
Role of Secondary Metabolites:
- (1) Some of them attract animals for pollination and seed dispersal.
- (2) They are used by the plants in their defence against herbivores and pathogens.
- (3) They act as agents of plant-plant competition.
What is the function of secondary metabolites?
Function of Secondary Metabolites - DEFENSE - ATTRACTION - PROTECTION (uv) - Most animalscan move-run away and posses an immune system -Plants are attacked by herbivores, microbes, (bacteria and fungi) and by other plants competing for light, space and nutrients - Abiotic stresses such as radiation Function of Secondary Metabolites:
How do secondary metabolites protect plants from herbivores?
Many secondary metabolites are toxic or repellant to herbivores and microbes and help defend plants producing them. Production increases when a plant is attacked by herbivores or pathogens. Some compounds are released into the air when plants are attacked by insects; these compounds attract parasites and predators that kill the herbivores.
What are the two types of metabolites in plants?
Plants have basically two types of metabolites namely Primary metabolites and Secondary metabolites. Primary metabolites are mainly used for photosynthesis, growth, development and respiration of plants. Secondary metabolites accumulate in plants and response as a defence mechanism of the plants. What is a secondary metabolite?
What is the role of secondary metabolism adjustment in plant defense mechanism?
However, most of the cases secondary metabolism adjustment play an important role in defense mechanism either increasing or decreasing their production in plant body. In this chapter the role and involvement of SMs in regulation of various biotic and abiotic stresses in plants has been discussed.
What is the function of secondary metabolites in plants?
Secondary metabolites serve: (i) as competitive weapons used against other bacteria, fungi, amoebae, plants, insects, and large animals; (ii) as metal transporting agents; (iii) as agents of symbiosis between microbes and plants, nematodes, insects, and higher animals; (iv) as sexual hormones; and (v) as ...
What are the functions of primary and secondary metabolites in plants?
primary and secondary plant metabolites can be distinguished from each other (Figure 1). While primary metabolites (sugars, fats, amino acids, etc.) serve for primar- ily nutrition and as starting materials for further biosynthesis (e.g., starch, cellulose, etc.), secondary metabolites do not play a role for diet. ...
How do secondary metabolites protect plants?
Secondary metabolites have shown to possess various biological effects, which provide the scientific base for the use of herbs in the traditional medicine in many ancient communities. They have been described as antibiotic, antifungal and antiviral and therefore are able to protect plants from pathogens.
What are the secondary metabolites found in plants?
Types of secondary metabolites in plantsClassTypeExamplesFlavonoids and TanninsWithout nitrogenLuteolin, tannic acidPhenylpropanoids, lignins, coumarins and lignansWithout nitrogenResveratrolPolyacetylenes, fatty acids and waxesWithout nitrogenPolyketidesWithout nitrogen10 more rows
What are the primary and secondary metabolites?
Metabolites are intermediate end products of metabolism. Primary metabolites are essential for the proper growth of microorganisms. Secondary metabolites are formed near the stationary phase of growth and are not involved in growth, reproduction and development.
What are primary metabolism in plants?
Central carbon metabolism, also known as primary metabolism, contributes to the synthesis of intermediate compounds that act as precursors for plant secondary metabolism. Specific and specialized metabolic pathways that evolved from primary metabolism play a key role in the plant's interaction with its environment.
What are the major differences between primary and secondary metabolites?
Difference Between Primary Metabolites and Secondary MetabolitesPrimary MetabolitesSecondary MetabolitesEasyDifficultOccurrenceThey produce the same products in every speciesThey produce different products in every speciesApplications12 more rows•Dec 31, 2020
What are the applications of secondary metabolites?
Secondary metabolites have been found to have interesting applications over and above their well-known medical uses, e.g., as antimicrobials, etc. These alternative applications include antitumor, cholesterol-lowering, immunosuppressant, antiprotozoal, antihelminth, antiviral and anti-ageing activities.
What is a secondary metabolite?
Secondary metabolites or Phytochemicals (Plant chemicals) are the natural products or plants constituents which are responsible for the medicinal properties of plants. There are thousands of secondary metabolites . some plants are classified on the basis of secondary metabolites found in them.
What is the most diverse group of secondary metabolites found in plants?
Terpenoid: General Structure. Terpenoids are the volatile substance which gives plants and flowers its unique fragrance, this is the largest and most diverse group of secondary metabolites found in plants.
What are the two types of metabolites in plants?
Types of metabolites in plants. Plants have basically two types of metabolites namely Primary metabolites and Secondary metabolites. Primary metabolites are mainly used for photosynthesis, growth, development and respiration of plants. Secondary metabolites accumulate in plants and response as a defence mechanism of the plants.
What are the three major groups of secondary metabolites?
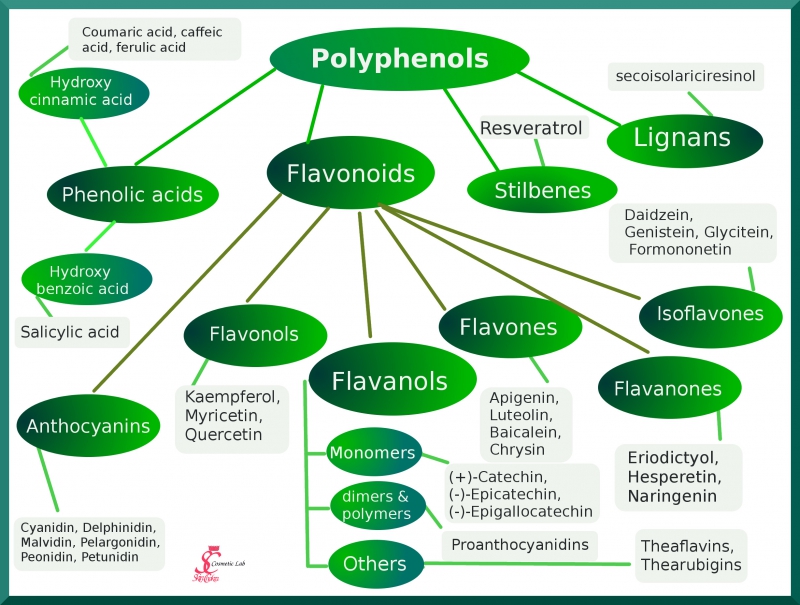
Secondary metabolites can be divided into three major groups. Flavonoids. Alkaloids. Terpenoids. 1. Flavonoids. Flavonoid: General structure. These are polyphenolic compounds comprise of 15 carbons with two aromatic rings connected by a three-carbon bridge. Subtypes of flavonoids are.
What are alkaloids known for?
Alkaloids are well known for their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and cardioprotective activities.
What are the functions of alkaloids in plants?
The major function of alkaloids in plants. Defence mechanism against bacteria and other microorganisms. Helps in plant metabolisms and catabolisms. Storage and reservoir of nitrogen. As growth regulators in plants. It also helps as a growth stimulator and inhibitors.
Which alkaloids are simple in structure?
They are simple in structure examples are hordenine, mescaline and yohimbine.
Why do plants have secondary metabolites?
The apparent lack of primary function in the plant, combined with the observation that many secondary metabolites have specific negative impacts on other organisms such as herbivores and pathogens , leads to the hypothesis that they have evolved because of their protective value. Many secondary metabolites are toxic or repellant to herbivores and microbes and help defend plants producing them. Production increases when a plant is attacked by herbivores or pathogens. Some compounds are released into the air when plants are attacked by insects; these compounds attract parasites and predators that kill the herbivores. Recent research is identifying more and more primary roles for these chemicals in plants as signals, antioxidants , and other functions, so "secondary" may not be an accurate description in the future.
How are secondary metabolites classified?
Secondary metabolites can be classified on the basis of chemical structure (for example, having rings, containing a sugar), composition (containing nitrogen or not), their solubility in various solvents, or the pathway by which they are synthesized ( e.g., phenylpropanoid, which produces tannins). A simple classification includes three main ...
What are the mechanisms that affect the growth of a plant?
Most herbivores and plant pathogens possess mechanisms that ameliorate the impacts of plant metabolites, leading to evolutionary associations between particular groups of pests and plants. Some herbivores (for example, the monarch butterfly) can store (sequester) plant toxins and gain protection against their enemies. Secondary metabolites may also inhibit the growth of competitor plants (allelopathy). Pigments (such as terpenoid carotenes, phenolics, and flavonoids) color flowers and, together with terpene and phenolic odors, attract pollinators.
Why are secondary chemicals important?
Secondary chemicals are important in plant use by humans. Most pharmaceuticals are based on plant chemical structures, and secondary metabolites are widely used for recreation and stimulation (the alkaloids nicotine and cocaine; the terpene cannabinol). The study of such plant use is called ethnopharmacology. Psychoactive plant chemicals are central to some religions, and flavors of secondary compounds shape our food preferences. The characteristic flavors and aroma of cabbage and relatives are caused by
What are the chemicals that protect plants from pests?
nitrogen-and sulfur-containing chemicals, glucosinolates, which protect these plants from many enemies. The astringency of wine and chocolate derives from tannins. The use of spices and other seasonings developed from their combined uses as preservatives (since they are antibiotic) and flavorings.
What are secondary metabolites used for?
Role of Secondary Metabolites: (1) Some of them attract animals for pollination and seed dispersal. (2) They are used by the plants in their defence against her bivores and pathogens. (3) They act as agents of plant-plant competition. (4) They are used in making drugs, insecticides, flavours, pigments, scents, rubber, ...
What are the chemicals that plants produce?
Plants produce thousands types of chemicals. Some of the organic compounds like carbohydrates, fats, proteins, nucleic acids, chlorophylls, hemes are required for their basic metabolic processes and found throughout the plant kingdom. These organic compounds are called primary metabolites or biomolecules. These are produced in large quantities and can easily be extracted from the plants.
Which organisms are not involved in primary metabolism?
Many plants, fungi and microbes of certain genera and families synthesize a number of organic compounds which are not involved in primary metabolism (photosynthesis, respiration, and protein and lipid metabolism) and seem to have no direct function in growth and development of plants.
Do metabolites accumulate in small quantities?
They accumulate in small quantities only in specific parts of plants. These are derivatives of primary metabolites. By the cultivation of plant cells in culture media, secondary metabolites can be produced on large scale. ADVERTISEMENTS:
Roles for Secondary Metabolites in Plants
Please review our Terms and Conditions of Use and check box below to share full-text version of article.
Summary
More than about 20 000 secondary metabolites have now been identified and their isolation and characterization continues at an undiminishing rate.
Abstract
Plants are constantly facing various threats posed by the biotic and abiotic stressors. To survive in these challenged environment, plants evolve a variety of defense mechanism.
1. Introduction
A hundred years ago it is reported that primary metabolites (carbohydrates, proteins, amino acids, vitamins, acetone, ethanol, etc.), are involved in various life functions in plants such as cell division, growth and development, photosynthesis, respiration, and reproduction [ 1 ].
2. Plant responses to stress factors
Plants throughout their life cycle are subjected to various forms of biotic and abiotic stresses, as a sessile organism plants lack the ability to escape from that danger areas. Plants express responses to stress conditions in three ways. Some plants avoid the stress altogether (e.g.
3. Mechanism of stress adaptation in plant
Generally, a stress signal transduction pathway comprises the following key steps: (i) signal perception; (ii) signal transduction; and (iii) stress response. The first step in the activation of signaling cascade for any given stress is the recognition of stress signals via receptors located on the membrane of plant cell.
4. Generation and diversity of secondary metabolites in plants
Plant SMs are classified into four major categories.
5. Terpenes for stress responses in plant
Plants produce various types of SMs, many of which have been subsequently exploited by humans for their beneficial roles in a diverse array of biological functions [ 28 ]. Terpenes are one of the diverse species of SMs contribute to the various biological process in plants.
6. Phenolics for stress responses in plant
Phenolics are one of the most ubiquitous groups of SMs which are synthesize in plants and possess biological properties like antifeedant [ 53 ], antioxidant, anti-apoptosis, anti-aging, anticarcinogenic, anti-inflammation, and cell proliferation activity. Phenolics consist of an aromatic ring with one or more hydroxyl groups.
Where are the secondary metabolites of basil produced?
Most secondary metabolites in Basil are produced in the Peltate Glands
Why are plants altered in the profile of terpenoids (and pool of precursors) important?
In addition, plants altered in the profile of terpenoids (and pool of precursors) make an important contribution to fundamental studies on their biosynthesis and regulation
What is the process of co-evolution between plants and their natural enemies?
The process of co-evolution between plants and their natural enemies is believed to have generated much of the earth's biological diversity This includes chemical diversity!!
Is canavanine toxic to plants?
Co-evolution in plant SMs - natural enemy. - Canavanine is toxic due to its incorporation into proteins that rise to functionally aberrant polypeptides - The tRNA- Arginine in insects uses also Canavanine - The insect mutated its tRNA and will not incorporate canavanine instead of Arginine .
Is SMs sequestered in a biomembrane?
SMs sequestration to a location with a solid barrier and not with a biomembrane (interfered by lipophilic SMs)
Do Arabidopsis leaves produce linalool?
Wild-type Arabidopsis leaves do not produce linalool
Introduction
- We are studying a lot about flavonoids and alkaloids in food and their health benefits in day-to-day blogs. Today with the concept of superfoods is getting more and more prominent so are the secondary metabolites present in them. Secondary metabolites are the main important components behind each health benefits and medicinal properties of the plants.
Types of Metabolites in Plants
- Plants have basically two types of metabolites namely Primary metabolites and Secondary metabolites. Primary metabolites are mainly used for photosynthesis, growth, development, and respiration of plants. Secondary metabolites accumulate in plants and respond as a defense mechanism of the plants.
What Is A Secondary Metabolite?
- Secondary metabolites or Phytochemicals (Plant chemicals) are the natural products or plants constituents which are responsible for the medicinal properties of plants. There are thousands of secondary metabolites. some plants are classified on the basis of secondary metabolites found in them (1).
Types of Secondary Metabolites and Their Medicinal Properties
- Three major groups of secondary metabolites
1. Flavonoids 2. Alkaloids 3. Terpenoids
Flavonoids
- These are polyphenolic compounds comprised of 15 carbons with two aromatic rings connected by a three-carbon bridge. Subtypes of flavonoids are (7). 1. Flavonol:Most widely distributed flavonoid. Examples are myricetin, quercetin, isorhamnetin, kaempferol. 2. Flavone:Mainly found in herbs like parsley and celery etc. The structure is almost similar to flavonols. Examples are lut…
Alkaloids
- In simple words, alkaloids are a group of chemical compounds having alkaline nature and heterocyclic nitrogen-containing basic compounds of plants (2). These are bi, tri, and tetracyclic derivatives of molecule quinolizidine. So far more than 12,000 alkaloids are discovered. They are bitter in taste and medicinally important. Alkaloids are used in many pharmaceutical companies …
Terpenoids
- Terpenoids are the volatile substance that gives plants and flowers their unique fragrance, this is the largest and most diverse group of secondary metabolites found in plants. Therefore terpenoids are hydrocarbons of plant origin having (C5H8(n as well as oxygenated, hydrogenated, and dehydrogenated derivatives (5). Classification of terpenoids is mainly dependent upon the n…