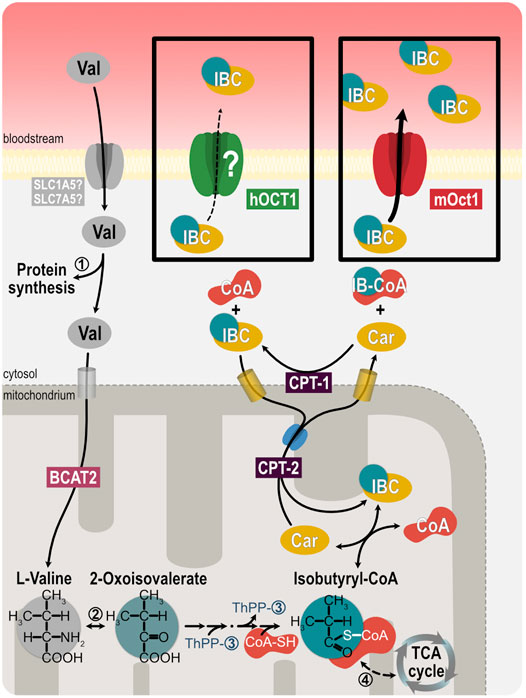
What is the role of carnitine in energy metabolism?
Carnitine plays an important role in energy metabolism by transferring long-chain fatty acids into mitochondria for β-oxidation. It also facilitates the oxidation of pyruvate and branched-chain amino acids, and it helps remove toxic acetyl coenzyme A metabolites by binding to them for excretion in the urine [9,46,47].
What is L-carnitine and how does it work?
L-carnitine is a nutrient and dietary supplement. It plays a crucial role in the production of energy by transporting fatty acids into your cells’ mitochondria ( 1, 2, 3 ). The mitochondria act as engines within your cells, burning these fats to create usable energy. Your body can produce L-carnitine out of the amino acids lysine and methionine.
Does L-carnitine improve β-oxidation in mitochondria?
Preclinical studies demonstrated that l -carnitine improves β-oxidation in mitochondria resulting in improved fertilization rate and blastocyte development [ 67, 68, 69 ].
What is the role of L-carnitine in cell membrane stability?
l -carnitine is also essential in maintaining membrane stability and function of plasma, mitochondria, and other organelles possibly via effects on acetylation of membrane phospholipids. Its amphiphilic nature would also allow for interaction with the surface charges on the cell membrane and may play a role in membrane stabilization [ 19, 20 ].
See more
What does carnitine do in the mitochondria?
l-carnitine is one of the key nutrients for proper mitochondrial function and is notable for its role in fatty acid oxidation. l-carnitine also plays a major part in protecting cellular membranes, preventing fatty acid accumulation, modulating ketogenesis and glucogenesis and in the elimination of toxic metabolites.
What would happen if carnitine would not get inside the mitochondria?
Intracellular carnitine deficiency impairs the entry of long-chain fatty acids into the mitochondrial matrix. Consequently, long-chain fatty acids are not available for beta-oxidation and energy production, and the production of ketone bodies (which are used by the brain) is also impaired.
How is carnitine used metabolically?
Essentially, L-carnitine transports the chains of fatty acids into the mitochondrial matrix, thus allowing the cells to break down fat and get energy from the stored fat reserves. Recent studies have started to shed light on the beneficial effects of L-carnitine when used in various clinical therapies.
What happens in carnitine deficiency?
Without carnitine, fatty acids cannot enter mitochondria and be used to make energy. Reduced energy production can lead to some of the features of primary carnitine deficiency, such as muscle weakness and hypoglycemia. Fatty acids may also build up in cells and damage the liver, heart, and muscles.
Is carnitine deficiency a mitochondrial disease?
Systemic primary carnitine deficiency (CDSP) is a rare metabolic disorder in which the body cannot properly process fats into energy. Carnitine functions to carry fatty acids obtained through diet to the energy centers in muscle cells (mitochondria).
What is the physiological function of carnitine?
Carnitine is stored primarily in skeletal muscle, with lower concentrations in plasma. Biologically, carnitine is essential for the transport of long-chain (carbon chain length = 10) fatty acids across the outer- and inner-mitochondrial membranes (carnitine palmitoyltransferanse I and II, respectively).
Does L-carnitine cause insulin resistance?
Conclusions: Considering the role of caloric restriction in increasing the intestinal uptake of carnitine, the results suggest that oral L-carnitine administration, when associated with a hypocaloric feeding regimen, improves insulin resistance and may represent an adjunctive treatment for IFG and DM-2.
Does carnitine improve fat oxidation?
L-Carnitine Improves Skeletal Muscle Fat Oxidation in Primary Carnitine Deficiency.
What can go wrong if the carnitine shuttle does not function properly?
Loss of carnitine in the kidney results in very low concentration in other tissues, resulting in severe impairment of long-chain FAO, which leads to hypoketotic hypoglycemia with fasting and stress. Age of presentation may range from infancy to adulthood, but neonatal hypoglycemia and sudden death may occur.
What would happen if each part were missing in mitochondria?
Mitochondria are known as power house of the cell. These organells contain many oxidative enzymes which oxidise the food and convert them into energy of the cell in the form if A.T.P. In the absence of mitochondria in the cell ,oxidation of food and release of energy does not takes place. Hence cell may die.
What would happen to the body if mitochondria stops working?
If your mitochondria are not working properly then you are less able to convert food into ATP. For cells that require a lot of ATP, for example your muscles, this is a problem and they may become weaker and get tired faster.
What will be affected if the mitochondria inside the cell malfunction?
The mitochondria's main function is to produce energy. More mitochondria are needed to make more energy, particularly in high-energy demand organs such as the heart, muscles, and brain. When the number or function of mitochondria in the cell are disrupted, less energy is produced and organ dysfunction results.
What are recommended intakes for carnitine?
The FNB has not established Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs)—including a recommended dietary allowance (RDA)—for carnitine [ 4 ].
What foods provide carnitine?
Animal products like meat, fish, poultry, and milk are the best sources. In general, the redder the meat, the higher its carnitine content. Dairy products contain carnitine primarily in the whey fraction [ 1, 3, 5 ]. The carnitine content of several foods is listed in Table 1.
Are there health risks from too much carnitine?
At doses of approximately 3 g/day, carnitine supplements can cause nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, diarrhea, and a " fishy" body odor [ 1, 2 ]. Rarer side effects include muscle weakness in uremic patients and seizures in those with seizure disorders.
What is the federal government's 2020-2025 diet?
The federal government’s 2020–2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans notes that “Because foods provide an array of nutrients and other components that have benefits for health, nutritional needs should be met primarily through foods. ….
What is the form of carnitine in asparagus?
Asparagus, cooked, ½ cup. 0.1. Carnitine occurs in two forms, known as D and L , that are mirror images (isomers) of each other. Only L-carnitine is active in the body and is the form found in food [ 1, 6 ].
How long does carnitine help with performance?
However, twenty years of research finds no consistent evidence that carnitine supplements can improve exercise or physical performance in healthy subjects—at doses ranging from 2–6 grams/day administered for 1 to 28 days [ 9-11 ].
What is the best source of carnitine?
Animal products like meat, fish, poultry, and milk are the best sources. In general, the redder the meat, the higher its carnitine content. Dairy products contain carnitine primarily in the whey fraction [ 1, 3, 5 ]. The carnitine content of several foods is listed in Table 1.
What are the different types of carnitine?
Here are several other types of carnitine: 1 D-carnitine: This inactive form may cause a carnitine deficiency in your body by inhibiting the absorption of other, more useful forms ( 7#N#Trusted Source#N#, 8#N#Trusted Source#N#). 2 Acetyl-L-carnitine: Often called ALCAR, this is possibly the most effective form for your brain. Studies suggest that it may benefit people with neurodegenerative diseases ( 9#N#Trusted Source#N#). 3 Propionyl-L-carnitine: This form is well-suited for circulatory issues, such as peripheral vascular disease and high blood pressure. It may boost production of nitric oxide, which improves blood flow ( 10#N#Trusted Source#N#, 11#N#Trusted Source#N#). 4 L-carnitine L-tartrate: This is commonly added to sports supplements due to its rapid absorption rate. It may aid muscle soreness and recovery in exercise ( 12#N#Trusted Source#N#, 13#N#Trusted Source#N#, 14#N#Trusted Source#N#).
What is the role of L-carnitine in the body?
L-carnitine is a nutrient and dietary supplement. It plays a crucial role in the production of energy by transporting fatty acids into your cells’ mitochondria ( 1. Trusted Source.
How long does it take for L-carnitine to appear?
L-carnitine’s benefits may be indirect and take weeks or months to appear. This differs from supplements like caffeine or creatine, which can directly enhance sports performance. L-carnitine may benefit: Recovery: May improve exercise recovery ( 46.
How much L-carnitine is needed for exercise?
L-carnitine L-tartrate: This form is most effective for exercise performance. Doses vary from 1,000–4,000 mg per day.
What is the mitochondria?
Trusted Source. ). The mitochondria act as engines within your cells, burning these fats to create usable energy. Your body can produce L-carnitine out of the amino acids lysine and methionine. For your body to produce it in sufficient amounts, you also need plenty of vitamin C ( 4. Trusted Source. ).
How much L-carnitine is absorbed?
Interestingly, food sources of L-carnitine have a greater absorption rate than supplements. According to one study, 57–84% of L-carnitine is absorbed when it’s consumed from food, compared to only 14–18% when taken as a supplement ( 61. Trusted Source.
What is L-carnitine?
L-carnitine is a naturally occurring amino acid derivative that’s often taken as a supplement.
What is niacin used for?
Niacin, also known as vitamin B3, is a precursor of the coenzymes nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and NAD phosphate (NADP), which are involved in many biological redox reactions. NAD and its reduced form NADH play an important role in energy metabolism by transferring electrons from intermediates to complex I in the mitochondrial ETC. NADP serves as a hydrogen donor in fatty acid and steroid synthesis and as a coenzyme for pentose synthesis via the pentose phosphate pathway. Niacin also has antioxidant properties and prevents oxidative stress [ 96, 97 ].
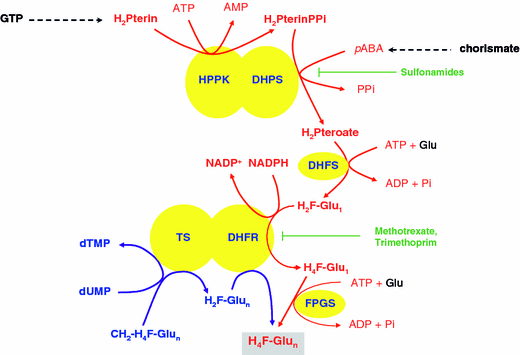
What is the role of folate in DNA synthesis?
Folate is the generic term for a family of compounds that act as coenzymes in the folate cycle, which plays an important role in DNA and RNA synthesis, creatine synthesis, and homocysteine remethylation. Folate also provides S-adenosylmethionine, the major methyl donor for methylation reactions [ 89 ].
What is the precursor of NO?
Citrulline serves as an intermediate in the urea cycle and as a precursor for arginine. Approximately 70% of the body’s citrulline is converted to arginine in the kidneys, accounting for 5–15% of arginine produced in the body [ 33 ]. Arginine is the precursor of NO, an important neurotransmitter and vasodilator.
How long does creatine monohydrate last?
No adverse effects have been reported in patients with PMDs after oral supplementation with up to 20 g/day creatine monohydrate for up to 6 weeks [ 84-86 ]. Creatine is generally considered safe for short-term use (5 days) by healthy adults at up to 20 g/day and up to 3 g/day for maintenance doses [ 87 ].
What is ALA in supplements?
In dietary supplements, ALA is typically a mixture of R-ALA (natural, biologically active form) and S-ALA (manufactured form) enantiomers, but some products contain only R-ALA [ 24 ]. Typical amounts in dietary supplements range from 50 to 600 mg ALA [ 25 ].
How long does arginine help with stroke?
Oral administration of 150 to 300 mg/kg/day arginine for 12–24 months significantly decreased the frequency and severity of stroke-like episodes. Patients did not have major stroke-like attacks, such as hemiconvulsions or hemiparesis (temporary muscle weakness on one side of the body), after arginine supplementation.
What is the role of ALA in the body?
ALA serves as a cofactor for enzymes that participate in intermediary cell metabolism that leads to ATP production . In addition, ALA and its reduced form, dihydrolipoic acid, can act as antioxidants by scavenging reactive oxygen species and helping regenerate other antioxidants, such as vitamin C, vitamin E, and glutathione [ 22 ]. Although the body makes sufficient amounts of ALA for basic metabolic functions (e.g., energy metabolism), it can only act as an antioxidant when it is present in greater amounts [ 22, 23 ].