while a decrease in the price of goods is deflation. Deflation Deflation is a decrease in the prices of goods and services caused by negative inflation ( below 0%).
Why did the price of a good increase in 1989?
The only reason was, because fiscal deficit bank had to print more money and that’s why the price increased, which proves the quantity theory of money phenomenon.
What happens to the price of goods if the money supply doubles?
So here we can say if the money supply in the economy gets doubles then the price of goods also gets doubled to $10.
What happens when the money in the economy doubles?
That means if the money in the economy doubles then the price level of the goods also gets doubled which will be causing inflation and consumer will have to pay double the price for the same amount of goods or services.
How to describe the value of money?
The value of money can be described by supply and demand of money the same as we determine the supply and demand of commodities. The equation for quantity theory of money can be described by.
Who developed the Quantity Theory of Money?
Quantity Theory of Money: Cambridge Version: ADVERTISEMENTS: An alternative version, known as cash balance version, was developed by a group of Cambridge economists like Pigou, Marshall, Robertson and Keynes in the early 1900s. These economists argue that money acts both as a store of wealth and a medium of exchange.
What is the theory of demand for money?
1. Quantity Theory of Money— Fisher’s Version: Like the price of a commodity, value of money is determinded by the supply of money and demand for money. In his theory of demand for money, Fisher attached emphasis on the use of money as a medium of exchange. In other words, money is demanded for transaction purposes.
How can an economy increase its output?
By utilising its resources efficiently and fully, an economy can increase its output level by increasing the volume of investment consequent upon an increase in money supply. Since there is a limit to output expansion due to full employment (i.e., beyond which output will not increase), an increase in money supply from (M 3 to M 4) will cause price level to rise from (P 3 to P 4) proportionally (shown in the upper panel).
What is the supply of money?
In this equation, supply of money consists of nominal quantity of money multiplied by the velocity of circulation.
How does money supply affect price level?
Before the attainment of full employment state (Y F ), an increase in money supply (from OM 1 to OM 2 and to OY F) causes national income (shown by the steep output curve) to rise more rapidly than the price level.
What does V mean in math?
V = velocity of circulation of money, that is, the number of times a unit of money changes its hand;
How are k and y determined?
k and Y are determined independently of the money supply. With k constant given by the transaction demand for money and Y constant because of full employment, increase or decrease in money supply leads to a proportional
What is the theory of money?
Definition: Quantity theory of money states that money supply and price level in an economy are in direct proportion to one another. When there is a change in the supply of money, there is a proportional change in the price level and vice-versa.
What is quantity supplied?
Quantity supplied is the quantity of a commodity that producers are willing to sell at a particular price at a particular point of time. This is a part of decision making practice wherein an individual/company exercises sensible choice making, which provides him with the optimum amount of benefit.
Which school of economics has criticized the Keynesian theory?
Description: The theory is accepted by most economists per se. However, Keynesian economists and economists from the Monetarist School of Economics have criticized the theory. According to them, the theory fails in the short run when the prices are sticky.
What is the quantity theory of money?
The quantity theory of money, sometimes called "The Fisherian Theory" simply states that a change in price can be related to a change in the money supply. In simple terms, it states that the quantity of money available (money supply) in the economy and the price levels have the same growth rates in the long run. When there is a fall in interest rates or a decrease in taxes and there is little restriction on how money can be accessed, consumers become less sensitive to changes in price, and hence, have a higher propensity to consume. As a result of this, there will be a rightward movement in the aggregate demand curve, and an upward movement in the equilibrium price level.
How is the Quantity Theory of Money Applied?
The quantity theory of money generally assumes that, if there is an increase in the quantity of money which is in circulation in the economy, there will likely be inflation, and vice versa. By examining the activities of the Federal Reserve or European Central Bank (ECB), we can see that if this body increases the supply of money in the economy by twice its normal quantity, there tends to be a sudden increase in prices of commodities in the economy in the long-run. This price increase can be associated with the excess money supply which will create more demand and spending. Although economists don't agree with the assumption of a sudden change in price after a change in the quantity of money in circulation. KEY TAKEAWAYS
Why was the relationship between price and money supply staunchly rejected by John Maynard Keynes?
The relationship between price and the money supply was staunchly rejected by John Maynard Keynes because he felt it didn't take interest rates into consideration.
Who rejected the relationship between price and money supply?
The relationship between price and the money supply was staunchly rejected by John Maynard Keynes because he felt it didn't take interest rates into consideration. Fisher's greatest antagonist was Knut Wicksell, a Swedish economist who developed his theories in continental Europe as opposed to Fisher's in the United States and Great Britain. Though he agreed to the relationship between money supply and price, he argued that there will be an uneven price distortion, especially in the capital goods sector if the money supply was artificially induced through the banking system.
How to calculate the Fisher equation?
The Fisher equation is mathematically expressed as: M (money supply) x V (velocity of money) = P ( average price level) x T ( volume of transactions in the economy). Despite the many strengths of the Fisher model which includes its simplicity and compatibility with mathematical models, its false assumptions usage to arrive at its simple nature which includes; a proportional supply of money, independent variables, and price stability raise doubts. Despite these doubts, there are still economists like the Chicago school of economics' monetary economists who advocate for the theory. Although many economists do not accept the stable increase in the money supply assumption, more economists accept the monetarists' claim that a change in the money supply cannot affect the real economic output in the long-run.
What is the quantity theory of money?
The quantity theory of money states that the value of money is based on the amount of money in the economy. Thus, according to the quantity theory of money, when the Fed increases the money supply, the value of money falls and the price level increases.
Why do people need money?
In general, consumers need money to purchase goods and services. If there is an ATM nearby or if credit cards are plentiful, consumers may demand less money at a given time than they would if cash were difficult to obtain.
Why does the new intersection of the money supply curve and the money demand curve have a lower value?
This happens because more money is in circulation, so each bill becomes worth less.
What happens if the average price level is low?
If, on the other hand, the average price level is low and goods and services tend to cost little money, consumers will demand less money. The value of money is ultimately determined by the intersection of the money supply, as controlled by the Fed, and money demand, as created by consumers.
Why is the money supply curve vertical?
The money supply curve is vertical because the Fed sets the amount of money available without consideration for the value of money. The money demand curve slopes downward because as the value of money decreases, consumers are forced to carry more money to make purchases because goods and services cost more money.
What is inflation in the Sparknote?
In the SparkNote on inflation we learned that inflation is defined as an increase in the price level. Based on this definition, the quantity theory of money also states that growth in the money supply is the primary cause of inflation. Previous section Problems Next page Quantity theory of money page 2.
What is the most important variable in determining money demand?
The most important variable in determining money demand is the average price level within the economy. If the average price level is high and goods and services tend to cost a significant amount of money, consumers will demand more money.
