
How does insulin interact with glucose?
- The Effect of Walking on Postprandial Glycemic Excursion in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes and Healthy People
- What Is the Connection Between Diabetes and Potassium?
- Effect of eating vegetables before carbohydrates on glucose excursions in patients with type 2 diabetes
Is insulin really a response to blood glucose?
Insulin is almost universally considered a hormone whose primary purpose is to regulate blood glucose levels. Indeed, it does this. But is that the whole picture? When we look at what governs pancreatic insulin secretion inside the beta-cell, it’s about total energy and the versatility of the short-term energy supply, not about glucose.
Why is insulin important in glucose metabolism?
- Glucose is broken down into smaller components
- Only 2 molecules of ATP per glucose are produced
- Other carbohydrates, glycogen, and lipid metabolites (glycerol) enter the glycolysis pathway
Does insulin raise or lower blood sugar?
Insulin therapy can sometimes be demanding, but it's an effective way to lower blood sugar levels. If you have any trouble with your insulin regimen, such as difficulty avoiding very low or very high blood sugar levels, be sure to talk to your doctor to see if any adjustments need to be made.
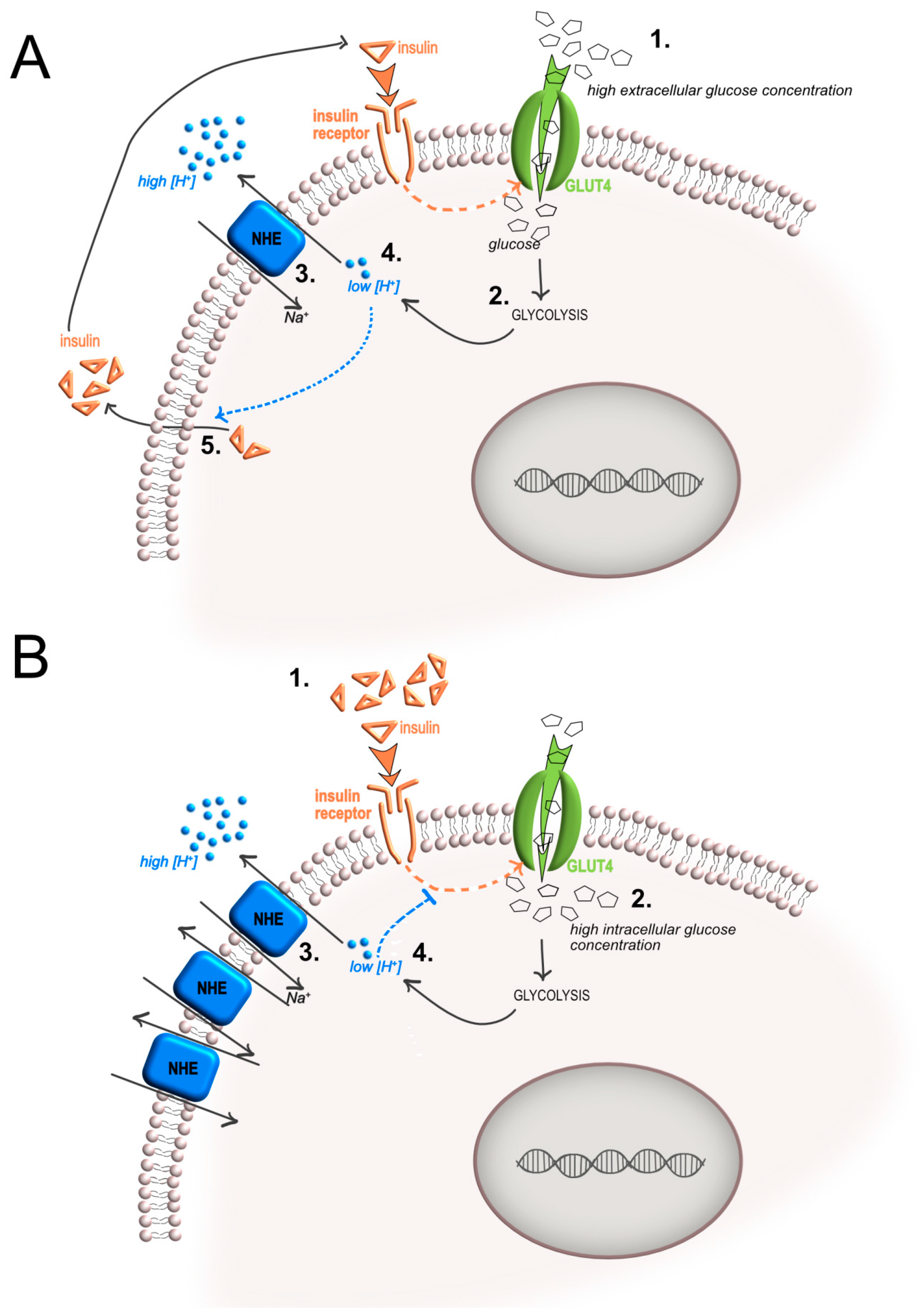
What is the relationship between insulin and glucose?
Insulin provides the glucose that cells use for energy. Without insulin, the glucose remains in your bloodstream, which can lead to dangerous complications like hyperglycemia. Along with glucose, insulin helps amino acids enter the body's cells, which builds muscle mass.
What is the relationship between insulin and glucose in type 2 diabetes?
Insulin is needed to move blood sugar (glucose) into cells. Inside the cells, glucose is stored and later used for energy. When you have type 2 diabetes, your fat, liver, and muscle cells do not respond correctly to insulin. This is called insulin resistance.
What is the relationship between insulin the pancreas glucose and diabetes?
The pancreas is the organ that produces insulin, and it plays a major role in regulating blood glucose levels. Type 1 diabetes occurs when the pancreas does not make enough or any insulin. Type 2 diabetes develops when the body cannot use insulin correctly.
Does insulin increase or decrease blood glucose?
Insulin is a hormone your pancreas makes to lower blood glucose, or sugar. If you have diabetes, your pancreas either doesn't make enough insulin or your body doesn't respond well to it. Your body needs insulin to keep the blood sugar level in a healthy range.
What happens to glucose without insulin?
Without enough insulin, glucose builds up in the bloodstream instead of going into the cells. This buildup of glucose in the blood is called hyperglycemia. The body is unable to use the glucose for energy.
Why do diabetics need insulin?
All people who have type 1 diabetes and some people who have type 2 diabetes need to take insulin to help control their blood sugar levels. The goal of taking insulin is to keep your blood sugar level in a normal range as much as possible. Keeping blood sugar in check helps you stay healthy.
What causes high insulin levels?
Hyperinsulinemia is most often caused by insulin resistance — a condition in which your body doesn't respond well to the effects of insulin. Your pancreas tries to compensate by making more insulin. Insulin resistance may eventually lead to the development of type 2 diabetes.
What is the main function of insulin?
The role of insulin in the body If you don't have diabetes, insulin helps: Regulate blood sugar levels. After you eat, carbohydrates break down into glucose, a sugar that is the body's primary source of energy. Glucose then enters the bloodstream.
Normal Regulation Of Blood Glucose
The human body wants blood glucose (blood sugar) maintained in a very narrow range. Insulin and glucagon are the hormones which make this happen. Both insulin and glucagon are secreted from the pancreas, and thus are referred to as pancreatic endocrine hormones.
Type 2 Diabetes: What Is It?
When it comes to your body, you probably spend more time thinking about your hair than your hormones. For some people, though, a problem with a hormone called insulin causes a health condition called type 2 diabetes (pronounced: dye-uh-BEE-tees).
How Insulin And Glucagon Work
Insulin and glucagon are hormones that help regulate the levels of blood glucose, or sugar, in your body. Glucose, which comes from the food you eat, moves through your bloodstream to help fuel your body. Insulin and glucagon work together to balance your blood sugar levels, keeping them in the narrow range that your body requires.
Diabetes Treatment: Using Insulin To Manage Blood Sugar
Understanding how insulin affects your blood sugar can help you better manage your condition. Insulin therapy is often an important part of diabetes treatment. Understand the key role insulin plays in managing your blood sugar, and the goals of insulin therapy. What you learn can help you prevent diabetes complications.
Video: How Diabetes Affects Your Blood Sugar
Your body uses glucose for energy. Glucose metabolism requires insulin, a hormone produced by your pancreas. Here's how normal glucose metabolism works, and what happens when you have diabetes — a disease where your body either can't produce enough insulin or it can't use insulin properly.
Relationships Between Glucose Levels And Insulin Secretion During A Glucose Challenge Test
Abstract The relationship between glucose and insulin levels was examined in a prospective study of 153 pregnant patients without diabetes who underwent a standard 50 gm glucose challenge test.
Glucose, Insulin & Pancreas Function
In a healthy person Normally, the pancreas makes enough insulin to keep the supply and use of glucose in balance. When the blood contains enough insulin, the liver temporarily shuts down its production of glucose, and glucose is transported from the blood into your cells. Cells use some of the glucose immediately.
Insulin Levels Vs. Glucose Levels
Diabetes is a disorder in which levels of blood sugar or glucose are above normal. In the five liters of blood that the average human has, only about a teaspoon of glucose is necessary to ensure proper function and regular health. Excess amounts of blood sugar hinder circulation and cause greater health problems over time.
How Insulin And Glucagon Work To Regulate Blood Sugar Levels
The pancreas secretes insulin and glucagon, both of which play a vital role in regulating blood sugar levels. The two hormones work in balance. If the level of one hormone is outside the ideal range, blood sugar levels may spike or drop. Together, insulin and glucagon help keep conditions inside the body steady.
Relationship Between Glucose And Insulin Levels In A Non-diabetic
Insulin, made by the pancreas, is an important hormone for blood sugar regulation. After consuming food, glucose (sugar) is extracted from the consumed carbohydrates and released into the bloodstream. In a healthy (non-diabetic) person, this increase in blood glucose levels triggers the pancreas to release insulin.
Glucose Insulin And Diabetes
Every cell in the human body needs energy to survive and do its different functions. If we're talking about a brain cell, it needs energy to keep stimulating other brain cells and sending on signals and messages. If it's a muscle cell, it needs energy to contract. They need energy just to do the basic functions of a cell.
The Relationship Between Glucose And Insulin
Glucose meet insulin, insulin meet glucose. The Relationship Between Glucose and Insulin What exactly is glucose? Or insulin? Glucose is basically a sugar found in food. Its job is to provide energy to the cell. Glucose gets into the body through digestion. It goes through the mouth, into the stomach, and then finally into the small intestine.
Insulin Basics
Diabetics need insulin therapy because they can't make their own. Insulin therapy tries to mimic natural insulin secretion — what happens automatically in non-diabetics. The ultimate goal of insulin therapy is to mimic normal insulin levels. Unfortunately, current insulin replacement therapy can only approximate normal insulin levels.
Facts About Diabetes And Insulin
Diabetes is a very common disease, which, if not treated, can be very dangerous. There are two types of diabetes. They were once called juvenile-onset diabetes and adult diabetes. However, today we know that all ages can get both types so they are simply called type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
How does insulin affect blood sugar?
Insulin has a number of actions on the body besides lowering your blood glucose levels. Insulin suppresses the breakdown and buildup of glycogen, which is the storage form of glucose, it blocks fat metabolism and the release of fatty acids, and it puts potassium into the cells by activating the sodium-potassium cellular channels. Insulin stimulates the uptake of glucose and potassium in all cells of the body but primarily fuels the muscle cells as well as some of the fat cells. In type 2 diabetes or metabolic syndrome (a form of metabolic disease), insulin is not functioning up to its normal level. The cells of the body become resistant to insulin and the blood sugar levels are elevated. The serum potassium (K+) level is a reflection of the total body stores of potassium, although it can be inaccurate in some conditions that affect the distribution of potassium in the body’s cells. The plasma potassium level determines the resting potential of the cells of the body. A person can have low potassium (hypokalemia) or high potassium (hyperkalemia), both of which are asymptomatic conditions that can be serious as they both cause heart arrhythmias. The Relationship between Insulin and Potassium Shortly after insulin was discovered, scientists revealed that insulin had something to do with the potassium levels in both the cells and in the blood. The insulin is the hormone in the body that keeps the potassium level in the blood within the normal range. When insulin is decreased, the potassium level rises and can rise even further if you eat something high in potassium, such as salt substitutes and bananas. When the potassium level is high, it causes the pancreas to release insulin in order to counteract the effects of high potassium levels. When you eat something that is high Continue reading >>
How do insulin and glucagon work together?
Both are hormones secreted by the pancreas but they are made from different types of cells in the pancreas. Both help manage the blood glucose levels in the body but they have opposite effects. Both respond to blood glucose levels but they have opposite effects. Each of us has insulin and glucagon in our systems because it is a strict requirement that the blood sugar level in the body is kept in a narrow therapeutic range. You need both insulin and glucagon to respond to various levels of glucose in the bloodstream. While insulin responds and is secreted by the pancreas upon having high glucose levels in the bloodstream, glucagon responds and is secreted by the pancreas upon having low glucose levels in the bloodstream. This maintains homeostasis in the body and keeps the blood sugar stable at all times. Function of Insulin Insulin is a protein-based hormone that is secreted by the beta cells inside the pancreas whenever the pancreas senses that the blood sugar is too high. Low levels of insulin are constantly being secreted into the bloodstream by the pancreas, even when blood glucose levels are normal. After you eat a meal, the glucose from the food you eat is taken up by the gastrointestinal tract, increasing the level of glucose in the blood. When this happens, the beta cells get activated and more insulin is secreted to help decrease the glucose levels, primarily by helping the glucose enter the cells to be used as cellular fuel. When the glucose level in the blood decreases, insulin levels by the islet (beta) cells of the pancreas return to a baseline status. In response to the elevated insulin level, the various cells of the body bind to insulin and the insulin facilitates the transfer of glucose from t Continue reading >>
How does carbohydrate affect blood sugar?
Diabetics and other people watching their blood sugar need to pay particular attention to the amount of carbohydrate-containing foods they eat because carbohydrates are the most responsible for increases in blood sugar levels. The type of carbohydrate-containing food also plays a role, however, in how quickly and how much blood sugar levels increase. Carbohydrates, with the exception of fiber, get broken down into sugars by your body. These sugars then enter the bloodstream, increasing your blood glucose levels. Higher blood sugar levels lead the body to produce and release insulin, which causes your cells to pull extra sugar out of the bloodstream for storage. Should blood levels of sugar become too low, another hormone, called glucagon, causes the stored sugar to be released back into the bloodstream. People with diabetes either don't produce enough insulin or their body doesn't respond properly to insulin, causing a problem with this cycle. Recommended Consumption The more carbohydrates you consume, the more sugars will get released into your bloodstream. This doesn't mean diabetics need to avoid carbohydrates. In fact, they should get the same 45 percent to 65 percent of their calories from carbohydrates as nondiabetics. They just need to spread their carbohydrate intake evenly throughout the day, including about 45 to 60 grams of carbohydrates in each meal. Foods high in fiber, such as legumes, fruits, vegetables and whole grains, are best because the fiber slows down the release of sugar into the bloodstream and limits sudden spikes in blood sugar. Glycemic Index and Glycemic Load On average, a gram of carbohydrate will raise blood glucose levels by about 4 points for someone weighing 150 pounds, or about 3 points for someone weighing 200 pounds. You can use the g Continue reading >>
How does diabetes affect the body?
What is diabetes? Diabetes is disease that causes the body to either not produce insulin or not react properly to the insulin. There are two types of diabetes: Type 1 diabetes is when the body simply does not produce insulin. This type develops in teens and is less common than Type 2. When you have Type 1 diabetes, your immune system turns on the pancreas, causing it not to produce insulin. This causes blood sugar levels to get too high. People with Type 1 take insulin injections to help regulate their blood glucose levels. Type 2 diabetes is when the cells in the body do not react properly with the insulin being produced. The signal to the GLUT4 is never sent from the receptors, so the cells don't allow glucose to enter. Insulin injections can sometimes help people with Type 2, however they usually can only watch what they eat and be careful to exercise a certain amount. How is glucose tolerance testing used to diagnose diabetes? The GTT is usually administered after an abnormal urine test. Doctors use glucose tolerance testing to monitor the amount of glucose in the patient's blood at a given moment in time and to see if their body reacts properly in response to the glucose. If the glucose levels rise drastically and don't fall back down this indicates that there is a high chance that the patient has diabetes. The insulin test can determine the difference between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes; if the levels of insulin in the blood are high, the patient has Type 2 diabetes, and if there is no insulin in the blood the patient has Type 1. How does the development of Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes relate to how the body produces and uses insulin? In type one diabetes the persons immune system attacks the pancreas causing it to shut down insulin production, leaving the person wit Continue reading >>
What is insulin used for?
This article is about the insulin protein. For uses of insulin in treating diabetes, see insulin (medication). Not to be confused with Inulin. Insulin (from Latin insula, island) is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets, and it is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. [5] It regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and protein by promoting the absorption of, especially, glucose from the blood into fat, liver and skeletal muscle cells. [6] In these tissues the absorbed glucose is converted into either glycogen via glycogenesis or fats (triglycerides) via lipogenesis, or, in the case of the liver, into both. [6] Glucose production and secretion by the liver is strongly inhibited by high concentrations of insulin in the blood. [7] Circulating insulin also affects the synthesis of proteins in a wide variety of tissues. It is therefore an anabolic hormone, promoting the conversion of small molecules in the blood into large molecules inside the cells. Low insulin levels in the blood have the opposite effect by promoting widespread catabolism, especially of reserve body fat. Beta cells are sensitive to glucose concentrations, also known as blood sugar levels. When the glucose level is high, the beta cells secrete insulin into the blood; when glucose levels are low, secretion of insulin is inhibited. [8] Their neighboring alpha cells, by taking their cues from the beta cells, [8] secrete glucagon into the blood in the opposite manner: increased secretion when blood glucose is low, and decreased secretion when glucose concentrations are high. [6] [8] Glucagon, through stimulating the liver to release glucose by glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis, has the opposite effect of insulin. [6] [8] The secretion of insulin and glucagon into the Continue reading >>
The basics of high blood sugar
Diabetes is a problem with your body that causes blood sugar (also called blood glucose) levels to rise higher than normal. This is also called hyperglycemia.
Type 1
In type 1 diabetes, your immune system mistakenly treats the beta cells in your pancreas that make insulin as foreign invaders and destroys them. This can happen over a few weeks, months, or years.
Type 2
If you have type 2 diabetes, your body does not use insulin properly. This is called insulin resistance. At first, the beta cells make extra insulin to make up for it. But, over time your pancreas can't make enough insulin to keep your blood sugar at normal levels.
Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is diabetes that develops during pregnancy. For most women, blood sugar levels will return to normal after giving birth. And if you've had gestational diabetes, you will need to be tested regularly since you are at much higher risk for developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
So, what affects my blood sugar levels?
It is important to understand what can make your blood sugar rise or fall, so that you can take steps to stay on target.
What is the role of insulin in diabetes?
Insulin. Insulin is a hormone which plays a key role in the regulation of blood glucose levels. A lack of insulin, or an inability to adequately respond to insulin, can each lead to the development of the symptoms of diabetes. In addition to its role in controlling blood sugar levels, insulin is also involved in the storage of fat.
How does insulin help with glucose?
Insulin helps control blood glucose levels by signaling the liver and muscle and fat cells to take in glucose from the blood. Insulin therefore helps cells to take in glucose to be used for energy.
What is the role of insulin in fat storage?
Insulin and fat storage. As well as being involved in the regulation of blood glucose, insulin is also involved in how fat is used by the body. When the liver is has taken up its capacity of glycoge, insulin signals fat cells to take up glucose to be stored as triglycerides. An additional effect of insulin is in inhibiting the breakdown of fats.
How does diabetes affect the body?
As a result the body is less able to take up glucose from the blood. In the earlier stages of type 2 diabetes, the body responds by producing more insulin than it would normally need to. If type 2 diabetes develops over a number of years, the extra demands on the pancreas to produce insulin can lead to a loss of insulin producing cells ...
How does the liver store glucose?
If the body has sufficient energy , insulin signal s the liver to take up glucose and store it as glycogen. The liver can store up to around 5% of its mass as glycogen. Some cells in the body can take glucose from the blood without insulin, but most cells do require insulin to be present.
What type of insulin is needed for type 1 diabetes?
Synthetic insulin. People with type 1 diabetes and a proportion of people with type 2 diabetes will need to take exogenous insulin (insulin that is not produced by one’s own body). Insulin is usually injected but can also be delivered by an insulin pump which continually infuses insulin through the day and night.
Can the body take glucose from the blood?
Without the presence of insulin, many of the body’s cells cannot take glucose from the blood and therefore the body uses other sources of energy. Ketones are produced by the liver as an alternative source of energy, however, high levels of the ketones can lead to a dangerous condition called ketoacidosis. People with type 1 diabetes will need ...
