
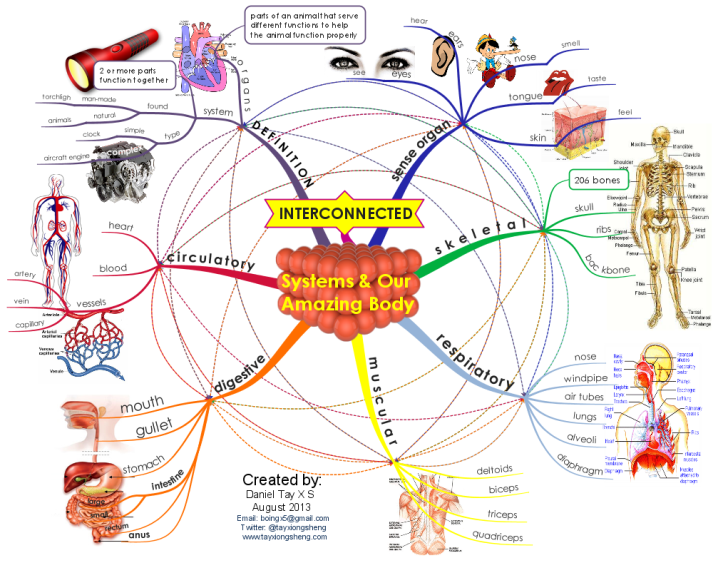
What is the respiratory system?
Title Respiratory System 1 We breath air into our lungs. 2 Oxygen is then transported around our body by our blood. 3 Air passes through the nose or mouth into the trachea 4 The trachea splits into 2 tubes called the bronchi, one going to each lung 5 The bronchi split into smaller tubes, called the bronchioles More items...
How does respiration occur in the respiratory system?
Respiration is where exercise causes muscles to release energy in the form of glucose. Air is warmed, moistened and filtered as it travels through the mouth and nasal passages. It then passes through the trachea and one of the two bronchi into one of the lungs.
What is the pathway of air in the respiratory system?
Air is warmed, moistened and filtered as it travels through the mouth and nasal passages. It then passes through the trachea and one of the two bronchi into one of the lungs.
What is the role of the respiratory system in gas exchange?
The human body is designed to take in oxygen and to remove carbon dioxide. The respiratory system, in combination with the cardiovascular system, is responsible for providing this function. Gas exchange occurs at the alveoli in the lungs and takes place by diffusion.
What is the respiratory system GCSE?
There are two lungs and a bronchus leads into each one. Each Bronchus splits into hundreds of smaller tubes, called bronchioles. Each bronchiole leads into tiny air sacs called an alveoli (singular, alveolus). Each alveoli is surrounded by at least 1 capillary.
How does the respiratory system work GCSE PE?
Air is warmed, moistened and filtered as it travels through the mouth and nasal passages. It then passes through the trachea and one of the two bronchi into one of the lungs. After passing into the many bronchioles, it finally arrives into some of the millions of tiny sacs called alveoli.
What is respiration BBC Bitesize GCSE?
Respiration is a chemical reaction which occurs in every one of the cells in the human body. It releases energy stored in glucose and without it, these cells would die. Aerobic respiration occurs in the presence of oxygen. The equation for aerobic respiration is: glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water.
What is respiratory system easy answer?
The respiratory system is the network of organs and tissues that help you breathe. It includes your airways, lungs and blood vessels. The muscles that power your lungs are also part of the respiratory system. These parts work together to move oxygen throughout the body and clean out waste gases like carbon dioxide.
What is the function of the respiratory system?
The respiratory system's main job is to move fresh air into your body while removing waste gases. Once in the lungs, oxygen is moved into the bloodstream and carried through your body. At each cell in your body, oxygen is exchanged for a waste gas called carbon dioxide.
What is the main function of the respiratory system BBC Bitesize?
The respiratory systemStructureFunctionNasal cavityAir is warmed and filtered as it enters the body.TracheaBrings air into the lungs. Supported by rings of cartilage that prevent it collapsing.BronchusBranches off the trachea to bring air into the lungs. Also supported by rings of cartilage.9 more rows
Why do we need respiration GCSE?
to drive the chemical reactions needed to keep organisms alive – the reactions to build complex carbohydrates , proteins and lipids from the products of photosynthesis in plants, and the products of digestion in animals, require energy.
What happens in respiration?
Respiration is the process that all living things go through to create the energy they need to live. This happens in the cells so it is also called cellular respiration. It usually involves exchanging two gases—oxygen and carbon dioxide. The cells take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide.
What are the three types of respiration?
Respiration is the process of gas exchange between the air and an organism's cells. Three types of respiration include internal, external, and cellular respiration.
What are the 5 main functions of the respiratory system?
The functions of the respiratory system include gas exchange, acid-base balance, phonation, pulmonary defense and metabolism, and the handling of bioactive materials.
How the respiratory system works step by step?
Every time you breathe in air, your diaphragm tightens, moving downward to make space in your chest. Your lungs expand, pulling air in through your nose and/or mouth. That air then moves down your trachea, through your bronchi and into the bronchioles, where it enters your alveoli.
What are the 7 functions of the respiratory system?
What are seven functions of the respiratory system? Move Air: The respiratory system is responsible for moving air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs. ... Produce Sounds: ... Gas Exchange: ... Protect: ... Acid-Base Balance: ... Olfactory: ... Regulating Blood Volume and Blood Pressure:
What is the process of gaseous exchange GCSE PE?
Gaseous exchange occurs at the alveoli in the lungs and takes place by diffusion. The alveoli are surrounded by capillaries so oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between the air in the alveoli and the blood in the capillaries.
What are the functions of respiratory system class 11 PE?
To exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide between the air and blood. To produce sound. To regulate blood PH. To protect against some micro organism.
What happens if you inhale GCSE?
Breathing in When you inhale: the internal intercostal muscles relax and the external intercostal muscles contract, pulling the ribcage upwards and outwards. the diaphragm contracts, pulling downwards. lung volume increases and the air pressure inside decreases.
What is respiratory system in physical education class 11?
Respiratory System : Respiratory system is a mechanism to take oxygen inside and throw away carbon dioxide. This sytem consists of nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea or wind pipe and the lungs (see fig.).
Which system transports oxygen from the air we breathe, through a system of tubes, into our lungs and then?
The respiratory system transports oxygen from the air we breathe, through a system of tubes, into our lungs and then diffuses it into the bloodstream, whilst carbon dioxide makes the opposite journey.
What are the two structures that separate the chest and lungs?
Breathing. Breathing is the term given to the process of taking air into and out of the lungs. Two important structures for breathing are the diaphragm and intercostal muscles. The diaphragm is a sheet of muscle that separates the chest (or thoracic) cavity from the rest of the body.
What are the walls of the alveoli made of?
They are made of semi-permeable membranes which allow oxygen and carbon dioxide to pass through them.
Which molecule carries oxygen to the working muscle and carbon dioxide to the lung?
Haemoglobin carries oxygen to be exchanged at the working muscle and carbon dioxide to be exchanged at the lung. As the blood moves through the capillaries in the alveoli, oxygen diffuses into it and carbon dioxide diffuses out of it. Capillaries surround the alveoli in the lungs.
Where does gas exchange occur?
Gaseous (or gas) exchange. Gas exchange occurs at the alveoli in the lungs and takes place by diffusion. The alveoli are surrounded by capillaries so oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between the air in the alveoli and the blood in the capillaries.
What is the name of the tube that the air travels through?
Each bronchus branches out into smaller tubes called bronchioles. Air travels through these bronchioles. At the end of the bronchioles , the air enters one of the many millions of alveoli where gaseous exchange takes place.
What is the movement of gas from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration?
Diffusion is the movement of gas from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. There is a high concentration of oxygen in the alveoli and a low concentration of oxygen in the blood, so oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into the blood.
Which system transports oxygen from the air we breathe, through a system of tubes, into our lungs and then?
The respiratory system transports oxygen from the air we breathe, through a system of tubes, into our lungs and then diffuses it into the bloodstream, whilst carbon dioxide makes the opposite journey.
How does air enter the lungs?
Passage of air into the lungs 1 Air enters the body and is warmed as it travels through the mouth and nose. 2 It then enters the trachea. 3 The trachea divides into two bronchi. One bronchus enters each lung. 4 Each bronchus branches out into smaller tubes called bronchioles. Air travels through these bronchioles. 5 At the end of the bronchioles, the air enters one of the many millions of alveoli where gaseous exchange takes place.
What is the process of gas exchange in muscles?
In the muscle there is a high concentration of carbon dioxide and in the bloodstream there is a high concentration of oxygen. Oxygen diffuses from the bloodstream into the muscles and carbon dioxide diffuses into the blood from the muscles.
What are the walls of the alveoli made of?
They are made of semi-permeable membranes which allow oxygen and carbon dioxide to pass through them.
How much oxygen is in the human body?
21% oxygen. 16% oxygen. 0.03% carbon dioxide. 4% carbon dioxide. The human body is designed to take in oxygen and to remove carbon dioxide. The respiratory system, in combination with the cardiovascular system, is responsible for providing this function.
Which molecule carries oxygen to the working muscle and carbon dioxide to the lung?
Haemoglobin carries oxygen to be exchanged at the working muscle and carbon dioxide to be exchanged at the lung. As the blood moves through the capillaries in the alveoli, oxygen diffuses into it and carbon dioxide diffuses out of it. Capillaries surround the alveoli in the lungs.
Where does gas exchange occur?
Gas exchange. Gas exchange occurs at the alveoli in the lungs and takes place by diffusion. The alveoli are surrounded by capillaries so oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between the air in the alveoli and the blood in the capillaries.
Which system transports oxygen from the air we breathe, through a system of tubes, into our lungs and then?
The respiratory system transports oxygen from the air we breathe, through a system of tubes, into our lungs and then diffuses it into the bloodstream, whilst carbon dioxide makes the opposite journey.
How does exercise affect the lungs?
This decreases the size of the chest and increases the air pressure in the chest so air is forced out of the lungs. During exercise, this passive process of relaxation becomes active as the abdominal muscles pull the ribs downwards and inwards even further.
What are the walls of the alveoli made of?
They are made of semi-permeable membranes which allow oxygen and carbon dioxide to pass through them.
What is the process of gas exchange at the muscles?
Describe the process of gaseous exchange at the muscles. In the muscle there is a high concentration of carbon dioxide and in the bloodstream there is a high concentration of oxygen. Oxygen diffuses from the bloodstream into the muscles and carbon dioxide diffuses into the blood from the muscles.
Where does gas exchange occur?
Gaseous exchange occurs at the alveoli in the lungs and takes place by diffusion. The alveoli are surrounded by capillaries so oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between the air in the alveoli and the blood in the capillaries.
Which molecule carries oxygen to the working muscle and carbon dioxide to the lung?
Haemoglobin carries oxygen to be exchanged at the working muscle and carbon dioxide to be exchanged at the lung. As the blood moves through the capillaries in the alveoli, oxygen diffuses into it and carbon dioxide diffuses out of it. Capillaries surround the alveoli in the lungs.
What is the name of the tube that the air travels through?
Each bronchus branches out into smaller tubes called bronchioles. Air travels through these bronchioles. At the end of the bronchioles , the air enters one of the many millions of alveoli where gaseous exchange takes place.
What is the respiratory system?
Breathing is part of the respiratory system, a complex process where air travels into and out of the lungs. Respiration is where exercise causes muscles to release energy in the form of glucose. Part of. Physical Education. Anatomy and physiology.
Where does air travel?
Air is warmed, moistened and filtered as it travels through the mouth and nasal passages. It then passes through the trachea and one of the two bronchi into one of the lungs. After passing into the many bronchioles, it finally arrives into some of the millions of tiny sacs called alveoli.
What is the system that we use to breathe and supply our bodies with oxygen?
The Respiratory System is everything we use to breathe and supply our bodies with oxygen.
What happens when you breathe?
When we breath, Carbon dioxide (CO 2) moves from the blood into the alveoli. Oxygen (O 2 )moves to the red blood cells, which contain haemoglobin. This combines with the O 2 to make oxyhaemoglobin. The red blood cells carry O 2 around the body, taking it to where its needed.
Where do bronchioles end up?
The bronchioles end up at small bags called the alveoli, where gaseous exchange takes place.
What are the adaptations of the alveoli?
The adaptations of the alveoli are explained: large surface area, moist, thin walls, good blood supply.
