What are some ways to calculate pH from Ka?
pKa = -log (Ka) and so we get an equation relating pH and pKa: pH = -log (Ka) + log ( [HA]/ [A-]) So, the only way to relate the two is if you know the concentrations of the acid and its conjugate base. If these values are known, then you can just put the values into this equation. If not, then there is no way to find the pKa from the pH.
How to find Ka with pH?
pH is the negative Log of the concentration of H30+. If you are given the Ka of a weak acid, the equation is Ka= [ (concentration of conjugate base)* (concentration of H3O+) ]/ [ (concentration of conjugate acid -concentration of conjugate base)]. This can be simplified (assuming Ka is quite small) to
How to calculate pH given Ka?
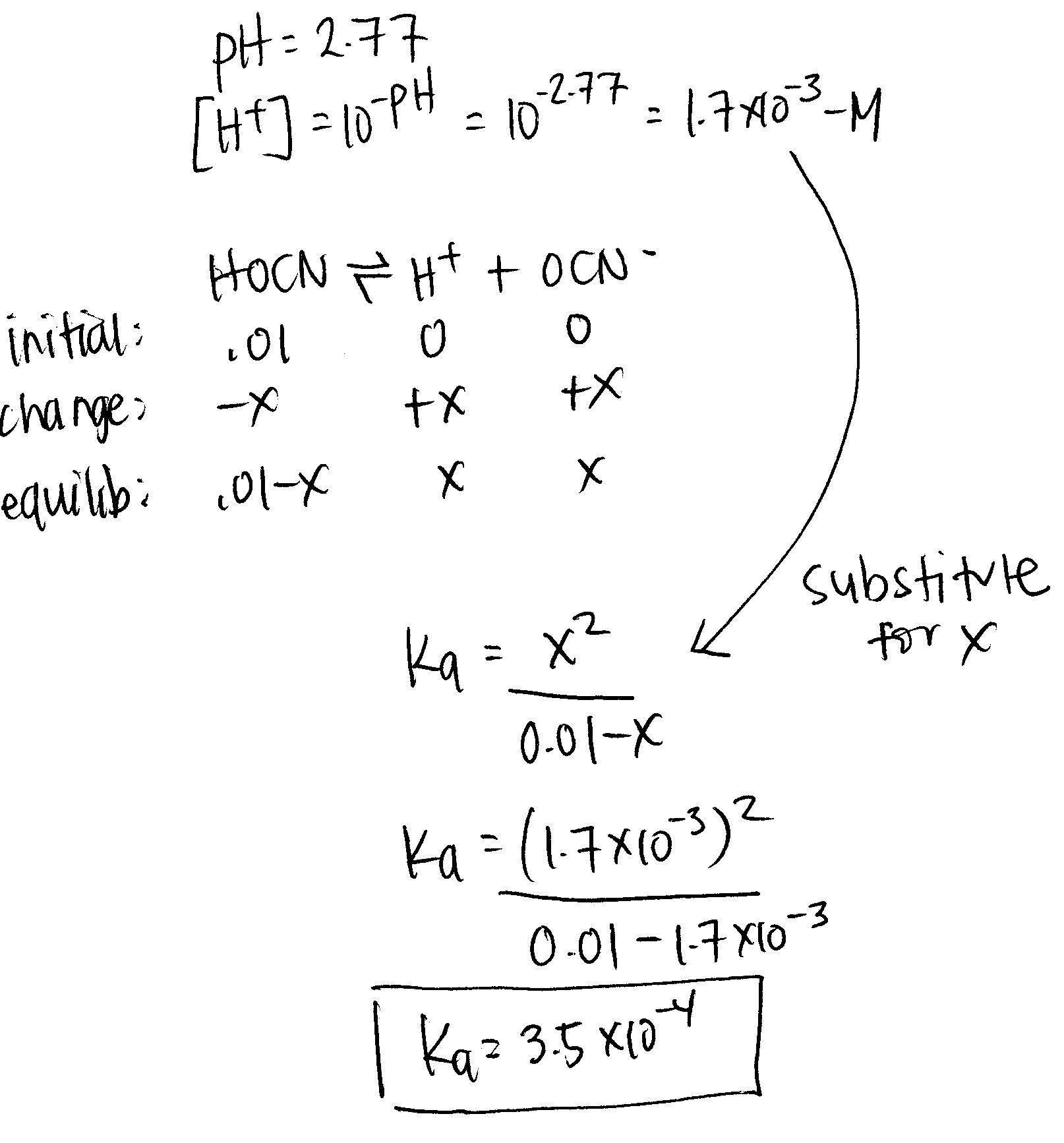
When given the pH value of a solution, solving for K a requires the following steps:
- Set up an ICE table for the chemical reaction.
- Solve for the concentration of H 3 O + using the equation for pH: (5) [ H 3 O +] = 10 − p H
- Use the concentration of H 3 O + to solve for the concentrations of the other products and reactants.
- Plug all concentrations into the equation for K a and solve.
What does Ka mean in chemistry?
What is Ka in Chemistry? The acid dissociation constant (Ka) is used to differentiate between strong and weak acids. The acid dissociates more as the Ka increases. Strong acids must therefore dissociate more in water. A weak acid, on the other hand, is less likely to ionise and release a hydrogen ion, leading to a less acidic solution.

What is the relationship between pH pKa and Ka?
Difference Between pKa and pH pKa is the negative value of the logarithm of Ka. pH is the logarithmic value of the inverse of H+ concentration. pKa indicates whether an acid is a strong acid or a weak acid. pH indicates whether a system is acidic or alkaline.
How does Ka affect pH?
Explanation: The Ka is the acid dissociation constant, and thus it is what determines how strong the acid is. Stronger acids dissociate to a greater extent and produce lower pH values.
How does Ka determine pH?
To find out the Ka of the solution, firstly, we will determine the pKa of the solution. At the equivalence point, the pH of the solution is equivalent to the pKa of the solution. Thus using Ka = – log pKa equation, we can quickly determine the value of Ka using a titration curve.
Does Ka vary with pH?
Ka is a better measure of the strength of an acid than pH because adding water to an acid solution doesn't change its acid equilibrium constant, but does alter the H+ ion concentration and pH.
Does higher ka mean more acidic?
The numerical value of Ka is used to predict the extent of acid dissociation. A large Ka value indicates a stronger acid (more of the acid dissociates) and small Ka value indicates a weaker acid (less of the acid dissociates).
What does higher ka mean?
The acid dissociation constant (Ka) is used to distinguish strong acids from weak acids. Strong acids have exceptionally high Ka values. The Ka value is found by looking at the equilibrium constant for the dissociation of the acid. The higher the Ka, the more the acid dissociates.
What is a high Ka value?
A large Ka value indicates a strong acid because it means the acid is largely dissociated into its ions. A large Ka value also means the formation of products in the reaction is favored. A small Ka value means little of the acid dissociates, so you have a weak acid.
What Ka value is a strong acid?
Strong acids completely dissociate in aq solution (Ka > 1, pKa < 1).
How do you find pH with KA and M?
0:003:45How to find pH from molarity and Ka - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipOkay times the anion concentration divided by the solution concentration alright and if you look atMoreOkay times the anion concentration divided by the solution concentration alright and if you look at this formula right here you're trying to find pH. They give you the solution concentration.
What is Ka affected by?
The ONLY factor that affect Ka is temperature, and therefore there is no influence of concentration change on the value of Ka .
How do you find the pH of a weak acid with Ka?
Finding the pH of a weak acid is a bit more complicated than finding pH of a strong acid because the acid does not fully dissociate into its ions. The pH equation is still the same (pH = -log[H+]), but you need to use the acid dissociation constant (Ka) to find [H+].
How do you compare Ka values?
1 Answer. The greater the Ka value for an acid is relative to the strength of the acid, or the magnitude at which it will disassociate in water. The closer the Ka value is to one the stronger it is (the term "strong acid" means that it completely disassociates).
Does pKa increase with pH?
Relative Acidity and pKa Values. An application of the Henderson-Hasselbach Equation is the ability to determine the relative acidity of compounds by comparing their pKa values. The stronger an acid, the greater the ionization, the lower the pKa, and the lower the pH the compound will produce in solution.
How do you find the pH of a weak acid with Ka?
Finding the pH of a weak acid is a bit more complicated than finding pH of a strong acid because the acid does not fully dissociate into its ions. The pH equation is still the same (pH = -log[H+]), but you need to use the acid dissociation constant (Ka) to find [H+].
What is difference between KA and pKa?
Ka is the acid dissociation constant. pKa is simply the -log of this constant.
Does higher KB mean stronger base?
A significant Kb value implies a strong base's high amount of dissociation. A lower pKb value indicates a stronger base. In an aqueous solution, a weak base ionizes just minimally. Keep in mind that a base is a material that takes a hydrogen ion from another chemical.
What is Ka?
Ka or acid dissociation constant is a standard used to measure the strength of an acid. It determines the extent of acid dissociation in an aqueous...
What is pH?
The pH or potential of hydrogen is a criterion for measuring the acidity or alkalinity of the solution. It determines the hydrogen ion concentratio...
Are Ka and pH the same?
No, Ka and pH are not the same. However, they were found to be associated. More the Ka, more would be its dissociation and thus stronger would be t...
What is the difference between Ka and pH?
S No. Ka pH 1 Ka or acid dissociation constant is a standard used to measure the strength of an acid. The pH or potential of hydrogen is a criterio...
What is the pH of pure water at 25℃?
The pH of pure water is equal to 7 at 25℃.
What is the Ka value of a weak acid?
The Ka value for most weak acids ranges from 10 -2 to 10 -14 . The pKa gives the same information, just in a different way. The smaller the value of pKa, the stronger the acid. Weak acids have a pKa ranging from 2-14.
How are Kb and Ka related?
Ka and Kb are related to each other through the ion constant for water, Kw: Ka is the acid dissociation constant. pKa is simply the -log of this constant. Similarly, Kb is the base dissociation constant, while pKb is the -log of the constant.
What Does the "p" Mean?
Whenever you see a "p" in front of a value, like pH, pKa, and pKb, it means you're dealing with a -log of the value following the "p". For example, pKa is the -log of Ka. Because of the way the log function works, a smaller pKa means a larger Ka. pH is the -log of hydrogen ion concentration, and so on.
What is the pH of a solution?
pH is a measure of hydrogen ion concentration, [H+], in an aqueous (water) solution. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14. A low pH value indicates acidity, a pH of 7 is neutral, and a high pH value indicates alkalinity. The pH value can tell you whether you're dealing with an acid or a base, but it offers limited value indicating the true strength of the acid of a base. The formulas to calculate pH and pOH are:
What does ka mean in math?
In the formulas, A stands for acid and B for base. Ka = [H+] [A-]/ [HA] pKa = - log Ka. at half the equivalence point, pH = pKa = -log Ka. A large Ka value indicates a strong acid because it means the acid is largely dissociated into its ions.
What is the Kb constant?
Kb is the base dissociation constant. The base dissociation constant is a measure of how completely a base dissociates into its component ions in water. A large Kb value indicates the high level of dissociation of a strong base. A lower pKb value indicates a stronger base.
What are the ka and pka?
Understanding Ka and pKa. Ka, pKa, Kb, and pKb are most helpful when predicting whether a species will donate or accept protons at a specific pH value. They describe the degree of ionization of an acid or base and are true indicators of acid or base strength because adding water to a solution will not change the equilibrium constant.
What is the difference between pH and pKa?
The pH is a measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions in an aqueous solution. pKa ( acid dissociation constant) and pH are related, but pKa is more specific in that it helps you predict what a molecule will do at a specific pH.
What does pH and pKa mean?
Once you have pH or pKa values, you know certain things about a solution and how it compares with other solutions: The lower the pH, the higher the concentration of hydrogen ions [H + ]. The lower the pKa, the stronger the acid and the greater its ability to donate protons. pH depends on the concentration of the solution.
How to determine pH of a solution?
Once you have pH or pKa values, you know certain things about a solution and how it compares with other solutions: 1 The lower the pH, the higher the concentration of hydrogen ions [H + ]. 2 The lower the pKa, the stronger the acid and the greater its ability to donate protons. 3 pH depends on the concentration of the solution. This is important because it means a weak acid could actually have a lower pH than a diluted strong acid. For example, concentrated vinegar (acetic acid, which is a weak acid) could have a lower pH than a dilute solution of hydrochloric acid (a strong acid). 4 On the other hand, the pKa value is constant for each type of molecule. It is unaffected by concentration. 5 Even a chemical ordinarily considered a base can have a pKa value because the terms "acids" and "bases" simply refer to whether a species will give up protons (acid) or remove them (base). For example, if you have a base Y with a pKa of 13, it will accept protons and form YH, but when the pH exceeds 13, YH will be deprotonated and become Y. Because Y removes protons at a pH greater than the pH of neutral water (7), it is considered a base.
What does pKa tell you?
Essentially, pKa tells you what the pH needs to be in order for a chemical species to donate or accept a proton. The relationship between pH and pKa is described by the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation .
How to find pH if you know pKa?
If you know either pH or pKa, you can solve for the other value using an approximation called the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation: pH is the sum of the pKa value and the log of the concentration of the conjugate base divided by the concentration of the weak acid.
How to find pH of conjugate base?
pH is the sum of the pKa value and the log of the concentration of the conjugate base divided by the concentration of the weak acid. At half the equivalence point: pH = pKa. It's worth noting sometimes this equation is written for the K a value rather than pKa, so you should know the relationship: pKa = -logK a.
Why is Henderson-Hasselbalch an approximation?
The reason the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is an approximation is because it takes water chemistry out of the equation. This works when water is the solvent and is present in a very large proportion to the [H+] and acid/conjugate base. You shouldn't try to apply the approximation for concentrated solutions.
What should a proficient student know about pH?
Proficient students should be able to calculate the pH, Molarity, percent ionization, and Ka of an acid or base, as well as create and evaluate particle diagram models depicting various acidic and basic solutions, construct and evaluate graphs and trends of this data, and analyze and interpret the patterns and trends in lab data. Proficient students should also be able to use these skills to make predictions and arguments about additional solutions to explain chemical phenomena. This lesson was created to strengthen the understanding of the relationships between these concepts and skills.
Is pH 3-7 strong?
Many students tend to associate pH values only with the strength of the acid. The major misconception is that acids with pH values approximately less than 2 are strong and acids with pH values of 3-7 are weak. This can be a fatal mistake, as the same student may think they can ingest all weak acids, like citric acid or vinegar, ...
Is acid pH strong or weak?
The major misconception is that acids with pH values approximately less than 2 are strong and acids with pH values of 3-7 are weak. This can be a fatal mistake, as the same student may think they can ingest all weak acids, like citric acid or vinegar, regardless of their concentration. Before this lesson, the concept of acids and bases was introduced with this misconception in mind. Students had to create models depicting many different concentrations of various weak and strong acids and bases. As lessons continued, my lessons had a strong focus on mathematical computations, required by the Advanced Placement Exam. This lesson was designed to refocus the instruction to the particulate, macroscopic, and symbolic representations of their calculations.

Ph and Pka
Relating Ph and Pka with The Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
- If you know either pH or pKa, you can solve for the other value using an approximation called the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation: pH = pKa + log ([conjugate base]/[weak acid]) pH = pka+log ([A-]/[HA]) pH is the sum of the pKa value and the log of the concentration of the conjugate base divided by the concentration of the weak acid. At half the equivalence point: pH = pKa It's worth …
Assumptions For The Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
- The reason the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is an approximation is because it takes water chemistry out of the equation. This works when water is the solvent and is present in a very large proportion to the [H+] and acid/conjugate base. You shouldn't try to apply the approximation for concentrated solutions. Use the approximation only when the following conditions are met: 1. −…
Example Pka and Ph Problem
- Find [H+] for a solution of 0.225 M NaNO2 and 1.0 M HNO2. The Ka value (from a table) of HNO2 is 5.6 x 10-4. pKa = −log Ka = −log(7.4×10−4) = 3.14 pH = pka + log ([A-]/[HA]) pH = pKa + log([NO2-]/[HNO2]) pH = 3.14 + log(1/0.225) pH = 3.14 + 0.648 = 3.788 [H+] = 10−pH = 10−3.788 = 1.6×10−4
Sources
- de Levie, Robert. “The Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation: Its History and Limitations.” Journal of Chemical Education, 2003.
- Hasselbalch, K. A. "Die Berechnung der Wasserstoffzahl des Blutes aus der freien und gebundenen Kohlensäure desselben, und die Sauerstoffbindung des Blutes als Funktion der Wasserstoffzahl." Bioche...
- de Levie, Robert. “The Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation: Its History and Limitations.” Journal of Chemical Education, 2003.
- Hasselbalch, K. A. "Die Berechnung der Wasserstoffzahl des Blutes aus der freien und gebundenen Kohlensäure desselben, und die Sauerstoffbindung des Blutes als Funktion der Wasserstoffzahl." Bioche...
- Henderson , Lawrence J. "Concerning the relationship between the strength of acids and their capacity to preserve neutrality." American Journal of Physiology-Legacy Content, vol. 21, no. 2, Feb. 19...
- Po, Henry N., and N. M. Senozan. “The Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation: Its History and Limitations.” Journal of Chemical Education, vol. 78, no. 11, 2001, p. 1499.