
How much radiation is in the Fukushima reactor?
Latest Radiation Readings From Inside The Fukushima Reactor Are Unexpectedly High. A new radiation reading taken deep inside Japan's damaged Fukushima Daiichi nuclear reactor No. 2 shows levels reaching a maximum of 530 sieverts per hour, a number experts have called "unimaginable".
How radioactive is the seawater near Fukushima?
A year after the disaster, in April 2012, sea fish caught near the Fukushima power plant still contain as much radioactive 134 Cs and 137 Cs compared to fish caught in the days after the disaster. At the end of October 2012 TEPCO admitted that it could not exclude radioactivity releases into the ocean, although the radiation levels were stabilised.
How dangerous is the air in Fukushima Prefecture?
According to this report, in several parts of Fukushima Prefecture – including Futaba and Okuma – the air would remain dangerously radioactive at levels above 50 millisieverts a year. This was all based on measurements done in November 2011.
What is the highest level of radiation in Japan?
The highest levels found (of Pu-239 and Pu-240 combined) were 15 becquerels per square meters in Fukushima prefecture and 9.4 Bq in Ibaraki prefecture, compared to a global average of 0.4 to 3.7 Bq/kg from atomic bomb tests.

Is there still radiation in Fukushima?
These areas still have relatively high radioactivity. The half-life of radiocesium is about 29 years, meaning the quantity of the radioactive material should drop by half by roughly 2041.
What is the highest radiation level in Fukushima?
530 Sv/hrWhile 530 Sv/hr is the highest measured so far at Fukushima Daiichi, it does not mean that levels there are rising, but that a previously unmeasurable high-radiation area has finally been measured.
Is Fukushima still radioactive 2021?
The EPA's air monitoring data have not shown any radioactive elements associated with the damaged Japanese reactors since late 2011. Even during the incident, the levels found in the air were very low—always well below any level of public health concern.
Is Fukushima still leaking radiation 2020?
In 2020, the Japanese government lifted bans on Fukushima seafood, saying they met safety standards that are stricter than American guidelines for cesium in food. The radiation levels offshore of Fukushima have dropped in the years since, but some of the reactors there are still leaking.
Is Fukushima more radioactive than Chernobyl?
According to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), there was less total atmospheric release of radioactivity from the Fukushima accident compared with Chernobyl due to the different accident scenarios and mechanisms of radioactive releases.
How long will Fukushima be uninhabitable?
100 yearsA large area around the Fukushima nuclear power plant will be uninhabitable for at least 100 years.
What is the most radioactive place on Earth?
Fukushima is the most radioactive place on Earth. A tsunami led to reactors melting at the Fukushima nuclear power plant. Even though it's been nine years, it doesn't mean the disaster is behind us.
Is Fukushima still leaking 2022?
Japan plans to release Fukushima nuclear plant's wastewater into the sea next year, 12 years on from the disaster. The country's nuclear regulator today approved plans by the site's operator to release the treated radioactive water in 2023, saying the environmental risks are minimal.
Is Fukushima safe to live in?
Highly contaminated areas close to the nuclear plant will remain off limits indefinitely. Conditions at the plant are "really stable," the plant manager, Akira Ono, recently told reporters. Radioactivity and heat from the nuclear fuel have fallen substantially in the past 5 years, he says.
How many died from Fukushima radiation?
Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster casualtiesSatellite image on 16 March 2011 of the four damaged reactor buildingsDate11 March 2011OutcomeINES Level 7 (ratings by Japanese authorities as of 11 April)Deaths1 confirmed from radiation (lung cancer, 4 years later), and 2,202 from evacuation.3 more rows
How long until Chernobyl is habitable?
How Long Will It Take For Ground Radiation To Break Down? On average, the response to when Chernobyl and, by extension, Pripyat, will be habitable again is about 20,000 years.
Is Fukushima a ghost town?
Ghost Towns of Fukushima Remain Empty After Decade-Long Rebuild.
What is the highest level of radiation recorded?
530 sieverts per hourAccording to the report, " the radiation level inside the containment vessel of reactor 2 the crippled Fukushima No. 1 power plant has reached a maximum of 530 sieverts per hour, the highest since the triple core meltdown." A person could die from even brief exposure if exposed to levels that high.
Where is the highest radiation on Earth?
As of today's date, 5 of the most radioactive places on earth are:Fukishima, Japan. On Friday, March 11, 2011 the Pacific coast of Japan experienced an earthquake with a magnitude upwards of 9.0. ... Chernobyl, Ukraine. Chernobyl was the nuclear event of the 1980s. ... The Polygon. ... Hanford, Washington – USA. ... Goias, Brazil.
What's the highest radiation level?
The current annual permitted dose for a radiation worker in the United States is 0.05 Sv (or 5 rem), i.e. an average of 5.7 μSv/h....Albert StevensKnown forSurviving the highest known radiation dose in any human6 more rows
What is the most radioactive place on Earth?
Fukushima is the most radioactive place on Earth. A tsunami led to reactors melting at the Fukushima nuclear power plant. Even though it's been nine years, it doesn't mean the disaster is behind us.
What is the maximum dose of radiation for Fukushima?
On 17 March, NISA set 250 mSv as the maximum allowable dose for Fukushima recovery workers, under health physics controls. At the end of October this was reduced to 100 mSv for new workers. The International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) allows up to 500 mSv for workers in emergency rescue operations.
What is the radiation level in 2011?
In December 2011 the government said that where annual radiation dose would be below 20 mSv/yr, it would help residents return home as soon as possible and assist local municipalities with decontamination and repair of infrastructure. In areas with radiation levels over 20 mSv/yr evacuees will be asked to continue living elsewhere for “a few years” until decontamination and recovery work was completed. The government said it would consider purchasing land and houses from residents of these areas if the evacuees wish to sell them.
What is the NRA emergency zone?
In October 2012 the new Nuclear Regulatory Authority (NRA) released new emergency preparedness guidelines. Its new emergency planning zones, in line with International Atomic Energy Agency standards, call for 'precautionary action zones' 5 kilometers around nuclear energy facilities and 'urgent protective action planning zones' 30 km around the plants. NRA then drew up specific evacuation criteria, which local municipalities will use to formulate emergency response plans.
How long does N-16 have a half life?
N-16 has a half-life of only 7 seconds but produces high-energy gamma radiation during decay. (It is the reason that access to a BWR turbine hall is restricted during actual operation.) There is also often some leakage from fuel elements of fission products, including noble gases and iodine-131.
What is the radioactivity in the cooling water flowing through the core?
Radioactivity in the cooling water flowing through the core is mainly the activation product nitrogen-16, formed by neutron capture from oxygen. N-16 has a half-life of only 7 seconds but produces high-energy gamma radiation during decay. (It is the reason that access to a BWR turbine hall is restricted during actual operation.) There is also often some leakage from fuel elements of fission products, including noble gases and iodine-131.
How are radioactive releases measured?
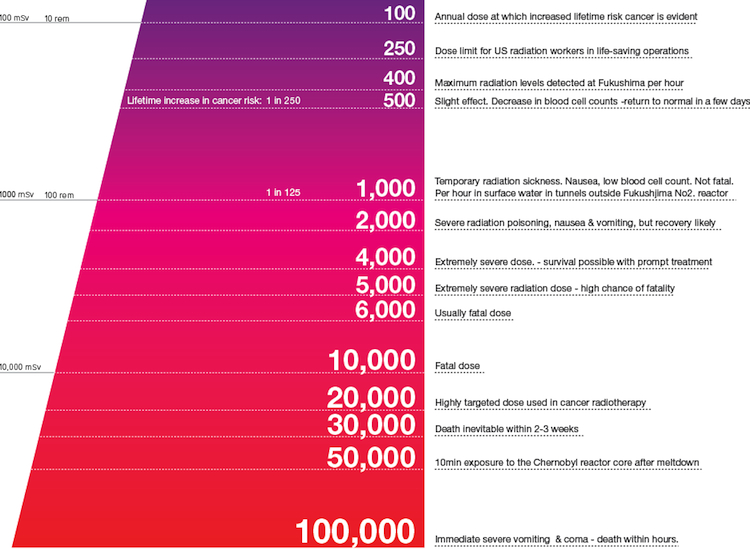
Radioactive releases are measured by the amount of (radio)activity in the material, and quoted in Be cquerels. Whether this is in the air or settled on the ground, it may expose people to ionizing radiation, and the effect of this is measured in Sieverts, or more typically milliSieverts (mSv). Exposure to ionizing radiation can also be by direct ...
When did the NRA change the way radiation exposure was estimated?
In November 2013 the NRA decided to change the way radiation exposure was estimated. Instead of airborne surveys being the basis, personal dosimeters would be used, giving very much more accurate figures, often much less than airborne estimates. The same criteria would be used, as above, with 20 mSv/yr being the threshold of concern to authorities.
What is the current radiation monitoring system?
Current Radiation Air Monitoring in the U.S. – Current, near-real-time, and historic air monitoring data is compiled for 140 U.S. cities by the EPA's RadNet system. This monitoring network evaluates the nation's air, precipitation and drinking water to track radiation in the environment, 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. For more information about current radiation levels in your area, visit RadNet.
Is Oregon monitoring the tsunami?
At the state level, the Oregon Public Health Division is monitoring the air, sand and water on the northern, central and southern coasts of Oregon for higher than normal levels of radiation due to the Japan tsunami. For more information, visit Japan Tsunami Marine Debris Information.
How long does Fukushima have a half life?
Beasley said research showed that one form of contamination that has a half-life of 30 years is still really high in Japan where the Fukushima accident happened.
What do researchers rely on to assess exposure to radionuclide activity?
Instead, researchers generally rely on computer modeling to assess exposure to radionuclide activity.
Radioactivity
Radioactive Releases
- Supplement to information in main page After the hydrogen explosion in unit 1 on 12 March, some radioactive caesium and iodine were detected in the vicinity of the plant, having been released via the venting. Further I-131 and Cs-137 and Cs-134 were apparently released during the following few days, particularly following the hydrogen explosion at unit 3 on 14 March and at unit 4 on 15 …
Radiation Effects
- Supplement to information in main page No harmful health effects were found in 195,345 residents living in the vicinity of the plant who were screened by the end of May 2011. All the 1,080 children tested for thyroid gland exposure showed results within safe limits, according to the report submitted to IAEA in June. By December, government health checks of some 1700 re…
Return of Evacuees
- Supplement to information in main page Permanent return remains a high priority, and the evacuation zone is being decontaminated where required and possible, so that evacuees (81,000 from this accident according to METI) can return. There are many cases of evacuation stress including transfer trauma among evacuees, and once the situation had stabilised at the plant the…
Managing Contaminated Water, Marine Effects
- Supplement to information in main page Removing contaminated water from the reactor and turbine buildings had become the main challenge by week 3 of the accident, along with contaminated water in trenches carrying cabling and pipework. This was both from the tsunami inundation and leakage from reactors. Run-off from the site into the sea was also carrying radio…