
Microtubules during this stage are said to fall into three categories:
- Astral microtubules point outward, toward the cell cortex, in order to anchor the whole spindle apparatus along the axis of cell division.
- Kinetochore microtubules attach to the kinetochore of chromatids.
- Polar microtubules, oriented parallel to each other but in opposing directions, are crucial for pushing the spindle apparatus apart during mitosis. ...
What is the function of microtubules?
Microtubules, nanoscopic tubular structures self-assembled ... is important for the development of novel approaches for the manipulation of molecular function as well as elucidating the bioeffects of electromagnetic fields, which could lead to new ...
What are the functions of microfilaments?
Microfilaments- Definition, Structure, Functions and Diagram
- Microfilaments Definition. Microfilaments, also called actin filaments, are polymers of the protein actin that are part of a cell’s cytoskeleton.
- Structure of Microfilaments. ...
- Functions. ...
- References. ...
- Microfilaments- Definition, Structure, Functions, and Diagram
What is the role of microtubules in interphase?
- G1 phase: The period prior to the synthesis of DNA. ...
- S phase: The period during which DNA is synthesized. ...
- G2 phase: The period after DNA synthesis has occurred but prior to the start of prophase. ...
- In the latter part of interphase, the cell still has nucleoli present.
What is the function of polar microtubules?
Tubulin-binding drugs and chemical effects
- The epothilones, e.g. Ixabepilone, work in a similar way to the taxanes.
- Vinorelbine, Nocodazole, vincristine, and colchicine have the opposite effect, blocking the polymerization of tubulin into microtubules.
- Eribulin binds to the (+) growing end of the microtubules. ...

What do microtubules do in cell division?
During mitosis, microtubules similarly extend outward from duplicated centrosomes to form the mitotic spindle, which is responsible for the separation and distribution of chromosomes to daughter cells.
What is the role of the microtubules in cell division quizlet?
Astral microtubules shorten—pull spindles apart. Separation of the genetic material is complete. Lengthening of the polar microtubules elongates the cell further. New nuclear membranes and nucleoli begin to form around each group of daughter chromosomes.
What is microtubules responsible for?
Microtubules are responsible for a variety of cell movements, including the intracellular transport and positioning of membrane vesicles and organelles, the separation of chromosomes at mitosis, and the beating of cilia and flagella.
What is the role of microtubules in mitosis mastering bio?
During mitosis, microtubules attach to chromosomes at the KINETOCHORE(S). 4. In dividing cells, most of the cell's growth occurs during INTERPHASE.
Why must microtubules assemble and disassemble for mitosis?
In plant cells, microtubules assemble and disassemble during the cell cycle to organize different microtubule arrays. Interphase cortical microtubules have a critical role in the construction of the cell wall by controlling the correct deposition of cell wall polymers (Lloyd and Chan, 2008).
What produces microtubules that aid in cell division?
The centrosome contains two centrioles positioned at right angles to each other. The centrosome is duplicated before a cell divides, and the paired centrosomes seem to play a role in organizing the microtubules that separate chromosomes during cell division.
What is made of microtubules help the cell divide by pulling chromosomes apart?
In animal cells, the centrioles near the nucleus begin to separate and move to opposite poles (sides) of the cell. As the centrioles move, a spindle starts to form between them. The spindle consists of fibers made of microtubules that pull chromosomes apart during cell division.
What do microtubules make up?
The cytoskeleton of a cell is made up of microtubules, actin filaments, and intermediate filaments. These structures give the cell its shape and help organize the cell's parts. In addition, they provide a basis for movement and cell division.
What is the function of microtubules in the cytoplasm?
Intracellular Organization of Microtubules. In the cytoplasm, microtubules form a structural network. The function of the cytoskeleton in microtubule includes chromosomes segregation, transport, mobility and mechanical support.
Where are microtubules found?
Microtubules are arranged in the form of microtubule-organizing centres. They are structures found in eukaryotic cells. During the interphase, most of the animal cells consist of microtubule-organizing centres. Several proteins are bound to microtubules namely dynein and kinesin.
What are microtubules made of?
What are Microtubules? “Microtubules are microscopic, hollow tubes made of alpha and beta tubulin that are a part of the cell’s cytoskeleton.”.
What are the structures that give cilia and flagella?
Microtubules give structures to cilia and flagella. They also facilitate the contraction and expansion of the cell helping them to move from one place to another.
Which axis of the cell is responsible for transporting organelles, vesicles, and proteins?
So that it would be easy to facilitate the transportation of organelles, vesicles, and proteins along the apical-basal axis of the cell. They play a vital role in cell migration as well. Also Read: Cytoskeleton.
Is tubulin a heterodimer?
This, tubulin is a heterodimer. Microtubules play a vital role in all eukaryotic cells. These cells release protein tubulin in a normal manner that involves transcription of the gene coding for tubulin, which yields RNA and is followed by transcription of mRNA to produce proteins.
What is the central hub of all microtubules in a quiescent cell?
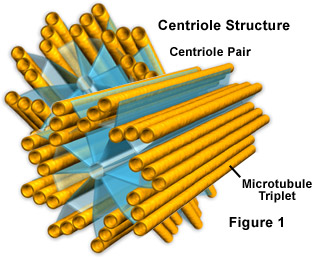
In animals, quiescent cells and even cells in interphase usually have just one MTOC, called a centrosome , which serves as the central hub for all microtubules in the cell. A centrosome is comprised of two centrioles as shown below (thanks again to Kelvinsong ):
Which microtubules point outward?
Microtubules during this stage are said to fall into three categories: Astral microtubules point outward, toward the cell cortex, in order to anchor the whole spindle apparatus along the axis of cell division. Kinetochore microtubules attach to the kinetochore of chromatids.
How many MTOCs are there in a cell?
The two centrioles disengage from each other and replicate themselves during S phase, and then separate to form opposite ‘poles’ of the cell during M phase, so that now there are two MTOCs, each of which will eventually be the sole MTOC of a new cell (another boss Kelvinsong image):
Why is it important to make sure that every chromatid is properly anchored?
Making sure that every chromatid is properly anchored is crucial for avoiding aneuploidy. By the way, other cytoskeletal elements besides microtubules also play a key role in the cell cycle. In cytokinesis , actin forms a contractile ring and, with the help of myosin II motor proteins, cinches the cell into two.
Which proteins move chromosomes?
A combination of motor proteins, microtubule interacting proteins and treadmilling serves to move the chromosomes. Meanwhile, dynein and dynactin – motor proteins which walk towards the (-) end – work on the astral microtubules, pulling the MTOCs toward the cell periphery.
Why is Xenopus important for cell cycle?
Xenopus (a kind of frog) proved critical for understanding cell cycle, because its reproduction involves a very large number of cells (i.e. enough starting material for Western blots, etc.) that are perfectly synchronized (i.e. all are in the same phase of cell cycle at the same moment. (Compare to yeast, for instance, where cells will not all be at the same phase at the same time). Also the egg itself is large and easy to work with, and multiple cell cycles follow fertilization. In frogs, eggs begin meiotic division but then arrest at the G2 phase for 8 months while they grow in size and stockpile things that will be needed for growth upon fertilization.
What is the process of cell division and replication called?
The cell cycle - the process of cell division and replication – is governed by a series of biochemical switches called the cell cycle control system.
What Are Microtubules?
Microtubules Structure
- Microtubules are arranged in the form of microtubule-organizing centres. They are structures found in eukaryotic cells. During the interphase, most of the animal cellsconsist of microtubule-organizing centres. Several proteins are bound to microtubules namely dynein and kinesin. Microtubules are made of subunits called tubulin. Each tubulin is made of an alpha and a beta-tu…
Intracellular Organization of Microtubules
- In the cytoplasm, microtubules form a structural network. The function of the cytoskeleton in microtubule includes chromosomes segregation, transport, mobility and mechanical support. It can either shrink or grow to generate energy which is due to the presence of motor proteins that allow cellular components and others to be carried along with microtubules. The arrangements i…