The role of the antenna pigments is to collect light energy from the sun and transfer it to reaction centers. In green plants and algae, these pigments are found in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts. … Other pigments, called accessory pigments, are carotenoids
Carotenoid
Carotenoids, also called tetraterpenoids, are organic pigments that are found in the chloroplasts and chromoplasts of plants and some other photosynthetic organisms, including some bacteria and some fungi. Carotenoids can be produced from fats and other basic organic m…
How do pigments help photosynthetic organisms?
How much land is needed for microalgae cultivation?
How do algae help the photosynthesis process?
What is the antenna pigment used in photosynthesis?
What are antenna pigments?
Why are algae considered biofuels?
Why are closed photobioreactors important?
See 4 more
About this website

What is the role of antenna pigment in LHC?
LHC contain pigments that absorb light for photosynthesis, transferring it to photosystem reaction centers that turn solar energy into chemical energy (Green, 2003).
What are antenna pigments?
The pigment molecules (accessory pigments) that surround the chlorophyll reaction centre and absorb and transfer sun energy to the reaction centre are referred to as antenna pigments. Examples include Chl-a, Chl-b Carotenoids and others.
What are the roles of pigment?
The primary function of pigments in plants is photosynthesis, which uses the green pigment chlorophyll and several colorful pigments that absorb as much light energy as possible.
What is the role of antenna in photosynthetic bacteria?
Most chlorophyll-type pigments in a photosynthetic organism function as an antenna, absorbing light and transferring excitations to a photochemical reaction center where energy storage takes place by a series of chemical reactions.
What are antenna pigments made of?
The antenna pigments are predominantly chlorophyll b, xanthophylls, and carotenes. Chlorophyll a is known as the core pigment. Their absorption spectra are non-overlapping and broaden the range of light that can be absorbed in photosynthesis.
What are the 3 types of pigment?
More complicated diagrams will be displayed to illustrate the structures of the three types of pigments that are present during the aging of leaves: chlorophylls, carotenoids, and anthocyanins.
What are the two main functions of pigments?
(i) Light energy is absorbed and transferred to chlorophyll for photosynthesis. (ii) To prevent photooxidation of the chlorophyll molecule.
What are the 4 pigments?
Types of Pigment in PlantsChlorophyll. Chlorophyll is one of the primary pigment found within the plant cells of all green plants. ... Carotenoids. Carotenoids are the pigments in the form of orange, red, yellow colours. ... Anthocyanins. ... Flavonoids.
What is called pigment?
Definition of pigment (Entry 1 of 2) 1 : a substance that imparts black or white or a color to other materials especially : a powdered substance that is mixed with a liquid in which it is relatively insoluble and used especially to impart color to coating materials (such as paints) or to inks, plastics, and rubber.
What is the role of chlorophyll and the antenna pigments in photosynthesis?
Photosynthetic pigments like chlorophyll b and carotenoids bond with protein to form a tightly packed antenna-like structure to capture incoming photons. Antenna pigments absorb radiant energy, somewhat like solar panels on a house.
How do the antennae pigments help to make photosynthesis more efficient?
(a) The pigments in the antennae molecule help in making photosynthesis more efficient by absorbing different wavelengths of light.
Why are antennae useful?
Antennas are the most physically visible component of a wireless infrastructure. Whether it be radio, LAN, or otherwise, an antenna is extremely important. The antennas primary function is to transmit and receive clear signals between multiple wireless points.
What are the 4 pigments?
Plant pigments are classified into four main categories: chlorophylls, anthocyanins, carotenoids, and betalains. They account for most of the naturally derived colors from plants.
What is the difference between antenna pigments and reaction center pigments?
Antenna complex is an array of proteins and chlorophyll b molecules that transfers light energy to the reaction center of a photosystem, while the reaction center is a complex of several proteins, pigments, and co-factors that execute the primary energy conversion reaction of photosynthesis.
How do antenna pigments transfer energy?
These pigments help to make photosynthesis more efficient by absorbing different wavelengths of light. The single chlorophyll a molecule forms the reaction center. So Antenna pigment molecules transfer the light energy to the reaction center of light-harvesting complex. This phenomenon is called as Shifting of light.
What are antenna molecules in photosynthesis?
Solution : Antenna molecules are light harvesting molecules that occur on the outer side of photosynthetic unit .
Photosynthetic Antenna Pigments (With Diagram)
ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about Photosynthetic Antenna Pigments. After reading this article you will learn about: 1. Composition of Photosynthetic Antenna Pigments 2. Role of the Antenna in Photosynthesis. Composition of Photosynthetic Antenna Pigments: All functional pigments in photosynthetic membranes are bound in a variety of pigment-protein complexes. In general ...
photosystem 1 and 2 Flashcards | Quizlet
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like photosystem I, photosystem II, NADPH and more.
PSII and PSI: Structure, Function and Organization
PSII complex can be divided into two main protein superfamilies differing in the number of membrane-spanning a-helices, that is, the six-helix protein superfamily, which includes the internal antennae CP43 and CP47 (CP stands for Chlorophyll–Protein complex), and the five-helix proteins of the reaction center core D1 and D2 (so-called because they were first identified as two diffuse bands ...
Why do plants without carotenoids not grow?
Thus, the carotenoid in photosynthetic antennae play the essential role of photo-protection by preventing the formation and accumulation of singlet O 2. This is the reason why plants without carotenoids cannot grow and survive in strong light conditions.
How is LHC II regulated?
In fact, the activity of LHC II can be regulated by phosphorylation by ATP through a protein kinase, and one threonine residue on the polypeptide is the site of phosphorylation. In addition, PSII contains three minor peripheral antenna complexes, CP29, CP26 and CP24 which provide connections between the main LHC antenna and PSII core.
How many Chl a are in the core antenna?
The core and the peripheral antenna complexes. In PSI, the core antenna consists of about 100-120 Chl a and 15 β-carotene molecules bound in the same complex that contains P700 reaction center.
What are the functions of the pigments in the photosynthesis membrane?
They function either as antennae or as reaction center. The antennae of plants consist of large number of protein-bound pigment molecules which absorb photons and transfer their energy to the reaction center.
Why do photosynthesis systems need to be controlled?
The relative light harvesting capacity of the two photosystems must be controlled in order to achieve maximum rates of electron transport at a particular light intensity (Allen, 1992). This is another mechanism in antenna complex of regulating the utilization of light energy in photosynthesis.
Which pigments are capable of direct absorption of sunlight?
All photosynthetic pigments either belonging to the reaction center or the antenna are capable of direct absorption of sunlight. Under average daily light intensities, the rate of light absorption by a reaction center pigment alone is far below the capacity for photosynthetic electron transport and would not provide sufficient energy to drive the process.
Which part of the antenna collects light?
The outer or the peripheral part which is formed by the light-harvesting complex (LHC) collects the light. The inner part of the antenna, which consists of the core complex, is generally an integral component of the reaction center, and transfers the excitons collected in the outer part of the antenna into the photosynthetic reaction centers.
How many molecules of ATP are consumed in the Calvin cycle?
A) stroma of the chloroplast. As a research scientist, you measure the amount of ATP and NADPH consumed by the Calvin cycle in 1 hour. You find 30,000 molecules of ATP consumed, but only 20,000 molecules of NADPH.
What is the energy transfer in a protein complex for the light reaction?
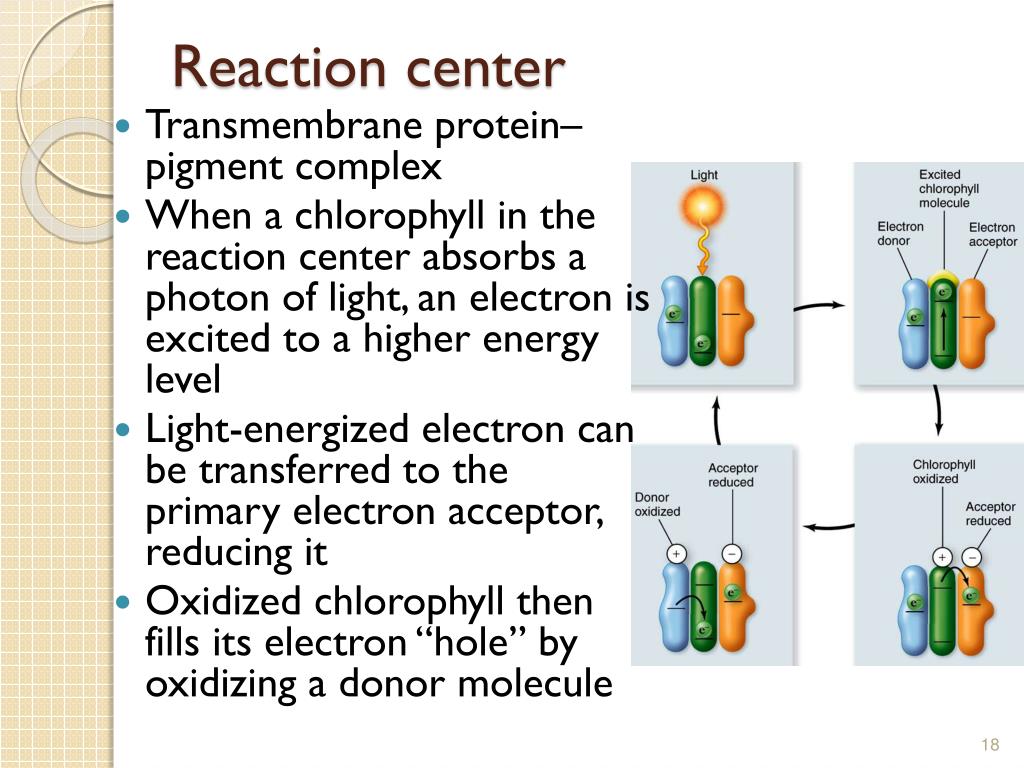
In a protein complex for the light reaction (a reaction center), energy is transferred from pigment molecule to pigment molecule, to a special chlorophyll a molecule, and eventually to the primary electron acceptor.
Which cycle does photosynthesis supply?
The light reactions of photosynthesis supply the Calvin cycle with
Is photosystem I used in both cases?
A) In bothcases, only photosystem I is used.
Where is the D in a nucleoid?
D) along the outer edge of the nucleoid
Do thylakoids interfere with photosynthesis?
E) In both cases, thylakoids are not involved in photosynthesis.
How does H+ produce ATP?
H+ moves down its concentration gradient from lumen into stroma, passing through ATP Synthase, which produces ATP using the energy of the H+ passing through. - Oxygen: Produced in Thylakoid Lumen by oxidation of water by PSII. Electrons removed from water, producing 2H+ and 1/2 Oxygen.
What is the energy source for heterotrophs?
This is responsible for the possibility of life on earth. - Photosynthesis produces Organic molecules (Glucose) and Oxygen. Glucose is an energy source for heterotrophs and Oxygen is needed for Cellular Respiration. - Cellular respiration produces CO2 and H20, CO2 is needed for Photosynthesis.
What is the name of the complex of proteins and pigment molecules in chloroplasts that generates oxygen from water during?
Photosystem II. - Distinct complex of proteins and pigment molecules in chloroplasts that generates oxygen from water during the light reactions of Photosynthesis. Pigment. - Molecules that can absorb light energy/wavelengths and reflect others.
What color are the leaves of a new flower?
A new flower species has a unique photosynthetic pigment. The leaves of this plant appear to be blue-green. What wavelengths of visible light does this pigment reflect?
What energy do organisms use to make organic molecules?
These organisms most specifically utilize light energy to make organic molecules from inorganic molecules.
What is the name of the process that uses light as a source of energy to create food/organic compounds?
Photoautotroph. - Autotroph that uses light as a source of energy to create own food/organic compounds. - Capable of photosynthesis; ;"food from light". - Plants, algae, and some bacteria. Photosynthesis. - Method of energy creation that captures energy from light and uses it to synthesize carbohydrates.
Which type of electron flow produces ATP?
Cyclic Electron Flow. - During Photosynthesis, a pattern of electron flow in the thylakoid membrane that is cyclic and generates ATP only. - 1) Capture of light energy by PSI, giving off electrons. 2) Electrons flow into CBFC, which produces H+ ions which powers ATP production.
How do pigments help photosynthetic organisms?
Pigment molecules of various kinds allow photosynthetic organisms to both capture light and convert the captured light energy into chemical energy. Light-harvesting pigments (primarily the chlorophylls) capture light from the sun and form excited pigments. The combined excitation energy of multiple pigment molecules is focused in a single pigment molecule known as the reaction center (RC) and used to reduce acceptor molecules. The light-harvesting apparatus (the RC plus multiple accessory pigments) or antenna pigments absorb light and excitation energy is produced. This excitation energy moves through the antenna molecules to the RC where an electron is excited and lost. The electron that is lost from the pigment is then replaced by an electron from another source in the environment. In photosynthetic bacteria, a wide variety of compounds may donate electrons to the oxidized pigment. In cyanobacteria, algae, bryophytes, ferns, and higher plants water is used as the source of electrons and diatomic oxygen (O2) is released:
How much land is needed for microalgae cultivation?
Cultivation of rapidly grown microalgae may acquire only 1% of land area needed of conventional crop-based plantation lands. A microalgae production scenario estimated the use of only 121,000 ha of open pond or 58,000 ha of photo-bioreactors footprint in meeting global annual gasoline requirements [4]. Furthermore, wastewaters enriched with nutrients such as nitrogen and/or phosphorous can be used as a growing medium for algal cultivation, negating the need for fertilizers derived from fossil fuel energy. Additionally, uptake of the nutrients by algae for biomass buildup per se is a form of treatment to the wastewater in meeting effluent discharge requirements. In addition to biofuel production, cultivated microalgae can be used as bulk commodities in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, nutraceuticals, and functional foods [5].
How do algae help the photosynthesis process?
Algae have a wide range of antenna pigments to convert solar energy to chemical energy via photosynthesis giving different strains of algae their characteristic colors. Early work done with algae contributed much to what is presently known about the carbon dioxide fixation pathway and the light harvesting photosynthetic reactions. The processes of photosynthesis in algae and terrestrial plants are very much alike. Amongst the three types of carbon dioxide fixation mechanisms known in photosynthetic organisms, two of which are found in the genus of algae [2]. Moreover, studies indicated that carbon dioxide fixation in algae is one to two orders of magnitude higher than terrestrial plants [3]. Thus, algae are believed to play a vital role in the global carbon cycle by capturing excess carbon dioxide from the air environment.
What is the antenna pigment used in photosynthesis?
Cyanobacteria and red algae utilize antenna pigments called phycobilins packed into complexes called phycobilisomes, which are attached to the photosynthetic membranes.
What are antenna pigments?
The principle antenna pigments are chlorophyll a and b in plants, chlorophyll c in some algae, and bacteriochlorophyll a, b, or c in bacteria. Other pigments, called accessory pigments, are carotenoids and phycobiliproteins. Following light absorption by a pigment molecule, the electronic excitation is transferred until it is trapped by ...
Why are algae considered biofuels?
Algae have been recognized as a promising biofuel resource due to their efficient conversion of solar energy into chemical energy. As algae biomass is capable of producing much more oil yield per cultivation broth area than other biofuels such as corn and soybean crops, algal biodiesel has attracted widespread attention because of its prospect for large-scale practical use [6].
Why are closed photobioreactors important?
A number of companies are developing closed photobioreactors, typically using one or more of these approaches to increase light conversion efficiency beyond that achievable in open ponds. Temperature and nutrient levels can also be more easily and continuously controlled in closed reactor systems, further improving productivity, although O 2 saturation also needs to be managed to avoid growth inhibition due to oxygen toxicity.