Definition Of Refractive Index Of A Medium The refractive index of a medium is defined as the ratio of speed of light in vacuum to that of speed of light in medium. Refractive Index = Speed of light in vacuum / Speed of light in medium
What is the refractive index of light?
The refractive index is a common phenomenon, which is being observed almost daily. A light ray changes its direction when it travels from one medium to another medium. It happens due to the variation in the speed of light in each medium. The speed of light in a vacuum is meters/second.
Why does the refractive index change?
The refractive index is a common phenomenon, which is being observed almost daily. A light ray changes its direction when it travels from one medium to another medium. It happens due to the variation in the speed of light in each medium. The speed of light in a vacuum is 3x108 meters/second, and the speed of light in air is 2.98x108 meters/second.
What is the absolute refractive index of the second medium?
But, when one of the two mediums is considered a vacuum, then the refractive index of the second medium, concerning the first medium, is known as Absolute Refractive Index. The symbol n₂ denotes the absolute Refractive Index. Therefore, n₂ = Speed of Light in Vacuum/Speed of light in the 2nd medium
How do you find the refractive index of a vacuum?
The refractive index, represented by symbol n, is the velocity of light in vacuum divided by the velocity of light in a medium. The formula of the refractive index is as follows: The vacuum has a refractive index of 1. The refractive index of other materials can be calculated from the above equation.

How do you determine refractive index of a medium?
Refractive index is also equal to the velocity of light c of a given wavelength in empty space divided by its velocity v in a substance, or n = c/v.
What is refractive index of the medium Mcq?
CONCEPT: Refractive index: The ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in a medium is called the refractive index of that medium. It is also called an absolute refractive index.
Can refractive index of a medium be equal to 1?
Refractive index of a medium is always greater than 1 (it cannot be less than 1) because the speed of light in any medium is always less than that in a vacuum.
What is the refraction Mcq?
Refraction of Light: The bending of the ray of light passing from one medium to the other medium is called refraction.
What is refractive index Class 10th?
The refractive index is the measure of bending of a light ray when passing from one medium to another. It can also be defined as the ratio of the velocity of a light ray in an empty space to the velocity of light in a substance, n = c/v.
What is 1 on the refractive index?
vacuumThis implies that vacuum has a refractive index of 1, and assumes that the frequency (f = v/λ) of the wave is not affected by the refractive index. The refractive index may vary with wavelength. This causes white light to split into constituent colors when refracted. This is called dispersion.
What happens if refractive index is less than 1?
Refractive index is a factor that slows down the speed of light in a vacuum. If the refractive index is less than one, it refers to the wave propagating faster than the speed of the light which is not possible.
What happens when refractive index 0?
A refractive index of zero implies that light enters a state of quasi-infinite phase velocity and infinite wavelength. It also means that every point within the metamaterial experiences a quasi-uniform phase of the light wave present, as though all the dipoles inside the metamaterial are oscillating in unison.
Does refractive index vary with color light Mcq?
The value of refractive index of a medium does not depend on the colour of light.
What is the index of refraction ratio?
The index of refraction, n, is the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum, c, to the speed of light in a medium, c': One consequence of this difference in speed is that when light goes from one medium to another at an angle, the propagation vector in the new medium has a different angle with respect to the normal.
Which of the following is the correct order of speed of light in glass Mcq?
2 Answers. Correct answer is C. The speed of light in air > the speed of light in water > the speed of light in glass. Higher the refractive index, lesser is the speed of light in that medium and vice versa.
When light passes from glass to water what is the speed of light Mcq?
The speed of light decreases when it enters from a rarer medium to denser medium and increases when it enters from a denser medium to rarer medium. Therefore, the speed of light increases when light ray passes from water to air and the speed of light decreases when light ray passes from water to glass.
What is refractive index?
The refractive index is the measure of bending of a light ray when passing from one medium to another. It can also be defined as the ratio of the v...
What is the refractive index of water?
The refractive index of water is 1.333.
What is the formula to calculate the refractive index of a medium?
The refractive index of a medium can be calculated using the following formula: n = c/v where n is the refractive index of the medium c is the v...
Is the speed of light faster in glass or water?
The speed of light is faster in water. The refractive index of water is 1.3 and the refractive index of glass is 1.5. From the equation n = c/v, we...
What is the refractive index of the medium in which the speed of light is 1.5 × 108 m/s?
The refractive index of the medium can be calculated using the formula: n = c/v Substituting the values in the equation, we get n = 3 × 108 m/s/...
What is the index of refraction?
Refractive index, also called index of refraction, measure of the bending of a ray of light when passing from one medium into another.
What is the refractive index of X-rays?
The refractive index of X-rays is slightly less than 1.0, which means that an X-ray entering a piece of glass from air will be bent away from the normal, unlike a ray of light, which will be bent toward the normal.
What is the refractive index of yellow light?
Some typical refractive indices for yellow light (wavelength equal to 589 nanometres [10 −9 metre]) are the following: air, 1.0003; water, 1.333; crown glass, 1.517; dense flint glass, 1.655; and diamond, 2.417. The variation of refractive index with wavelength is the source of chromatic aberration in lenses. The refractive index of X-rays is slightly less than 1.0, which means that an X-ray entering a piece of glass from air will be bent away from the normal, unlike a ray of light, which will be bent toward the normal. The equation n = c / v in this case indicates, correctly, that the velocity of X-rays in glass and in other materials is greater than its velocity in empty space.
What is the refractive index of a substance?
Most of the substances we know have a positive refractive index having value more than zero. The material will have a negative refractive index when it has negative permittivity and permeability. The refractive index provides a measure of the relative speed of light in different media.
What Is Refractive Index?
The ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to its speed in a specific medium.
What is the speed of light dependent on?
In electromagnetic waves, the speed is dependent on the optical density of the medium. Optical density is the tendency of the atoms in a material to restore the absorbed electromagnetic energy. The more optically dense material is, the slower the speed of light. One such indicator of the optical density of a medium is the refractive index.
What is the speed of light in an unknown medium?
The speed of light in an unknown medium is 1.76 × 108 m/s. Calculate the refractive index of the medium.
When light travels in a medium other than vacuum, the atoms of that medium continually absorb and re?
In this article, let us discuss the r efractive index of water and various mediums. Refractive Index Definition Formula of Refractive Index Example of Refractive Index .
Is the speed of light in water faster than the speed of light through glass?
Since the refractive index of glass is higher than the water, the speed of light in water is faster than the speed of light through glass. If the refractive index of a medium is greater than that of another, then the first medium is said to be optically denser.
Is the refractive index gradient vector?
The refractive index gradient is a vector point function.
What Is a Refractive Index?
The refractive index, also called the index of refraction, is defined as the quotient of the speed of light as it passes through two media. It is a dimensionless number that depends on temperature and on the wavelength of the light beam. In simple words, the refractive index describes how fast a light beam travels through media, and this relationship is described by the formula:
Why does the thinnest layer of an old sample have a significant impact on the refractive index?
Because these instruments measure the angle of total reflection off the surface of the prism, even the thinnest layer of old sample will have a significant impact on the refractive index measurement of any new sample added to it.
What is the purpose of a refractometer?
Based on Snell's law (explained above), refractometers were developed to measure the refractive index of liquids and semi-solid samples.
How does a digital refractometer work?
A digital refractometer measures the refractive index or related values of a liquid sample using the total reflection method. This measurement is done automatically, which reduces operator influence and enhances accuracy. Using a small sample volume (0.5 to 1 mL), highly accurate measurements of the index of refraction are performed in seconds.
Why does light travel faster in a medium?
If a medium is less optically dense due to a temperature increase, the light will travel faster, which causes the deflected angle to shift slightly. In other words, the higher the temperature, the lower the refractive index, as shown in the graph below which uses water as the sample medium.
What is total internal reflection?
Total internal reflection is defined as a process whereby all light traveling from an optically more dense medium towards an optically less dense one is reflected back into the optically more dense medium. Here is a detailed explanation of this phenomenon using the figure at left.
How is reflected light deflected?
The reflected light (angle of incidence > critical angle) is deflected via a lens (6) to the optical sensor CCD (7) that determines the critical angle. In addition, modern digital refractometers automatically control the temperature in the prism/sample boundary to enhance the accuracy of the measurement.
What is the refractive index?
Refractive Index (Index of Refraction) is a value calculated from the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to that in a second medium of greater density. The refractive index variable is most commonly symbolized by the letter n or n' in descriptive text and mathematical equations.
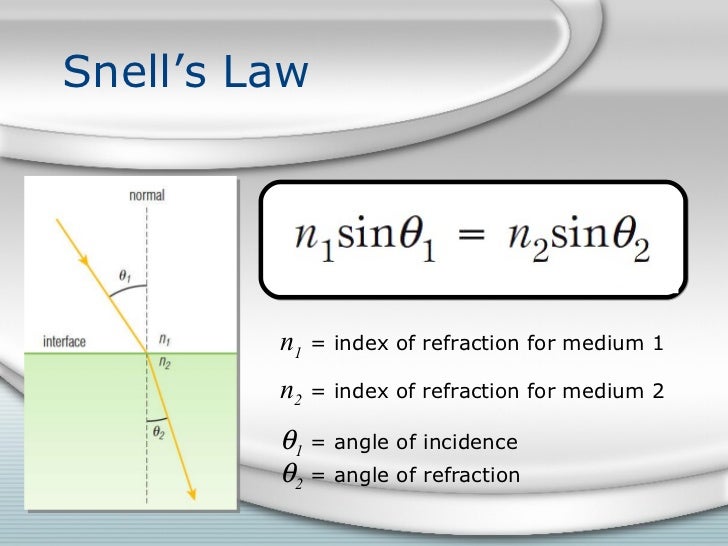
What is the refractive index of Snell's law?
The refractive index or index of refraction is the ratio between the velocity of light ( c) in free space (for all practical purposes, either air or a vacuum) and its velocity η in a particular medium:
What happens to the refractive index of a material as the refractive index increases?
As the refractive index of a material increases, the greater the extent to which a light beam is deflected (or refracted) upon entering or leaving the material. The refractive index of a medium is dependent (to some extent) upon the frequency of light passing through, with the highest frequencies having the highest values of n. For example, in ordinary glass the refractive index for violet light is about one percent greater than that for red light. A consequence of this phenomenon is that each wavelength experiences a slightly different degree of refraction when a heterogeneous light beam containing more than one frequency enters or leaves the medium. This effect is termed dispersion and is responsible for chromatic aberration in microscope objectives.
When is the angle of refraction always larger than the angle of incidence?
When n (1) is greater than n (2) , the angle of refraction is always larger than the angle of incidence. Alternatively when n (2) is greater than n (1) the angle of refraction is always smaller than the angle of incidence. When the two refractive indices are equal ( n (1) = n (2) ), then the light is passed through without refraction.