
Importance of Glycolysis
- Most of the energy used by cells comes from glucose.
- It is the first pathway that is used to convert glucose into energy.
- It is one of the ancient pathways that is seen as it is used by all living organisms.
- It is the first main metabolic pathway of cellular respiration that produces energy in the form of ATP.
What does glycolysis make and why is it important?
What are the end products of Glycolysis?
- Pyruvate. Pyruvic acid is extremely important because it supplies energy to cells through the citric acid cycle, which is also known as the Krebs cycle when oxygen is present.
- ATP. ATP is the primary and most important end product of Glycolysis, because Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) provides energy to drive many processes in living cells.
- NADH. ...
What are the various steps in glycolysis?
Step 1: Hexokinase. The first step in glycolysis is the conversion of D-glucose into glucose-6-phosphate. The enzyme that catalyzes this reaction is hexokinase. Details: Here, the glucose ring is phosphorylated. Phosphorylation is the process of adding a phosphate group to a molecule derived from ATP.
How much energy does glycolysis produce?
The percentage of the energy released by the breakdown of glucose to lactate that is “captured” by the organism when ADP is phosphorylated to ATP is the efficiency of energy use in glycolysis; it is (61.0/184.6) X100, or about 33%.
What does glycolysis literally mean?
What does the term glycolysis literally mean? Glycolysis, which literally means “breakdown of sugar,” is a catabolic process in which six-carbon sugars (hexoses) are oxidized and broken down into pyruvate molecules. The corresponding anabolic pathway by which glucose is synthesized is termed gluconeogenesis.
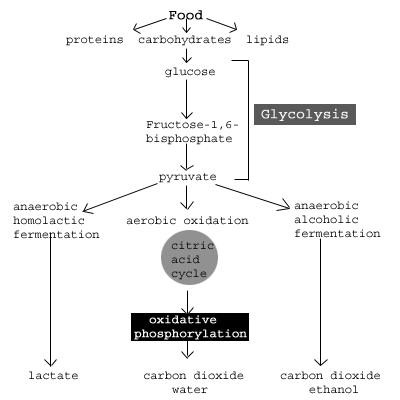
What is the main function of glycolysis?
Glycolysis is a cytoplasmic pathway which breaks down glucose into two three-carbon compounds and generates energy. Glucose is trapped by phosphorylation, with the help of the enzyme hexokinase.
What is glycolysis and why is it important?
The essential metabolic pathway of glycolysis involves the oxidative breakdown of one glucose into two pyruvate with the capture of some energy as ATP and NADH. Glycolysis is important in the cell because glucose is the main source of fuel for tissues in the body.
What is the role of glycolysis in cellular respiration?
Figure: Cellular Respiration: Glycolysis is the first pathway of cellular respiration that oxidizes glucose molecules. It is followed by the Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation to produce ATP. Glycolysis is the first of the main metabolic pathways of cellular respiration to produce energy in the form of ATP.
What is the role of glucose in glycolysis?
During glycolysis, glucose ultimately breaks down into pyruvate and energy; a total of 2 ATP is derived in the process (Glucose + 2 NAD+ + 2 ADP + 2 Pi --> 2 Pyruvate + 2 NADH + 2 H+ + 2 ATP + 2 H2O). The hydroxyl groups allow for phosphorylation. The specific form of glucose used in glycolysis is glucose 6-phosphate.
What is glycolysis short answer?
(gly-KAH-lih-sis) A process in which glucose (sugar) is partially broken down by cells in enzyme reactions that do not need oxygen. Glycolysis is one method that cells use to produce energy.
What is the most important step in glycolysis?
The most important regulatory step of glycolysis is the phosphofructokinase reaction. Phosphofructokinase is regulated by the energy charge of the cell—that is, the fraction of the adenosine nucleotides of the cell that contain high‐energy bonds.
What is the role and output of glycolysis?
1: Glycolysis produces 2 ATP, 2 NADH, and 2 pyruvate molecules: Glycolysis, or the aerobic catabolic breakdown of glucose, produces energy in the form of ATP, NADH, and pyruvate, which itself enters the citric acid cycle to produce more energy.
What is the purpose of glycolysis quizlet?
What is the goal of Glycolysis? To turn Glucose into pryuvate, so it can enter into the Krebs cycle to produce more energy and generate ATP (Energy) in the process.
What is the function of glycolysis quizlet?
What is the function of glycolysis? to break down glucose into two molecules of pyruvate . Additionally 2 NADH form and 4 ATP molecules are made.
What is glycolysis also called?
The scheme of glycolysis was given by Embden, Meyerhof and Parnas. Hence it is also known as the EMP pathway.
What are the major features of glycolysis?
Glycolysis has several important features: It breaks down one molecule of glucose, a 6-carbon molecule, into two molecules of pyruvate, a 3-carbon molecule, in a controlled manner by ten or more enzymatic reactions.
How does glycolysis produce ATP?
Anaerobic glycolysis serves as a means of energy production in cells that cannot produce adequate energy through oxidative phosphorylation. In poorly oxygenated tissue, glycolysis produces 2 ATP by shunting pyruvate away from mitochondria and through the lactate dehydrogenase reaction.
Is glycolysis part of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
What happens in glycolysis of cellular respiration quizlet?
1-Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration. 2-During glycolysis, glucose is broken down into 2 molecules of the 3-carbon molecule pyruvic acid. -Pyruvic acid is a reactant in the Krebs cycle. 3-ATP and NADH are produced as part of the process.
1. Is there any evolutionary significance of Glycolysis?
Life on Earth has developed in millions of years through gradual evolution. The very first creatures to inhabit the planet were unicellular organis...
2. Which class books should I refer to get a detailed study on the topic of Glycolysis?
The metabolic activities taking place inside the body of animals including humans are covered under the subject of Biology. Students of CBSE, ICSE,...
3. Which is the best Book available in the market for the subject of Biology of 11 Class?
Biology as a subject carries equal importance as other subjects of Class 11 and for the students preparing for the National Eligibility Entrance Ex...
4. Is it sufficient for my final exams to learn about the process of Glycolysis through the study ma...
The website for Vedantu Online Courses has a well-structured and planned study course of all the chapters of any subject for all classes. These stu...
5. What is the price of the Biology course materials for self-studies provided by Vedantu?
The good news for the students who need to prepare for their various term exams and final exams is that they can do so without paying any price. Al...
6. What are the three main steps involved in Glycolysis?
The Main Steps Involved in Glycolysis are:Glucose is trapped and destabilized as it is the main component.The interconvertible three-carbon molecul...
7. What are the different types of Glycolysis?
There are 2 different types of glycolysis, they are:Aerobic respirationAnaerobic respirationIn aerobic conditions, the pyruvate enters the citric a...
How is acetyl-CoA produced?
Acetyl-CoA is produced from pyruvate molecules generated via glycolysis and enters the TCA cycle to generate the high-energy molecules NADH, FADH2, and ATP. More efficient than glycolysis: oxidative respiration yields 30-36 molecules of ATP per glucose molecule.
What are the two major pathways that cells use to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine tri?
Glycolysis and Oxidative Respiration are the two major metabolic pathways cells employ in order to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to fuel cellular function.
What is the primary mechanism that cells use to release chemical energy stored in nutrients (primarily glucose) to fuel cellular activity?
Oxidative respiration is the primary mechanism that cells use to release chemical energy stored in nutrients (primarily glucose) to fuel cellular activity. Occurs in mitochondria, and as its name implies, requires oxygen.
How is energy released from the breakdown of ATP to Adenosine diphosphate (ADP)?
Energy is released from the breakdown of ATP to Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) via hydrolysis to fuel various cellular processes .
What is the Warburg effect?
Although oxidative respiration is the predominant metabolic energy-producing pathway in normal cells, cancer cells reprogram their metabolism and more readily rely on glycolysis, even in the presence of oxygen, for energy production. This phenomenon is known as the Warburg effect.
Where does glycolysis occur?
Occurs in the cytosol and is oxygen-independent. The free energy released during the biochemical reactions in glycolysis is used to generate a net gain of two molecules of ATP.
Who is Chris Sumner?
Chris Sumner is the Editor-in-Chief of Lab Expectations. When he's not reading/writing about curing disease, he's hiking in the woods, playing guitar, or searching for the world's best lobster roll.
How does glycolysis work in heterotrophic cells?
Glucose enters heterotrophic cells in two ways. One method is through secondary active transport in which the transport takes place against the glucose concentration gradient.
What is the mechanism of glucose transport?
These transporters assist in the facilitated diffusion of glucose. Glycolysis is the first pathway used in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy. It takes place in the cytoplasm of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
What is the first phase of glycolysis?
The first phase of glycolysis requires energy , while the second phase completes the conversion to pyruvate and produces ATP and NADH for the cell to use for energy. Overall, the process of glycolysis produces a net gain of two pyruvate molecules, two ATP molecules, and two NADH molecules for the cell to use for energy.
Which metabolic pathway uses glucose to produce pyruvic acid and ATP?
glycolysis: the cellular metabolic pathway of the simple sugar glucose to yield pyruvic acid and ATP as an energy source. heterotroph: an organism that requires an external supply of energy in the form of food, as it cannot synthesize its own.
Which pathway of cellular respiration produces energy in the form of ATP?
Figure: Cellular Respiration: Glycolysis is the first pathway of cellular respiration that oxidizes glucose molecules. It is followed by the Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation to produce ATP. Glycolysis is the first of the main metabolic pathways of cellular respiration to produce energy in the form of ATP.
Where does the metabolic pathway take place?
It takes place in the cytoplasm of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. It was probably one of the earliest metabolic pathways to evolve since it is used by nearly all of the organisms on earth. The process does not use oxygen and is, therefore, anaerobic.
Is glycolysis present in all living things?
Glycolysis is present in nearly all living organisms.
What is Glycolysis?
Glycolysis is the process in which glucose is broken down to produce energy. It produces two molecules of pyruvate, ATP, NADH and water. The process takes place in the cytoplasm of a cell and does not require oxygen. It occurs in both aerobic and anaerobic organisms.
What is the substrate of trise phosphate isomerase?
Triose-phosphate isomerase converts dihydroxyacetone phosphate into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate which is the substrate in the successive step of glycolysis.
How is phosphoenolpyruvate transferred to ADP?
A phosphate from phosphoenolpyruvate is transferred to ADP to form pyruvate and ATP by the action of pyruvate kinase. Two molecules of pyruvate and ATP are obtained as the end products.
How many molecules of phosphoglycerate are in ATP?
Phosphate is transferred from 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to ADP to form ATP with the help of phosphoglycerokinase. Thus two molecules of phosphoglycerate and ATP are obtained at the end of this reaction.
What is the primary step of cellular respiration?
Glycolysis is the primary step of cellular respiration. In the absence of oxygen, the cells take small amounts of ATP through the process of fermentation. This metabolic pathway was discovered by three German biochemists- Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas in the early 19th century and is known as the EMP pathway ...
How is a phosphate group added to glucose?
A phosphate group is added to glucose in the cell cytoplasm, by the action of enzyme hexokinase. In this, a phosphate group is transferred from ATP to glucose forming glucose,6-phosphate.
Which enzyme is responsible for the phosphoglycerate molecule?
The phosphate of both the phosphoglycerate molecules is relocated from the third to the second carbon to yield two molecules of 2-phosphoglycerate by the enzyme phosphoglyceromutase.
What is the function of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (?
First, it dehydrogenates GAP by transferring one of its hydrogen (H⁺) molecules to the oxidizing agent nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD⁺) to form NADH + H⁺.
What happens to the phosphoglycerokinase in BPG?
The enzyme phosphoglycerokinase transfers a phosphate from BPG to a molecule of ADP to form ATP. This happens to each molecule of BPG. This reaction yields two 3-phosphoglycerate (3 PGA) molecules and two ATP molecules.
How many molecules does glycolysis produce?
Glycolysis produces two molecules of pyruvate, two molecules of ATP, two molecules of NADH, and two molecules of water.
How many ATP molecules does pyruvate kinase produce?
This happens for each molecule of PEP. This reaction yields two molecules of pyruvate and two ATP molecules.
How many ATP molecules are produced in glycolysis?
A net of two ATP molecules are produced through glycolysis (two are used during the process and four are produced.) Learn more about the 10 steps of glycolysis below.
How many ATP molecules are in a multistep process?
This multistep process yields two ATP molecules containing free energy, two pyruvate molecules, two high energy, electron-carrying molecules of NADH, and two molecules of water.
What is the isomer of G6P?
The enzyme phosphoglucomutase isomerizes G6P into its isomer fructose 6-phosphate or F6P. Isomers have the same molecular formula as each other but different atomic arrangements.