
Putting in the drops
- Position the head so that the ear faces upward. ...
- If the bottle has a dropper, draw some liquid into the dropper. ...
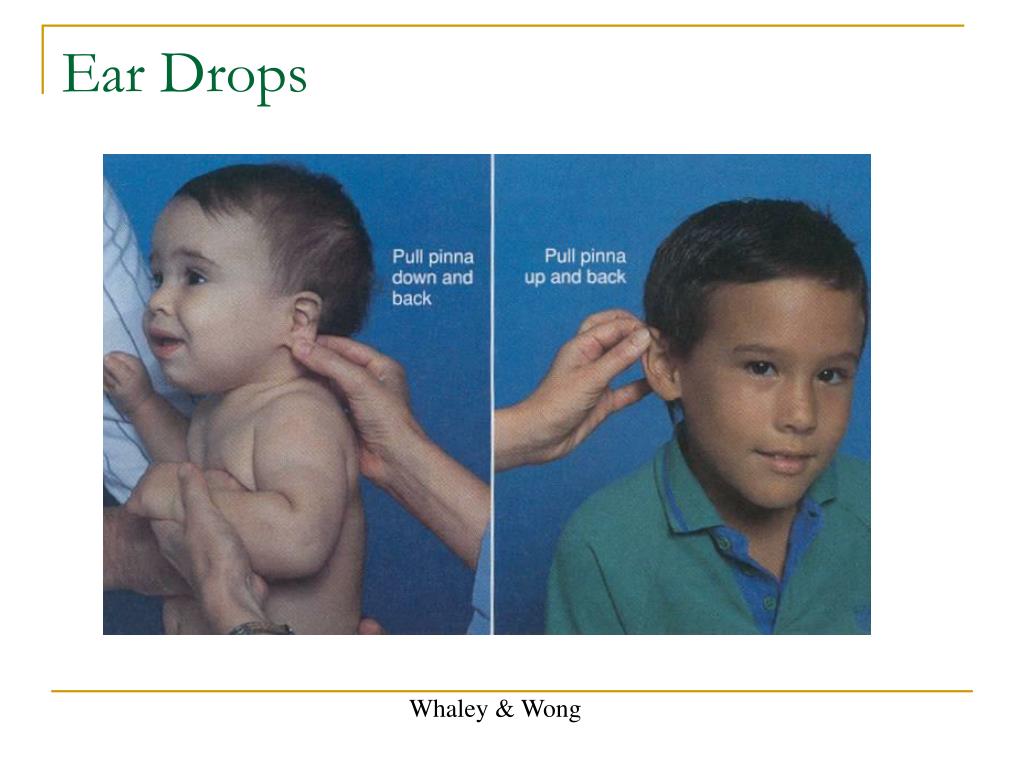
- For adults, gently pull the upper ear up and back. ...
- Gently pull the earlobe up and down to allow the drops to run into ear. ...
- Wipe away any extra liquid with a tissue or clean cloth.
- Put the cap back on the bottle.
What is the route of administration of ear drops?
This route may be considered time-consuming by the patient as they need to remain on their side/tilt the ear for a few minutes after instillation of ear drops Administration of drug into the eye. Absorption of the drug through the skin and into the systemic circulation.
How do I use ear drops?
Gently pull and hold your ear up and back. Gently squeeze the bottle to drop the correct number of drops into your ear. Your healthcare provider may tell you to use a cotton ball to keep the medicine in place. Place the cotton ball gently just inside your ear. Do not push it into the canal. Use a clean cotton ball each time you use the ear drops.
How do you administer ear medication?
Administering ear medication is a fundamental skill that requires the nurse to either irrigate the ear canal or carefully place drops into the ear canal. Be sure to administer the medication as ordered and in the correct ear. While performing the procedure, educate the patient on proper techniques for home care.
Should you touch the tip of the bottle to your ear?
Do not touch the tip of the bottle to your ear. Germs from your ear can spread to the medicine bottle if your ear touches the tip. Gently pull and hold your ear up and back. Gently squeeze the bottle to drop the correct number of drops into your ear.
What is the route of administration of ear drops?
If you are using the eardrops for a middle ear infection—Drop the medicine into the ear canal. Then, gently press the tragus of the ear (see the diagram in the Medication Guide) four times in a pumping motion. This will allow the drops to pass through the hole or tube in the eardrum and into the middle ear.
What is otic route of administration?
AURICULAR (OTIC) Administration to or by way of the ear.
What is the route of medication?
A medication administration route is often classified by the location at which the drug is administered, such as oral or intravenous. The choice of routes in which the medication is given depends not only on the convenience and compliance but also on the drug's pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamic profile.
What are the 5 routes of medication administration?
Routes of administrationOral.Sublingual.Rectal.Topical.Parenteral – Intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous.
What are otic medications?
Otic antibiotics are solutions or suspensions that are topically administered into the ear canal. Otic antibiotics are used to treat or prevent infections in the following conditions or treatment procedures: Otitis externa: External ear infection.
Which drugs are used in otic cavity?
TablesOtotopical AgentComponentsAdvantagesFloxin OticOfloxacinEfficacy and potency against common pathogens, no ototoxicity, bid dosingVoSol HCAcetic acid, hydrocortisoneEfficacy for some bacteria and fungiDomeboro solutionAluminum acetate, acetic acidEfficacy for some bacteria and fungi2 more rows•Dec 10, 2021
What is ophthalmic route?
Ophthalmic drug administration is the administration of a drug to the eyes, most typically as an eye drop formulation. Topical formulations are used to combat a multitude of diseased states of the eye. These states may include bacterial infections, eye injury, glaucoma, and dry eye.
What is the use of otic preparations?
Otic preparations are products applied to or in the ear to treat conditions of the external and middle ear. These products are used to treat dermatitis of the ear, cerumen build up and ear infection.
How do I use ear drops?
Read the instructions carefully before you use ear drops. Wash your hands before and after you use the drops.
How to drop a syringe into your ear?
Gently squeeze the bottle to drop the correct number of drops into your ear.
How to get ear drops out of a medicine bottle?
Germs from your ear can spread to the medicine bottle if your ear touches the tip. Gently pull and hold your ear up and back. Gently squeeze the bottle to drop the correct number of drops into your ear.
What does it mean when your ear rings?
You have changes in your hearing, such as ringing in your ears. Your ear itches, stings, or burns. You have a rash in or around your ear. You are dizzy. You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
How long do you have to stay on your side after instilling ear drops?
This route may be considered time-consuming by the patient as they need to remain on their side/tilt the ear for a few minutes after instillation of ear drops
Where is buccal route administered?
The buccal route is administered by placing the buccal dosage form between the gum and the inner cheek. The drug is rapidly absorbed from the buccal mucosa and enters the systemic circulation, thus avoiding first-pass metabolism. In addition, this route can also be used for a local effect (e.g. hydrocortisone muco-adhesive buccal tablet for the treatment of aphthous ulceration of the mouth).
What are the advantages of intravenous route?
Advantages of the Intravenous Route. Immediate effect (suitable for emergencies) Can be given to unconscious patients. Avoids first-pass metabolism. Achieves predictable and precise control over drug plasma levels compared to other routes.
What is the most commonly used route for drug administration?
Oral Route. The drug is administered to or by way of the mouth. 1 A drug given via this route is absorbed into the systemic circulation from the gastrointestinal tract. The oral route is the most frequently used route for drug administration.
Which route is given directly into the muscle?
The intramuscular (IM) route is given directly into the muscle (e.g. gluteus medius and deltoid).
Where does a drug go in the body?
Absorption of the drug through the skin and into the systemic circulation.
Can you use ocular drops with contact lenses?
May cause temporary blurring of vision upon instillation of eye drops/ointment. Barriers to administration e.g. poor manual dexterity, poor vision. Not all ocular dosage forms can be used with contact lenses.
What is the role of a nurse in administering ear drops?
Administering ear medication is a fundamental skill that requires the nurse to either irrigate the ear canal or carefully place drops into the ear canal. Be sure to administer the medication as ordered and in the correct ear. While performing the procedure, educate the patient on proper techniques for home care.
How to straighten out the ear canal?
To straighten out the ear canal you need to pull the Pinna/Auricle (outer part of ear) back and upwards for adult patients. This allows for a drop to be more accurately administered into the ear canal allowing gravity to pull it down. “Adult” has a “U” for Upward.
What is the skill of administering ear medication?
Picmonic. Administering ear medication is a fundamental skill that requires the nurse to either irrigate the ear canal or carefully place drops into the ear canal. Be sure to administer the medication as ordered and in the correct ear.
Can earwax be irrigated?
Some individuals produce an excess of earwax. In some cases a blockage or impaction of cerumen can occur, and the ear may need to be irrigated to clean the canal out.
Can you put ear drops in the ear canal?
If drainage is present, confirm that the patient’s eardrum is not perforated. This would be a contraindication for administering the ear drops. If irrigating the ear canal, never put syringe directly into canal or forcefully put medication in ear canal. The pressure could perforate the eardrums.
How To Use Ear Drops Solution?
This is the part of using the medicines which are commonly ignored. But preparing properly before using these ear drops can ensure that the medicines work more effectively.
What Are The Precautions of Ear Drops Solution?
There are some precautions that should be taken before using medicines that contain antipyrine and benzocaine. Some precautions one should look out for are-
What Are The Medicines Used For Treating Ear Infection?
Doctors prescribe medicines that contain Antipyrine and Benzocaine otic to get relief from the ear pain and swelling that occur due to middle ear infections. These medicines are used along with antibiotics to treat ear infections.
How to avoid spilling ear drops?
To avoid spilling the ear drops on the floor or bed, place a clean towel folded in half. Lay your head on the towel such that the affected ear faces upwards. You can ask someone to keep the head steady. Now comes the most important part. Putting the ear drops inside the ear.
What is the best treatment for ear pain?
Antibiotics to treat bacterial infections inside the ear. Acid-based detergents to break up excess earwax. Anesthetics can help in curing excessive ear pain. Also Read: Homeopathic Medicines for Ear Pain: Uses, Effectiveness and Side Effects.
How to straighten auditory tube?
Ask someone to gently pull the earlobe up and down to straighten the auditory tube. Put the prescribed number of eardrops. Immediately close the ear by gently pushing on the flap of the ear or put a cotton ball. This prevents the drops from spilling. Make sure that you stay in this position for a couple of minutes.
What are the side effects of ear drops?
However, people have reported the following minor side effects after using these ear drops-. A feeling of stinging or burning in the ear canal. Pain, redness, swelling in or around the ears. Rash. Itching or swelling of the ear, face, tongue or throat. Feeling of dizziness.
What is the intra- and endo- prefix?
In addition, since the prefixes intra- and endo- both mean within, the NSC generally felt that most US clinicians prefer the intra- prefix rather than the endo- prefix for route terms, with some exceptions (e.g., endotracheal). Some general terms (e.g., parenteral) should be reserved for instances when a particular route ...
Where is the administration directed?
Administration directed toward the cheek, generally from within the mouth. Administration to the conjunctiva, the delicate membrane that lines the eyelids and covers the exposed surface of the eyeball. Administration to the skin. Administration to a tooth or teeth.
