What is the reticuloendothelial system of the liver?
The reticuloendothelial system of the liver includes endothelial cells, Kupffer cells, fat storing cells and pit cells. Kupffer cells have special surface structures, the so-called fuzzy coat and immunological receptors, which are responsible for phagocytotic activity.
How is the reticuloendothelial system involved in the nervous system?
The reticuloendothelial system is also under the leading role of the nervous system and is regulated by chemicals in the body fluids. The state of the cerebral cortex has a great influence on the activity of macrophages in the reticular endothelium.
What is the composition of the reticuloendothelial system?
The composition of the reticuloendothelial system includes Macrophages in the intestine and other tissues. The reticuloendothelial system is also under the leading role of the nervous system and is regulated by chemicals in the body fluids.
What is reticuloendothelial tuberculosis (res)?
Tuberculosis of the reticuloendothelial system (RES) is usually a manifestation of extrapulmonary TB involving the bone marrow, liver or spleen and being demonstrable as tubercles on liver or bone marrow biopsy.

What is the function of reticuloendothelial system?
The reticuloendothelial system, composed of tissue macrophages and their blood-borne counterparts, monocytes, removes particulate matter, including microbes, from the lymph and blood.
Is the liver part of the reticuloendothelial system include?
The Reticuloendothelial System (RES) consists of cells descending from the monocytes which are able to perform phagocytosis of foreign materials and particles. 90% of the RES are located in the liver.
What are the main components of the reticuloendothelial system?
The composition of the reticuloendothelial system includes Kupffer cells of the liver, microglia of the brain, alveolar macrophages and bone marrow lymph nodes, and macrophages in the intestine and other tissues.
Why is it called the reticuloendothelial system?
In anatomy the term "reticuloendothelial system" (abbreviated RES), often associated nowadays with the mononuclear phagocyte system (MPS), was originally launched by the beginning of the 20th century to denote a system of specialised cells that effectively clear colloidal vital stains (so called because they stain ...
What is another name for reticuloendothelial cells?
macrophage systemmononuclear phagocyte system, also called macrophage system or reticuloendothelial system, class of cells that occur in widely separated parts of the human body and that have in common the property of phagocytosis, whereby the cells engulf and destroy bacteria, viruses, and other foreign substances and ingest worn-out ...
Are Kupffer cells reticuloendothelial cells?
Kupffer cells, also known as stellate macrophages and Kupffer–Browicz cells, are specialized cells localized in the liver within the lumen of the liver sinusoids and are adhesive to their endothelial cells which make up the blood vessel walls....Kupffer cellFMA14656Anatomical terms of microanatomy9 more rows
What do reticular cells do?
A network of reticular cells that ensheathe a mesh of collagen fibers crisscrosses the tissue in each lymph node. This reticular cell network distributes key molecules and provides a structure for immune cells to move around on. During infections, the network can suffer damage.
Where do Kupffer cells come from?
These cells are derived from bone marrow stem cells or monocytes and are highly active in removing particulate matter and toxic or foreign substances that appear in the portal blood from the intestine. Kupffer cells are located in the sinusoidal lumen and are in direct contact with endothelial cells (seeFig. 72.1).
Where Kupffer cells are found?
the liverKupffer cells (also known as stellate sinusoidal macrophages or Kupffer-Browicz cells) are macrophages found in the sinusoids of the liver. In fact, Kupffer cells make up 80% to 90% of all the macrophages in the entire human body.
Who discovered reticuloendothelial system?
The systematic analysis of tissues and dyes led Karl Albert Ludwig Aschoff (1924) to coin the term “reticuloendothelial system” (RES) to describe this group of cells, with their ability to incorporate vital dyes from the circulation (18).
Is thymus part of reticuloendothelial system?
The cells of the RES are produced in the bone marrow. The thymus is also included as it is the required site for T cell maturation.
How do you pronounce reticuloendothelial system?
0:051:01How To Say Reticuloendothelial - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipPero el 12 o yo pero el 12 o yo pero el 12 o yo pero chequeo el 12o yo.MorePero el 12 o yo pero el 12 o yo pero el 12 o yo pero chequeo el 12o yo.
Is thymus part of reticuloendothelial system?
The cells of the RES are produced in the bone marrow. The thymus is also included as it is the required site for T cell maturation.
Is the bone marrow part of the reticuloendothelial system?
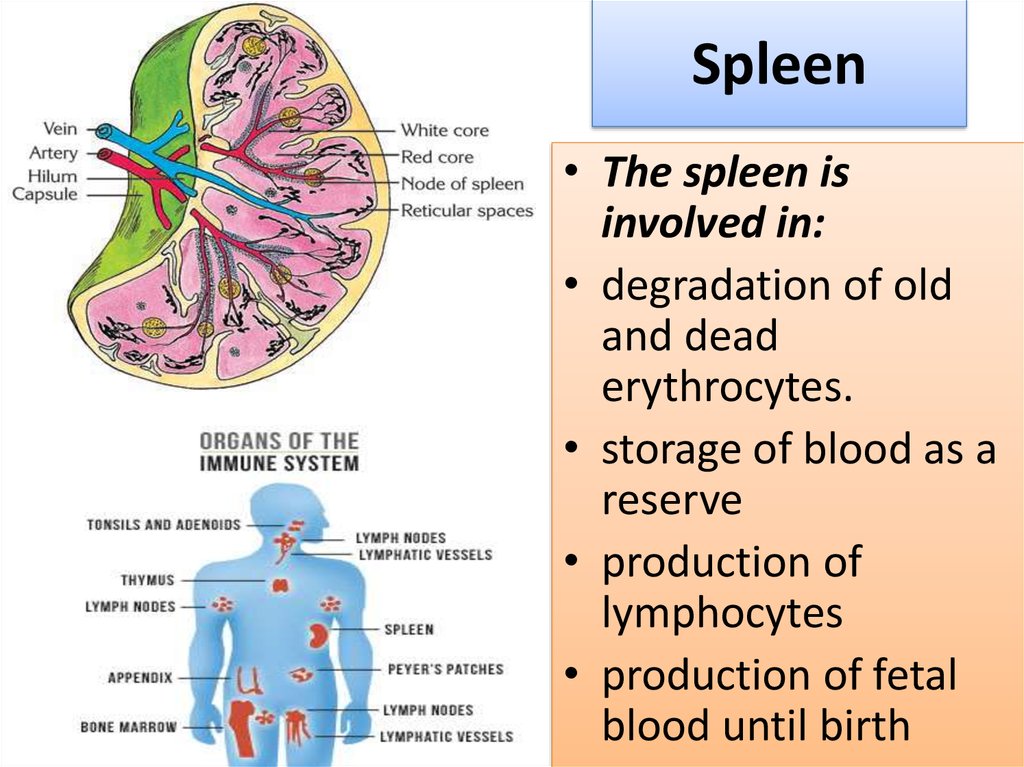
reticuloendothelial system a network of cells and tissues found throughout the body, especially in the blood, general connective tissue, spleen, liver, lungs, bone marrow, and lymph nodes.
Where is the reticular connective tissue located?
Reticular connective tissue is found around the kidney, liver, the spleen, and lymph nodes, Peyer' patches as well as in bone marrow.
What is a reticular tissue?
Reticular tissue is a special type of connective tissue that predominates in various locations that have a high cellular content. It has a branched and mesh-like pattern, often called reticulum, due to the arrangement of reticular fibers (reticulin). These fibers are actually type III collagen fibrils.
What are the functions of the liver?
The liver is an essential organ of the body that performs over 500 vital functions. These include removing waste products and foreign substances from the bloodstream, regulating blood sugar levels, and creating essential nutrients. Here are some of its most important functions: 1 Albumin Production: Albumin is a protein that keeps fluids in the bloodstream from leaking into surrounding tissue. It also carries hormones, vitamins, and enzymes through the body. 2 Bile Production: Bile is a fluid that is critical to the digestion and absorption of fats in the small intestine. 3 Filters Blood: All the blood leaving the stomach and intestines passes through the liver, which removes toxins, byproducts, and other harmful substances. 4 Regulates Amino Acids: The production of proteins depend on amino acids. The liver makes sure amino acid levels in the bloodstream remain healthy. 5 Regulates Blood Clotting: Blood clotting coagulants are created using vitamin K, which can only be absorbed with the help of bile, a fluid the liver produces. 6 Resists Infections: As part of the filtering process, the liver also removes bacteria from the bloodstream. 7 Stores Vitamins and Minerals: The liver stores significant amounts of vitamins A, D, E, K, and B12, as well as iron and copper. 8 Processes Glucose: The liver removes excess glucose (sugar) from the bloodstream and stores it as glycogen. As needed, it can convert glycogen back into glucose.
What is the liver?
The liver is reddish-brown and shaped approximately like a cone or a wedge, with the small end above the spleen and stomach and the large end above the small intestine. The entire organ is located below the lungs in the right upper abdomen. It weighs between 3 and 3.5 pounds.
How many lobes are there in the liver?
The liver consists of four lobes: the larger right lobe and left lobe, and the smaller caudate lobe and quadrate lobe. The left and right lobe are divided by the falciform (“sickle-shaped” in Latin) ligament, which connects the liver to the abdominal wall. The liver’s lobes can be further divided into eight segments, which are made up of thousands of lobules (small lobes). Each of these lobules has a duct flowing toward the common hepatic duct, which drains bile from the liver.
What does the liver store?
Stores Vitamins and Minerals: The liver stores significant amounts of vitamins A, D, E, K, and B12, as well as iron and copper. Processes Glucose: The liver removes excess glucose (sugar) from the bloodstream and stores it as glycogen. As needed, it can convert glycogen back into glucose.
What is the function of albumin in the body?
Albumin Production: Albumin is a protein that keeps fluids in the bloodstream from leaking into surrounding tissue. It also carries hormones, vitamins, and enzymes through the body. Bile Production: Bile is a fluid that is critical to the digestion and absorption of fats in the small intestine.
Which ligament separates the two lobes of the liver and connects it to the abdominal wall?
Falciform Ligament: A thin, fibrous ligament that separates the two lobes of the liver and connects it to the abdominal wall. Glisson’s Capsule: A layer of loose connective tissue that surrounds the liver and its related arteries and ducts.
How to avoid liver disease?
The best way to avoid liver disease is to take active steps toward a healthy life. The following are some recommendations that will help keep the liver functioning as it should: Avoid Illicit Drugs: Illicit drugs are toxins that the liver must filter out. Taking these drugs can cause long-term damage.
What is the reticuloendothelial system?
The reticuloendothelial system (RES) is a heterogeneous population of phagocytic cells in systemically fixed tissues that play an important role in the clearance of particles and soluble substances in the circulation and tissues, and forms part of the immune system. Substances that are cleared include immune complexes, bacteria, ...
What is reticular connective tissue?
Definition: A type of connective tissue characterized by the predominance of reticular fibers made of type III collagen and forming a labyrinth-like stroma (framework) for cells such as lymphocytes. Connective tissue is one of the major animal tissues.
What are reticular fibers made of?
The reticular fibers are made up mainly of type III collagen (100-150 nm in diameter) synthesized by special fibroblasts, reticular cells. Reticular fibers crosslink, forming a fine meshwork. The reticular connective tissues are found in the kidney, the spleen, lymph nodes, and bone marrow.
What is the function of the reticuloendothelial system?
The reticuloendothelial system consists of the various cells of the body that primarily function to remove dead or abnormal cells, tissues, and foreign substances. Not surprisingly the cells are highly phagocytic, and abnormalities either in the cells or in the biological mechanisms for controlling the cells results in disease. There are very few reports of reticuloendothelial diseases in the paleopathological literature in part because these diseases are uncommon, but also because some of the changes that occur in the skeleton resemble other diseases, making differential diagnosis challenging.
Where do reticuloendothelial agents take place?
Uptake of reticuloendothelial system agents occurs in endothelial and Kupffer cells of the liver. This class of agents includes superparamagnetic iron oxide particles coated with dextran, ferumoxide (AMI-25), and ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide agents like SHU-555A and AMI-227.233–235 They function as T2 relaxation promoters and lower the normal signal of reticuloendothelial system containing tissue. Reticuloendothelial system agents are used primarily for lesion detection. Their effect depends on the strength of the applied magnetic field. 236 These agents characterize a lesion by determining the absence of Kupffer cells within the mass.
How is doxorubicin encapsulated?
Doxorubicin was encapsulated using the pH gradient-dependent entrapment technique and quantification of plasma levels of liposomes and doxorubicin were accomplished as described in the legend to Figure 2.
What is RES in biology?
The RES is also known as the mononuclear phagocyte system. This system consists of cellular and noncellular components. The release of the cytokines takes place when nanoparticles bind to phagocytic cells, leading to the increased clearance of particles from the bloodstream ( von Roemeling et al., 2017 ). The surface of the nanoparticles can be modified by using hydrophilic moieties which helps them to get escaped from RES uptake thus increasing time in bloodstream and prevents unnecessary exposure to normal tissues. Examples of modifications include the addition of zwitterionic ligands such as cysteine and glutathione ( Garcia et al., 2014 ). PEG can also be linked to nanoparticles. The blood circulation time of nanoparticle can, thus, be increased by coating the membranes with leukocytes or erythrocyte derivatives.
What is the role of RES in the biological system?
The RES is primarily responsible for clearance of NPs from the biological system , which leads to the attainment of the subtherapeutic concentration of therapeutic agent at the target tissue. Macrophages are one of the main components of RES.
Which organs are associated with RES?
The primary organs associated with the RES are the liver, spleen and lung. The liver exhibits the largest capacity for liposome uptake while the spleen can accumulate liposomes such that the tissue concentration (liposomal lipid/gm tissue) is 10-fold higher than that which can be achieved in other organs.
Where is the RES located?
The RES is a part of the immune system that is mainly present in the liver and spleen and takes up foreign bodies from the circulation to protect the body from their harmful effects. This system also preferentially captures vesicles and the encapsulated drug in the vesicles is released before reaching the target site.