Gas exchange is achieved by diffusion. This is a process by which particles move naturally from a region where they are in high concentration to a region where they are in lower concentration. They move down a concentration gradient: the steeper the gradient, the faster the rate of diffusion.
How is gas exchange achieved by diffusion?
Gas exchange is achieved by diffusion. This is a process by which particles move naturally from a region where they are in high concentration to a region where they are in lower concentration. They move down a concentration gradient: the steeper the gradient, the faster the rate of diffusion.
What is meant by the term diffusion?
Diffusion is the spread of molecules from regions of high to regions of low concentration. Molecules that are concentrated will randomly move about (diffuse) and eventually, after colliding, they get distributed uniformly, reaching an equilibrium.
How does simple diffusion work in the human body?
This process is accomplished through simple diffusion which is a form of diffusion where a higher concentration will move to an area of lower concentration without the aid of a protein. In the case of respiration, the higher concentration of oxygen in the lungs will move into the bloodstream which has a low concentration of oxygen.
What is the role of oxygen and carbon dioxide gas exchange?
Oxygen diffuses into the blood at the site of the heart, and carbon dioxide diffuses into the blood at the site of the alveoli. Carbon dioxide diffuses into the blood at the site of the heart, and oxygen diffuses into the blood at the site of the tissues. Subsequently, question is, what is the role of gas exchange?
What is the role of diffusion in gas exchange GCSE?
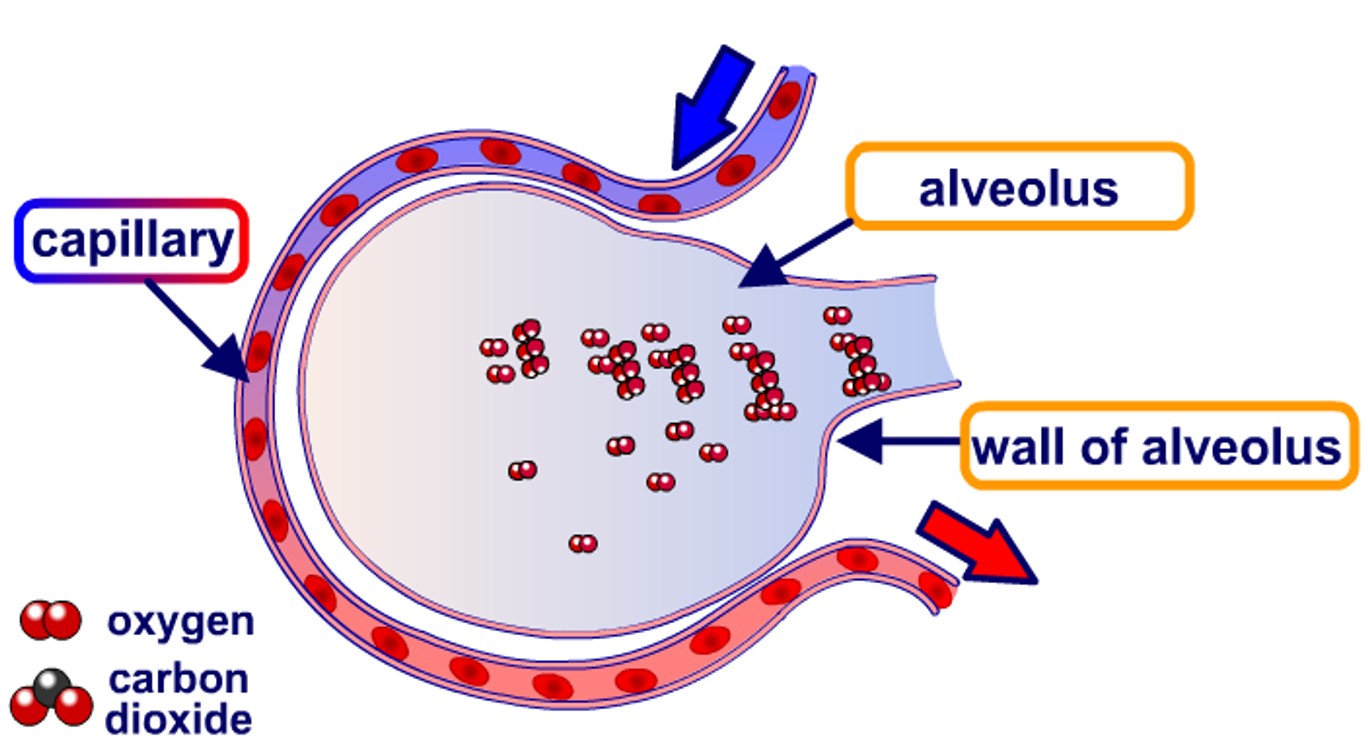
Gaseous exchange occurs at the alveoli in the lungs and takes place by diffusion. The alveoli are surrounded by capillaries so oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between the air in the alveoli and the blood in the capillaries.
What type of diffusion is gas exchange?
The gases on either side of the gas exchange membrane equilibrate by simple diffusion. This ensures that the partial pressures of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood leaving the alveolar capillaries, and ultimately circulates throughout the body, are the same as those in the FRC.
What is diffusion and how does it play a role in respiration?
Diffusion is the process whereby gases move from an area of high pressure to low pressure. This includes during - Internal respiration - this is the movement in the internal tissues between cells and capillaries, and - External respiration - when gas is exchanged between the alveoli and lung capillaries.
What is the role of diffusion in the movement of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs?
Once the oxygen diffuses across the alveoli, it enters the bloodstream and is transported to the tissues where it is unloaded, and carbon dioxide diffuses out of the blood and into the alveoli to be expelled from the body.
How does diffusion work?
In terms of gas exchange, the respiratory gases oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged at the thin, moist respiratory surface called alveoli, air sacs located in the lungs. These are surrounded by blood capillaries, thin-walled vessels which allow diffusion across their surface. When oxygen is transported into the respiratory system when one inhales, the high concentration of oxygen in the alveoli, diffuses through these thin- walled air sacs and enters the blood capillaries. There, oxygen is absorbed by hemoglobin-bearing red blood cells and carried throughout the body. There is a gradient between the high concentration of oxygen in the alveoli and a lower concentration of oxygen in the circulating blood. This causes the movement of oxygen into the bloodstream, from the external environment. When cells produce the waste product carbon dioxide, it is transported by the blood back to the alveoli. Because there is a higher concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood capillaries, relative to the alveoli, carbon dioxide will then diffuse from the bloodstream, to the alveoli and one can then exhale it to the environment. Therefore, respiratory gases rely on diffusion through thin, moist surfaces between the external environment and the internal body.
What is diffusion in biology?
Diffusion is the spread of molecules from regions of high to regions of low concentration. Molecules that are concentrated will randomly move about (diffuse) and eventually, after colliding, they get distributed uniformly, reaching an equilibrium.
Where are oxygen and carbon dioxide exchanged?
In terms of gas exchange, the respiratory gases oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged at the thin, moist respiratory surface called alveoli, air sacs located in the lungs. These are surrounded by blood capillaries, thin-walled vessels which allow... (The entire section contains 231 words.)
How are gases exchanged?
Gases are exchanged between the alveolar air and the blood by diffusion, the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, where concentration refers to how much of one substance is present in a mixture of substances.
How does oxygen move into and out of the blood?
Oxygen and carbon dioxide move into and out of our blood by diffusion. The rate of diffusion is determined by partial pressure gradients across the respiratory membrane in our lungs. Partial pressure is a function of both concentration and atmospheric pressure. Updated: 10/31/2019.
What is the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the alveolar air?
As you can see in the picture above, the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the alveolar air is about 40 mmHg. Diffusion and Henry's Law. As we have stated, gas exchange occurs across a respiratory membrane. The respiratory membrane separates the alveolar air on one side from the blood on the other.
What is the atmospheric pressure of oxygen?
At sea level, atmospheric pressure is 760 mmHg; therefore, the partial pressure of oxygen would be 160 mmHg, or 760 mmHg x 0.21. The base camp for Mount Everest is about 5000 meters above sea level, and the atmospheric pressure there is only about 400 mmHg. As the concentration of oxygen is still 21%, the partial pressure of oxygen is only 84 mmHg, or 400 mmHg x 0.21. So you see, at base camp, only 84 mmHg pressure pushes the oxygen into our blood, compared with 160 mmHg at sea level.
What is the difference between oxygen and carbon dioxide?
As you can see from the image below, oxygen moves out of the alveolus into the capillary, while carbon dioxide moves in the opposite direction - hence, the term gas exchange. Gas exchange refers to oxygen moving into the capillary and carbon dioxide moving into the alveolus. Gases are exchanged between the alveolar air and the blood by diffusion, ...
What causes partial pressure of oxygen to drop?
Once in the alveoli, the partial pressure of oxygen drops due to water vapor and carbon dioxide.
Which membrane separates the alveolar air on one side from the blood on the other?
The respiratory membrane separates the alveolar air on one side from the blood on the other. Let's take a look at Henry's law. Henry's law tells us that pressure gradients affect the movement of gas into and out of a solution in a liquid. For example, carbon dioxide is added to soda pop under high pressure.
How does gas exchange work?
Gas exchange is achieved by diffusion. This is a process by which particles move naturally from a region where they are in high concentration to a region where they are in lower concentration. They move down a concentration gradient: the steeper the gradient, the faster the rate of diffusion.
What is gas exchange?
gas exchange. The diffusion of gases from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, especially the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between an organism and its environment. In plants, gas exchange takes place during photosynthesis. In animals, gases are exchanged during respiration.
What is the function of alveoli?
Alveoli are an important part of the respiratory system whose function it is to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide molecules to and from the bloodstream. These tiny, balloon-shaped air sacs sit at the very end of the respiratory tree and are arranged in clusters throughout the lungs.
How does gas exchange occur during respiration?
Gas exchange during respiration occurs primarily through diffusion. Diffusion is a process in which transport is driven by a concentration gradient. Blood that is low in oxygen concentration and high in carbon dioxide concentration undergoes gas exchange with air in the lungs.
What is the blood gas test?
The test is commonly known as a blood gas analysis or arterial blood gas (ABG) test. Your red blood cells transport oxygen and carbon dioxide throughout your body. These are known as blood gases. As blood passes through your lungs, oxygen flows into the blood while carbon dioxide flows out of the blood into the lungs.
What are the three processes that are essential for the transfer of oxygen from the outside air to the blood flowing through the?
Three processes are essential for the transfer of oxygen from the outside air to the blood flowing through the lungs: ventilation, diffusion , and perfusion . Ventilation is the process by which air moves in and out of the lungs.
Where does gas exchange occur?
It occurs in the lungs between the alveoli and a network of tiny blood vessels called capillaries, which are located in the walls of the alveoli.
What are the processes that contribute to gas exchange in animals?
For an organism to function, substances must move into and out of cells. Three processes contribute to this movement – diffusion, osmosis and active transport. Part of. Biology (Single Science) Exchange and transport in animals.
How do substances move into and out of living cells?
Some substances move into and out of living cells by diffusion.
Why do particles spread evenly in a liquid?
Because of this movement, particles will spread themselves evenly throughout a liquid or a gas. If there is a situation where particles of a substance are in a higher concentration, they will move from this region to where they are in a lower concentration.
What is the term for the movement of particles in both directions?
This is called diffusion. It is important to remember that the particles: will move in both directions, but there will be a net movement from high to low concentration. will end up evenly spread throughout the liquid or gas, but will continue to move.
Where does gas exchange occur?
Gas exchange occurs at two sites in the body: in the lungs, where oxygen is picked up and carbon dioxide is released at the respiratory membrane, and at the tissues, where oxygen is released and carbon dioxide is picked up. External respiration is the exchange of gases with the external environment, and occurs in the alveoli of the lungs.
Which gas diffuses out of the capillary and into the cells?
Figure 22.4.3 – Internal Respiration: Oxygen diffuses out of the capillary and into cells, whereas carbon dioxide diffuses out of cells and into the capillary.
How does the partial pressure of oxygen in the alveoli compare to the partial pressure of oxygen in the blood of the?
This difference is about 64 mm Hg: The partial pressure of oxygen in the alveoli is about 104 mm Hg, whereas its partial pressure in the blood of the capillary is about 40 mm Hg. This large difference in partial pressure creates a very strong pressure gradient that causes oxygen to rapidly cross the respiratory membrane from the alveoli into the blood.
What is the purpose of internal respiration?
Describe the process of internal respiration. The purpose of the respiratory system is to perform gas exchange. Pulmonary ventilation provides air to the alveoli for this gas exchange process. At the respiratory membrane, where the alveolar and capillary walls meet, gases move across the membranes, with oxygen entering the bloodstream ...
Where does external respiration occur?
External respiration is the exchange of gases with the external environment, and occurs in the alveoli of the lungs. Internal respiration is the exchange of gases with the internal environment, and occurs in the tissues. The actual exchange of gases occurs due to simple diffusion.
How is ventilation regulated?
Ventilation is regulated by the diameter of the airways, whereas perfusion is regulated by the diameter of the blood vessels. The diameter of the bronchioles is sensitive to the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the alveoli.
What is the total pressure of a gaseous mixture?
Dalton’s law describes the behavior of nonreactive gases in a gaseous mixture and states that a specific gas type in a mixture exerts its own pressure; thus, the total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases is the sum of the partial pressures of the gases in the mixture.
