How to perform an oxidase test?
#4 – Test Tube Method
- A fresh culture of bacteria (grow within 24 hours) in placed in a 4.5 ml of nutrient broth.
- A Gaby and Hadley reagent is added (0.2 ml).
- Gently and thoroughly shake to make sure that there is a thorough oxygenation of the culture.
- Watch out for any changes in the color. A change in color within 15 to 30 seconds indicates a positive oxidase test. ...
How is oxidase test performed?
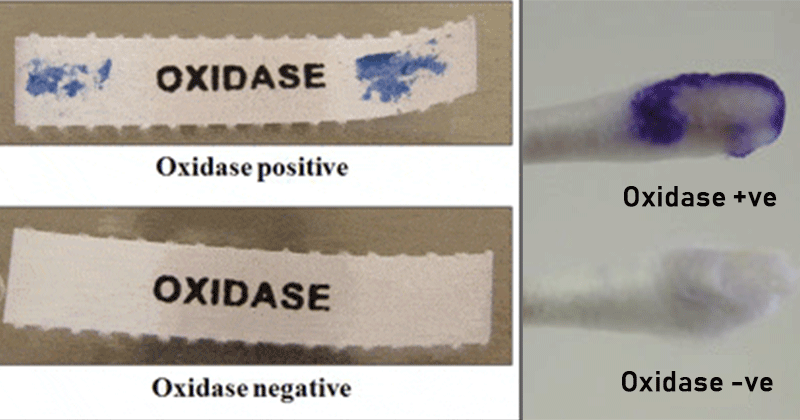
How is oxidase test performed? Use the dropper to add a drop of oxidase reagent to the bacteria on the filter paper, and look for the appearance of blue or purple spots – a positive result. After 15 seconds, if no color appears, the test is negative for the presence of cytochrome oxidase.
How do you identify limiting reagent and excess reagent?
So, here’s the solution:
- Balance the equation. ...
- Determine the limiting reagent if 100 g of ammonia and 100 g of oxygen are present at the beginning of the reaction. ...
- Identify the excess reagent, as well as how many grams of the excess reagent will remain when the reaction reaches completion. ...
What is the principle of the oxidase test?
Oxidase test
- Objective:
- Principle of oxidase test: Oxidase is a terminal enzyme in aerobic respiration. ...
- Requirements:
- Procedure of Oxidase test: Place a small portion of culture on the filter paper with the help of a sterile glass rod and make a smear on it.
- Result interpretation:

What is the name of the reagent used for the oxidase test quizlet?
The oxidase test requires the use of reagent known as oxidase reagent, or tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine. Kovac's reagent is used for detecting indole production.
What happens to the reagent of the oxidase is present?
When present, the cytochrome c oxidase oxidizes the reagent (tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride) to indophenols, a purple or dark blue color end product. When the enzyme is not present, the reagent remains reduced and is colorless.
How do you make a oxidase reagent?
Prepare a 1.0% Kovac's oxidase reagent by dissolving 0.1 g of tetramethyl-p- phenylenediamine dihydrochloride into 10 ml of sterile distilled water. 2. Mix well and then let stand for 15 minutes. The solution should be made fresh daily and the unused portion should be discarded.
How do you use oxidase reagent?
0:533:23oxidase test - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipRub this sample onto the oxidase reagent on the filter paper a positive result is indicated by theMoreRub this sample onto the oxidase reagent on the filter paper a positive result is indicated by the almost immediate formation of a blue color flame your loop when you're finished.
How do you do a oxidase test?
Test Tube Method Add 0.2 ml of 1% α-naphthol, then add 0.3 ml of 1% p-aminodimethylaniline oxalate (Gaby and Hadley reagents). Shake vigorously to ensure mixing and thorough oxygenation of the culture. Observe for color changes. Microorganisms are oxidase positive when the color changes to blue within 15 to 30 seconds.
Is the reagent used for the catalase test?
To observe the action of these enzymes, catalase reagent, a dilute solution of hydrogen peroxide, is added to a pure bacterial culture. Any immediate bubbling is indicative of a positive result since oxygen is a byproduct of hydrogen peroxide decomposition.
Why do we do oxidase test?
The oxidase test is used to determine if an organism possesses the cytochrome c oxidase enzyme. The test is used as an aid for the differentiation of Neisseria, Moraxella, Campylobacter and Pasteurella species (oxidase positive). It is also used to differentiate pseudomonads from related species.
What is catalase and oxidase test?
The catalase test is a particularly important test used to determine whether a gram-positive cocci is a staphylococci or a streptococci. Catalase is an enzyme that converts hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen gas. The test is easy to perform; bacteria are simply mixed with H2O2.
What is oxidase test in microbiology?
The oxidase test identifies organisms that produce the enzyme cytochrome oxidase. Cytochrome oxidase participates in the electron transport chain by transferring electrons from a donor molecule to oxygen.
What reagent is used for indole test?
To test for indole production, add 5 drops of Kovács reagent directly to the tube (3, 5). A positive indole test is indicated by the formation of a pink to red color ("cherry-red ring") in the reagent layer on top of the medium within seconds of adding the reagent (Fig. 1b).
Why does the oxidase reagent need to be fresh quizlet?
The oxidase test is performed by placing filter paper on towel, using a loop and transferring some of the culture onto the filter paper. The culture must be 24 hours fresh because older cultures may bot have enough active oxidase to produce color change.
Is the oxidase test selective or differential?
Jakes Microbiology LAB #2ABIs the Oxidase test Differential or Selective?DifferentialIs the Citrate test Differential or Selective?DifferentialIs the Phenylethyl alcohol test Differential or Selective?Selective.Is the Eosin Methylene blue agar Differential or Selective?Both96 more rows
What is the action of oxidase?
In biochemistry, an oxidase is an enzyme that catalyzes oxidation-reduction reactions, especially one involving dioxygen (O2) as the electron acceptor. In reactions involving donation of a hydrogen atom, oxygen is reduced to water (H2O) or hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
How do you know that cytochrome c oxidase is present?
The Oxidase TestOxidase positive bacteria contain cytochrome c oxidase and produce a change in color of the reagent from colorless to bluish or purplish in less than 30 seconds.Oxidase negative bacteria do not contain cytochrome c oxidase and do not change the color of oxidase reagent in less than 30 seconds.
What is the oxidase reagent in Gordon and Mcleod's?
The Gordon Mcleod reagent (oxidase reagent) is used to carry out the oxidase test, to determine the presence of oxidase enzymes. The oxidase test, originally devised to identify all Neisseria spp., was later used to distinguish the Pseudomonadaceae from the oxidase - negative members of the Enterobacteriaceae.
Why is it important to read oxidase results within 30 seconds?
Why should you read the results of the oxidase test within 30 seconds? -The reagents of this test are unstable, therefore they may oxidize independently shortly after becoming moist. Therefore it is important to read within 30 seconds.
What is the function of oxidase reagent?
Therefore, we can say that the oxidase reagent performs dual functions as a redox indicator and mediator. The enzyme cytochrome oxidases carry an iron-containing haemoprotein and generally exist within the mitochondrial cells of aerobic organisms.
What is the oxidase test?
Oxidase test refers to a biochemical test that differentiates organisms into oxidase-positive and oxidase-negative microorganisms based on the existence of cytochrome oxidase enzyme in the electron transport chain system. The living organisms that possess cytochrome oxidases can oxidize the TMPD reagent ...
What is the principle of oxidase test?
The principle of oxidase test depends upon the mechanism of oxidation reaction, in which the organisms possessing cytochrome oxidase enzyme can oxidize the TMPD reagent into the end products like blue-coloured complex ( Indophenol) and water. Oxidase test remarkably differentiates microorganisms into two specific groups, ...
What is the TMPD reagent?
TMPD reagent works as a redox reagent that ascertains the presence of cytochrome-c oxidase in the electron transport chain. It also serves as an artificial donor, which passes the electron to the cytochrome-c complex.
What is the role of cytochrome oxidase in the respiratory chain?
The enzyme cytochrome oxidases contribute to a part of the respiratory chain and use oxygen as a final electron acceptor. This post describes the definition, principle, procedure, result, uses and limitations of the oxidase test. In addition, you would also get to know the preparation of the test reagents, along with the overview ...
What is the oxidase test for aerobic bacteria?
Aerobic bacteria possess cytochrome oxidase that constitutes a part of the aerobic respiratory chain. Thus, the oxidase test also distinguishes aerobic organisms from the facultative aerobes, strict and facultative anaerobes. Oxidase test is useful in speciation, as it differentiates Pseudomonas from other related species.
How does cytochrome C oxidase work?
Cyt-c oxidase performs a significant role by receiving electrons from the cytochrome-c complexes and transferring them to the dioxygen electron acceptor. The final electron acceptor releases two water molecules by binding with the four proton ions.
What is the oxidation of a bacterium?
OX+ normally means the bacterium contains cytochrome c oxidase (aka. Complex IV) and can therefore use oxygen for energy production by converting O 2 to H 2 O 2 or H 2 O with an electron transfer chain . The Pseudomonadaceae are typically OX+. The Gram-negative diplococci Neisseria and Moraxella are oxidase-positive.
What is TMPD test?
TMPD. The oxidase test is used to determine if an organism possesses the cytochrome oxidase enzyme. The test is used as an aid for the differentiation of Neisseria, Moraxella, Campylobacter and Pasteurella species (oxidase positive). It is also used to differentiate pseudomonads from related species..
How long to inoculate trypticase soy agar plates?
The inoculated plates are incubated at 37 °C for 24–48 hours to establish colonies. Fresh bacterial preparations should be used. After colonies have grown on the medium, 2-3 drops of the reagent DMPD are added to the surface of each organism to be tested.
Is Moraxella oxidase positive?
The Gram-negative diplococci Neisseria and Moraxella are oxidase-positive.
What is the oxidase test?
What is Oxidase Test ? Principle, Composition, Interpretation of Results. Oxidase test is a procedure used to determine the existence of cytochrome c oxidase enzyme. What the system does is it helps the movement of electrons between redox dye- tetramethyl-p-phenylene-diamine and the bacteria’ electron donors. ...
Why is the oxidase test called the oxidase test?
It is called oxidase test because if the enzyme is present, the enzyme will not lead to oxidation of the reagent thereby producing purple color end product (indophenols). There is no oxidation if no enzyme is found. Hence, the color of the reagent remains the same. (1, 2, and 3)
How long should a reagent be fresh?
For the reagent to be considered fresh, it should no longer than one week. It is important to check the colonies on the media that do not contain excessive sugar like nutrient agar and tryptic soy agar. A high concentration of glucose in the media leads to a false positive result.
What is the purpose of oxydase test?
Oxidase test is helpful in identifying Neisseria as well as identifying and differentiating gram-negative bacilli. To find out the gram reaction and morphology of the organism being tested, it should be checked using gram stain.
Can platinum loops be used for oxidase?
Always use platinum loops. Using loops that contain iron may lead to a false-positive result. A false negative result is possible if the reagent or strips used are less sensitive. Make sure that the colonies used for oxidase test are 18 to 24 hours old.
What is the procedure for oxidase test?
These include, but are not limited to, the filter paper test, filter paper spot test, direct plate method, and test tube method.
What is the oxydase test?
Oxidase test is used as a major characteristic for the identification of Gram-negative rods that are not in the Enterobacteriaceae family. Colonies suspected of belonging to other genera Aeromonas, Pseudomonas, Neisseria, Campylobacter, and Pasteurella are oxidase positive.
How much Kovács oxidase to use on organism smear?
Place 1 or 2 drops of 1% Kovács oxidase reagent on the organism smear.
How long can Kovács oxidase be stored in water?
Kovács oxidase reagent (1% tetra-methyl-p-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride, in water). Store refrigerated in a dark bottle for no longer than 1 week.
What does it mean when a bacteria is oxidase positive?
All bacteria that are oxidase-positive are aerobic and can use oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor in respiration. This does NOT mean that they are strict aerobes. Bacteria that are oxidase-negative may be anaerobic, aerobic, or facultative; the oxidase negative result just means that these organisms do not have the cytochrome c oxidase that oxidizes the test reagent. They may respire using other oxidases in electron transport.
How long does it take for a oxidase positive to change to a purple?
Oxidase positive: color changes to dark purple within 5 to 10 seconds. Delayed oxidase-positive: color changes to purple within 60 to 90 seconds. Oxidase negative: color does not change or it takes longer than 2 minutes.
What is the color of the end product of cytochrome C oxidase?
When present, the cytochrome c oxidase oxidizes the reagent (tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride) to indophenols, a purple or dark blue color end product. When the enzyme is not present, the reagent remains reduced and is colorless. Mechanism of the Cytochrome Oxidase Reaction. All bacteria that are oxidase-positive are aerobic ...
What is the Kovac oxidase test?
Kovac’s oxidase test determines the presence of cytochrome oxidase. Kovac’s oxidase reagent, tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride, is turned into a purple compound by organisms containing cytochrome c as part of their respiratory chain. This test helps in the recognition of Neisseria meningitidis, but other members of the genus Neisseria, as well as unrelated bacterial species, may also give a positive reaction. Positive and negative quality control (QC) strains should be tested along with the unknown isolates to ensure that the oxidase reagent is working properly.
What color is oxydase?
Oxidase test manually prepared is as shown above image. It was then tested with Pseudomonas aeruginosa and result found positive i.e. purple color.
How cold can reagent be stored?
Alternatively, the reagent could be dispensed into 1 ml aliquots and stored frozen at -20°C.
What is OxiDrop reagent?
OxiDrop™, Oxidase Test is a liquid ready-to-use reagent that is used in procedures to detect cytochrome oxidase activity in bacteria . For testing the oxidase reaction, contains tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine. Simply place one drop on the suspect colony (directly on the plate) and look for…
What is oxidase dropper?
Oxidase Reagent Droppers are used in the Kovacs oxidase test as a qualitative reaction in the identification of nonfermenters and miscellaneous gram-negative bacteria. Used in the identification of organisms which produce oxidase enzyme Oxidase Reagent Droppers contain 0.5 mL of a 1%…
What is adidin glucose oxidase conjugate?
Avidin Glucose Oxidase Conjugated is a useful detection reagent for primary antibodies conjugated to biotin. Avidin Glucose Oxidase Conjugated can be utilized in both Western Blotting and ELISA experiment formats in combination with the proper substrate (TMB-1000 or FEMTOMAX-110).
What is the first step in cholesterol catabolism?
Cholesterol oxidase (CHOD) catalyzes the first step in cholesterol catabolism. Cholesterol oxidase from Streptomyces has been used in a study to assess the relationship between the micellar structure of model bile and the activity of esterase. Cholesterol oxidase from Streptomyces has also been…
What yeasts use alcohol oxidase?
Alcohol Oxidase from Pichea Pastoris. Alcohol oxidase has been detected in several strains of yeast, such as Candida, Pichia, and Hansenula, that utilize methanol as a sole carbon and energy source. Some of these enzymes have been isolated and partially characterized.
Does glucose oxidase require activators?
Glucose oxidase does not require any activators, but it is inhibited by Ag+, Hg2+, Cu2+, phenylmercuric acetate, and p-chloromercuribenzoate. It is not inhibited by the nonmetallic SH reagents: N-ethylmaleimide, iodoacetate, and iodoacetamide. Glucose oxidase can be utilized in….
What does the oxidase test determine?
Oxidase Test - Virtual Interactive Bacteriology Laboratory. The oxidase test is used to identify bacteria that produce cytochrome c oxidase, an enzyme of the bacterial electron transport chain. (note: All bacteria that are oxidase positive are aerobic, and can use oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor in respiration.
What does a oxidase do?
Oxidases are enzymes that catalyze the oxidation of CN and CO bonds at the expense of molecular oxygen, which is reduced to hydrogen peroxide. The three principal substrates classes for oxidase enzymes are amino acids, amines, and alcohols.
What does a color change indicate in the oxidase test?
Microbes that possess cytochrome c, contain cytochrome c oxidase to facilitate electron and proton transfer to oxygen. ... It produces a color change when it gives up its electrons. This reducing agent readily transfers its elections to cytochrome c oxidase. As the colorless CRA becomes oxidized, it becomes deep purple.
