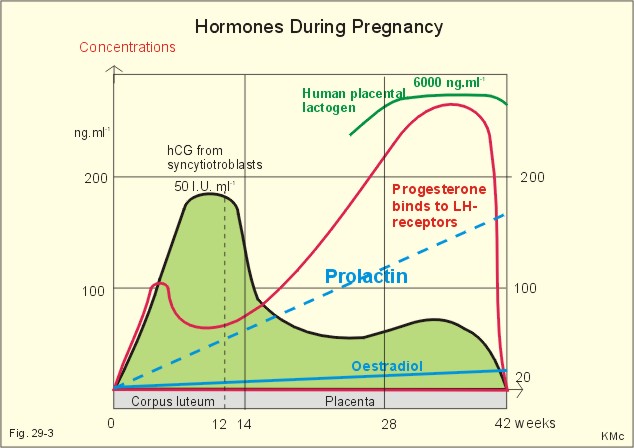
How does progesterone affect your cycles?
The Top 8 Impacts.
- Sustains the uterine lining. High levels of progesterone after ovulation help thicken and maintain the uterine lining. ...
- Builds strong bones. ...
- Boosts metabolism. ...
- Helps you quit bad habits. ...
- Aids sleep. ...
- Protects against breast and endometrial cancer. ...
- It makes you constipated. ...
- Protects against coronary artery disease. ...
How does estrogen affect menstrual cycle?
How does estrogen affect periods? When the menstrual cycle begins, estradiol and progesterone levels drop. That drop in hormone levels signals the endometrium layer to shed, resulting in menstrual bleeding. During menstrual bleeding, the level of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) increases and stimulates the growth of multiple ovarian follicles.
Can your period start while on the progesterone?
Most women who take progestin-only pills will see lighter periods, a reduction in severe premenstrual symptoms, and less cramping, because progestin thins the endometrial lining there is less lining to shed. Some women on progestin-only birth control will eventually experience few or no periods at all.
What hormones trigger the menstrual cycle?
The menstrual cycle is regulated by a number of different hormones. But the main ones are: Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH): Stimulates egg development and the release of oestrogen. Luteinising hormone (LH): Stimulates the release of the egg (called ovulation). Stimulates oestrogen and progesterone production.
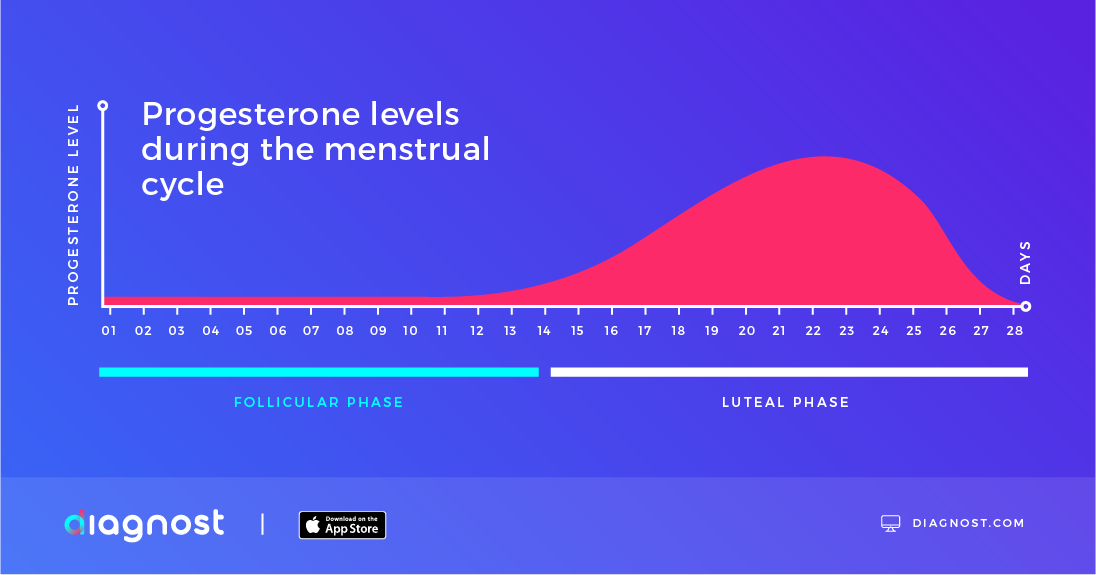
What is the role and effect of progesterone?
Progesterone is a hormone released by the ovaries. Changing progesterone levels can contribute to abnormal menstrual periods and menopausal symptoms. Progesterone is also necessary for implantation of the fertilized egg in the uterus and for maintaining pregnancy.
What are the roles of estrogen and progesterone in the menstrual cycle?
Luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone, which are produced by the pituitary gland, promote ovulation and stimulate the ovaries to produce estrogen and progesterone. Estrogen and progesterone stimulate the uterus and breasts to prepare for possible fertilization.
What is the role of progesterone in the menstrual cycle GCSE?
Several hormones are involved in the menstrual cycle of a woman: follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) causes the maturation of an egg in the ovary. luteinising hormone (LH) stimulates the release of the egg. oestrogen is involved in repairing and thickening the uterus lining, progesterone maintains it.
Which of the following is the main role of progesterone?
Progesterone is mainly secreted by the corpus luteum in the ovary during the second half of the menstrual cycle. It plays an important role in the menstrual cycle and in maintaining the early stages of pregnancy.
Which hormone is responsible for menstrual cycle?
The hormone responsible for these changes is progesterone, which is manufactured by the corpus luteum.
Which hormones are responsible for menstruation?
Brain structures called the hypothalamus and pituitary gland control the menstrual cycle. The hypothalamus triggers the pituitary gland to make hormones that trigger the ovaries to make oestrogen and progesterone. These hormones make the lining of the uterus (womb) thicker to prepare the body for pregnancy.
Which hormones causes release of progesterone?
In the female ovary, this release of FSH and LH on the gonads causes the release of progesterone. Excess amounts of progesterone will cause negative feedback inhibition on each prior organ, resulting in the cessation of the release of hormones. This process allows for regulated control of hormone levels.
What is the difference between progesterone and estrogen?
Estrogen is the hormone that regulates the menstrual cycle while progesterone is the hormone that supports pregnancy. During pregnancy, these two work together and are responsible for the changes that take place during pregnancy.
Does progesterone stop your period?
Progesterone is also used to bring on menstruation (period) in women of childbearing age who have had normal periods and then stopped menstruating. Progesterone is in a class of medications called progestins (female hormones).
What happens when progesterone is low?
Without enough progesterone, women will become estrogen dominant, which can cause heavy or painful periods, headaches, low libido, fatigue, breast tenderness and other symptoms. Estrogen dominance can also lead to serious health issues such as endometriosis, breast cancer, uterine fibroids and hormonal weight gain.
What happens if progesterone levels are high?
If your progesterone levels are higher than normal, it may mean you: Are pregnant. Have a cyst on your ovaries. Have a molar pregnancy, a growth in the abdomen that causes symptoms of pregnancy.
What are the roles of estrogen and progesterone quizlet?
-supports cervical glands, endometrium, lining of the fallopian tubes. -And it enhances growth of the myometrium. -Estradiol appears necessary to maintain oocytes in the ovary. Progesterone accelerates the movement of the oocyte along the uterine tube and prepares the uterus for arrival of a developing embryo.
What is the relationship between estrogen and progesterone?
Progesterone decreases the target organs response to estrogen by decreasing the number of receptors the organ has for estrogen. Receptors are molecules on the cells that recognize specific hormones and allows them to carry their message to the cell.
What is the role of estrogen in females?
In addition to regulating the menstrual cycle, estrogen affects the reproductive tract, the urinary tract, the heart and blood vessels, bones, breasts, skin, hair, mucous membranes, pelvic muscles, and the brain.
What hormones are involved in the menstrual cycle?
Progesterone during the Menstrual Cycle. The menstrual cycle is a biofeedback system, meaning that each gland and structure is affected by the activity of others. One of the principal sex hormones intricately involved with the healthy functioning of this monthly process is progesterone.
Why is progesterone produced during pregnancy?
Progesterone produced during this time serves to maintain the thickened lining of the uterus in preparation for the fertilized egg to implant itself. It also prohibits uterine muscle contractions that would cause the body to reject an egg.
What hormones are in the luteal phase?
The luteal phase is characterized by a gradual rise in progesterone. This hormone level increase begins shortly after ovulation and lasts until the beginning of the following menstrual cycle.
What is the luteal phase defect?
Luteal phase defect is marked by the failure to develop a fully mature secretory endometrium, preventing embryo implantation. This could lead to infertility or a miscarriage.
How long does the first half of the menstrual cycle last?
It begins with the first day of menses and lasts until ovulation, usually ranging from 10 to 16 days.
Which hormone is produced during the follicular phase?
It is reported that the progesterone produced during the follicular phase is important for subsequent ovulation, but it is after ovulation that progesterone dominates.
Where does progesterone come from?
The small amount of progesterone produced is derived from the adrenal cortex. It is converted from an endogenous steroid known as pregnenolone. At this point, the contribution of the ovaries to the blood plasma levels of progesterone is minor. It is reported that the progesterone produced during the follicular phase is important for subsequent ...
How does progesterone help with pregnancy?
The progesterone prepares the body for pregnancy in the event that the released egg is fertilised. If the egg is not fertilised, the corpus luteum breaks down, the production of progesterone falls and a new menstrual cycle begins. If the egg is fertilised, progesterone stimulates the growth of blood vessels that supply the lining of the womb ...
How is progesterone controlled?
The formation of the corpus luteum (which produces the majority of progesterone) is triggered by a surge in luteinising hormone production by the anterior pituitary gland. This normally occurs at approximately day 14 of the menstrual cycle and it stimulates the release of an egg from the ovary (ovulation) and the formation of the corpus luteum from the remnant of the follicle. The corpus luteum then secretes progesterone, which prepares the body for pregnancy. If the egg is not fertilised and no embryo is conceived, the corpus luteum breaks down and the production of progesterone decreases. As the lining of the womb is no longer maintained by progesterone from the corpus luteum, it breaks away and menstrual bleeding occurs, marking the start of a new menstrual cycle.
What happens if I have too little progesterone?
If progesterone is absent or levels are too low, irregular and heavy menstrual bleeding can occur. A drop in progesterone during pregnancy can result in a miscarriage and early labour. Mothers at risk of giving birth too soon can be given a synthetic form of progesterone to delay the onset of labour.
What happens to the corpus luteum when the egg is not fertilised?
If the egg is not fertilised and no embryo is conceived, the corpus luteum breaks down and the production of progesterone decreases. As the lining of the womb is no longer maintained by progesterone from the corpus luteum, it breaks away ...
What is the name of the hormone that secretes progesterone?
Synthetic hormones that have a similar action to progesterone are called ‘progestins’. Progesterone is mainly secreted by the corpus luteum in the ovary during the second half of the menstrual cycle. It plays an important role in the menstrual cycle and in maintaining the early stages of pregnancy.
What does it mean when your ovary is not releasing eggs?
Lack of progesterone in the bloodstream can mean the ovary has failed to release an egg at ovulation, as can occur in women with polycystic ovary syndrome.
When does the corpus luteum start to produce?
This normally occurs at approximately day 14 of the menstrual cycle and it stimulates the release of an egg from the ovary (ovulation) and the formation of the corpus luteum from the remnant of the follicle. The corpus luteum then secretes progesterone, which prepares the body for pregnancy.
How does progesterone help with pregnancy?
Progesterone helps to prepare the body for pregnancy by stimulating glandular development and the development of new blood vessels. This provides a good environment for implantation by a fertilized egg. If the egg isn’t fertilized, the corpus luteum breaks down, leading to a drop in progesterone levels. This decrease causes the endometrium ...
Which organs produce progesterone?
The adrenal glands and the placenta can also produce progesterone.
What hormones affect sleep?
Low progesterone. Takeaway. Hormones are chemical messengers in your body that affect a range of bodily functions, from sleep-wake cycles to digestion. Progesterone is one of two female sex hormones, the other being estrogen. Its main functions are regulating menstruation and supporting pregnancy in the female body.
Why is progesterone low?
Low levels of progesterone can also contribute to certain conditions, including: absence of menstruation. miscarriage.
What hormone is produced during pregnancy?
Progesterone is a hormone that’s vital for menstruation, pregnancy, and sperm production. It’s be produced in a variety of locations, including the corpus luteum, placenta, and adrenal glands. Progesterone levels fluctuate throughout the cycle and reach high levels during pregnancy. However, if levels get too low, it can lead to health issues, ...
How is progesterone measured?
Progesterone levels are measured through a blood test. It’s important to remember that progesterone levels fluctuate throughout the menstrual cycle, so levels can vary throughout the month.
What is the normal progesterone level?
Progesterone is found in much lower levels in men and isn’t typically tested unless adrenal gland dysfunction is suspected. Normal levels are less than 0.20 ng/mL. Keep in mind that results can vary between laboratories. If you’re unsure about your test results, contact your healthcare provider.
What hormones are involved in each period?
In each cycle, your uterus grows a new. Both your estrogen and progesterone can do & play a key role in each of your menstrual period.
What hormones are involved in the first half of the cycle?
As mentioned before, estrogen is one of the most crucial hormones in regulating the cycle of your menstruation. Estrogen plays a key role in the first half phase of your menstrual cycle. In general, there are two main functions that your body needs to prepare in this first half phase. These include [2]:
What happens to the corpus luteum during ovulation?
The ruptured follicle during ovulation then will go into the structure called corpus luteum. The female body can maintain the corpus luteum if there is egg fertilized by sperm and implant on the lining of the uterus. If there is no pregnancy, the corpus luteum will disappear and your body returns to the first phase of your menstrual cycle ...
How long is a woman's period?
The length of the cycle can vary from woman to woman (about 21 to 35 days). In each cycle, your uterus grows a new. Both your estrogen and progesterone can do & play a key role in each of your menstrual period.
How long does it take for a woman to bleed during her period?
On average, the length of this bleeding is about 3 day to 7 days. Advertisement. During menstrual flow, it’s important ...
What are the phases of a period?
The following are 3 major phases of your period [1]. ”Follicular”. ”Ovulation”. ”Luteal”. Follicular phase is the first half of the period. It occurs from the first day you notice the bleeding of menstruation and will ends with the release of egg (ovulation). In each follicular phase, the female body can make around 5-20 cysts or tiny nodules ...
How long does ovulation last?
How long does ovulation last? Typically, it can take about 2 days. But the life span of egg is not more than a day (24 hours).