
What is the base of the sacrum called?
The base of the sacrum is the widest part and is connected to the L5 lumbar vertebra via the lumbosacral joint. Even though it's called the base, it is actually at the top (superior aspect) of the sacrum rather than at the bottom.
What does the sacrum do?
Overview Overview The sacrum is the triangle-shaped bone at the end of the spine between the lumbar spine and the tailbone. The sacral spine consists of five segments, S1 - S5, that together affect nerve communication to the lower portion of the body. It is important to understand that the spinal cord does not extend beyond the lumbar spine.
What does the sacral canal connect to?
The sacral canal is a hollow space that runs from the top (base) of the sacrum to the bottom (apex). The sacral canal serves as a channel at the end of the spinal cord. The sacrum connects (articulates) to the iliac bone on either side at an attachment point called the auricular surface.
What is the sacral angle of the lumbar spine?
The Lumbosacral Angle Defined. The degree of sacral base tilts vary in individuals; they can be, relatively speaking, steep or flat, or places in between. As the base of support for the spine, then, this sacral angle determines, at least in part, the degree of curve in the lumbar, thoracic and cervical areas.
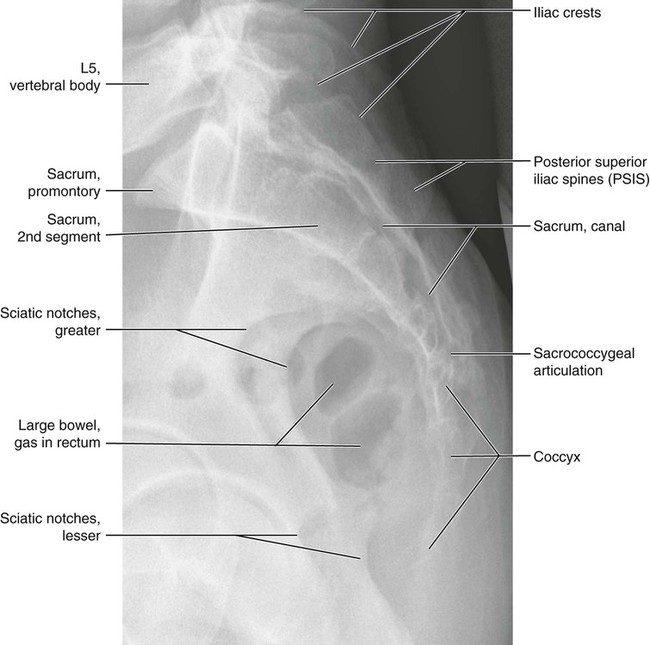
Where is the sacral area?
The sacral spine, also called the sacrum region, is the portion of your spine between your lower back and tailbone. It is a triangular-shaped bone that includes five vertebra that are fused together.
What is the function of sacral?
The sacral bone is very sturdy as it is responsible for supporting the entire weight of the body. Many important muscles that facilitate leg motion originate on the sacral surface. The sacrum also acts as a protective shield, enclosing the nerves of the lower back.
What is the sacral in the human body?
The sacrum, sometimes called the sacral vertebra or sacral spine (S1), is a large, flat triangular shaped bone nested between the hip bones and positioned below the last lumbar vertebra (L5). The coccyx, commonly known as the tailbone, is below the sacrum.
Is the sacrum the base of the spine?
The sacrum is a large triangular-shaped bone found at the base of the spinal column. It consists of the last four or five vertebrae that by adulthood, fuse together to form a single bone.
What causes pain in the sacral area?
Potential causes of sacroiliac pain include arthritis, traumatic injury, pregnancy and post-partum, systemic inflammatory conditions, and infection. Other potential contributors include spinal scoliosis, leg length discrepancy, and previous lumbar spine fusion. Sometimes, there is no clear cause for sacroiliac pain.
What nerves are affected by the sacrum?
Depending on the type of sacral injury or nerve damage, its location affects the nerves in that area and leads to lack of control and pain:S1 nerves affect the hips and the groin area.S2 nerves affect the backs of the thighs.S3 nerves affect the medial buttock area.S4 nerves affect the perineal area.
What causes sacral nerve damage?
The most common causes of spinal cord injuries to the sacrum are: Motor vehicle accidents. Trauma. Falls.
What happens when your sacrum is out of place?
The most common symptoms of a sacral or SI problem are: low back pain, sciatic nerve pain, stiffness, inflammation, and muscle spasms in the buttocks, hips, down the legs, and even the bladder and reproductive organs.
What age does the sacrum fuse?
30 years of ageThe adult sacrum consists of five fused sacral vertebrae. At birth, each vertebral body is separated by an intervertebral disc. The two caudal bodies fuse at approximately the 18th year of life, and the process of fusion continues rostrally until the S1–2 interspace finally fuses by 30 years of age.
How do you treat sacrum pain?
Home treatments for sacroiliitis pain include:Over-the-counter pain relievers. Drugs such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) may help relieve pain associated with sacroiliitis. ... Rest. ... Ice and heat.
How do you adjust the sacrum?
1:165:14How To Align Your Pelvis | Self Adjustment For the SI joint - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd you're going to drop one leg down make it longer and then shorter. And what i'm doing is movingMoreAnd you're going to drop one leg down make it longer and then shorter. And what i'm doing is moving that pelvis on that sacrum. In these positions right here so making it long.
How do you pop your sacrum back in place?
4:4811:14How to SELF RELEASE Your SI Joint for Instant Pain Relief - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipTake one hand place it on the outside of a knee it doesn't really matter which one you do take theMoreTake one hand place it on the outside of a knee it doesn't really matter which one you do take the other hand and place it on the inside of the knee.
What is the difference between sacral and sacrum?
The sacral region (sacrum) is at the bottom of the spine and lies between the fifth segment of the lumbar spine (L5) and the coccyx (tailbone). The sacrum is a triangular-shaped bone and consists of five segments (S1-S5) that are fused together.
What happens when your sacrum is out of place?
The most common symptoms of a sacral or SI problem are: low back pain, sciatic nerve pain, stiffness, inflammation, and muscle spasms in the buttocks, hips, down the legs, and even the bladder and reproductive organs.
What are symptoms of S1 nerve damage?
S1 radiculopathy typically results in numbness down the back of the leg into the outside or bottom of the foot. Weakness is another symptom of nerve root compression. However, it is less common than pain and numbness. This displays as decreased function in the muscles supplied by the nerve root that is compressed.
Where is your sacral nerve?
The sacral plexus (plexus sacralis) is a nerve plexus that provides motor and sensory nerves for the posterior thigh, most of the lower leg, the entire foot, and part of the pelvis (see the following image). It is part of the larger lumbosacral plexus.
What is the angle of the sacral base?
What we now know is that the efficiency of the low back architecture in a person is much greater from an engineering point of view when the sacral base falls between 36°-42°. If the angle is outside this range, the efficiency of the supportive joints and tissues goes down proportionately, and increases the vulnerability of the individual with regard to injury and degenerative potentials in their life.
Why is sacral base angle important?
The importance of the sacral base angle is huge when considering your patient from an engineering, or architectural perspective. When the angle is increased or decreased from normal, there will be a significantly reduced capacity of the low back over the life of that patient. Secondly, imbalances and abnormal weight distribution have been shown to accelerate degenerative changes in the over-burdened joints. The sacral base angle is also important when determining the extent of work needed on a patient. Regardless of the location of the spinal condition a patient is suffering with, the sacral base angle will play an important role in insuring maximum recovery for the patient. If this angle doesn't become part of the initial examination, it's impossible to know what the accurate prognosis and recommendations should be. Thirdly, it's critically important to collect data for the verification of the benefits of chiropractic care, and this measurement provides a solid reference point to measure benefits of treatment. If an abnormal sacral base angle can be found on the initial exam and the patient is put through a corrective treatment/conditioning program and improvements can be seen on re-x-rays, that becomes powerful evidence-based protocols that will get the attention of the medical community. And if this protocol can be duplicated and shown to be directly associated with pain relief and improved capacity, then chiropractic will have a much stronger stance in the medical community, as well as with the eyes of the general public.
What is the angle of the sacrum on a standing x-ray?
This is the angle formed with a line drawn along the top of the sacrum and intersecting with another line parallel to the ground (Fig. 1). A normal sacral base angle is 36°-42°. Of course, this should only be measured when the subject is x-rayed in the standing position with shoes off.
What are the factors that affect the sacral base angle?
The most influencing factors affecting the sacral base angle are heredity, prior injuries, poor conditioning, foot imbalances, leg length differences, weight problems, bad habits, poor posture, job, mattress, shoe style and quality, diet and frequency of getting adjusted. There certainly are many other influencing factors, but from a practical point of view, we must efficiently work with those we know and can improve upon.
Does anterior angling of the saddle reduce back pain?
The authors of this study claim that anterior angling of the saddle represents one step that the general public can take to reduce the incidence and severity of low-back pain.
How to treat sacral pain?
Any deficiency of micro or macronutrient can lead to chronic aches in the body including in the sacral area. Maintain your weight in the normal range of body mass index. Obesity leads to extra pressure exertion to the sacral area which results in chronic lower back pain. Do not overstress yourself.
How to diagnose sacral bone pain?
To diagnose sacral bone pain, your doctor will ask for your complete medical history and perform a thorough physical examination to look for any abnormality in your posture, gait, shape of vertebral column and range of movements.
Why does my sacrum hurt?
Sacral Bone Pain – Causes, Treatment, and Anatomy of Sacrum. Sacral bone pain is perceived in the lower part of the back and saddle area. Commonly, the underlying reason for pain is injury or trauma to the joint present between the hip and vertebral column. Sacroiliac pain can be misunderstood as some other conditions like buttocks problem ...
How does backrack work?
The Backrack™ decompresses your spine naturally through simple exercises that you can perform in the comfort of your own home. It works on the whole spine as there are several special exercises designed to decompress different regions of your spinal column. Backrack™ device mirrors the natural curvature of the spine so when you lie down on the rack your spine rests in the neutral position. And when you perform the recommended exercises, the rack gently decompresses your spine and eradicates the cause of pain within few days.
What is spinal anomaly?
Spinal Anomalies. In the persons having any vertebral column deformity, pain is a common happening in the lumbar and sacral area. The anomalies may be congenital or acquired. Pain in this situation is sudden in onset, continuous, severe in nature and felt when a load is exerted to the vertebral column.
What to do if you have sacral bone pain?
When you go to your doctor for sacral bone pain, he takes a complete history from you and performs a thorough physical examination to look for any abnormality in your posture, gait, shape of vertebral column and range of movements. If the doctor suspects any injury or any pathological process in the bones or joints of the vertebral column, a radiological investigation may be ordered (i.e. X-Ray, CT scan or MRI) . if there is any mild injury to the sacrum, urgent medical intervention is not needed for the healing of bone but it can prevent further complications like nerve damage or disc slip.
How to help lower back pain?
Stretching activities are also very helpful for relieving lower back pain. Focus on stretching exercises that target your hip flexors, hamstrings and glutes muscles
Where do sacral nerves originate?
While there is no spinal cord in the sacral spine region, the sacral nerves actually originate in the lumbar spine. Damage done to the nerve roots in the lower lumbar spine and into the sacrum may have similar symptoms as spinal cord damage. Patients with sacral nerve injuries may have symptoms on one or both sides of the body.
How many segments are there in the sacral spine?
The sacral spine consists of five segments, S1 - S5, that together affect nerve communication to the lower portion of the body. It is important to understand that the spinal cord does not extend beyond the lumbar spine. L2 is the lowest vertebral segment that contains spinal cord. After that point, nerve roots exit each ...
What is the least likely area for spinal nerves to compress?
Sacral (S1-S5) Spinal Cord Injuries. Injuries to the sacral spine are less common than injuries to other areas of the spine. It is also the least likely area for spinal nerves to compress. Author: Spinalcord.com Team. Publish Date: Dec 03, 2020.
Which vertebral segment contains the spinal cord?
L2 is the lowest vertebral segment that contains spinal cord. After that point, nerve roots exit each of the remaining vertebral levels beyond the spinal cord. Damage to the spine at the sacrum levels affects the nerve roots as follows: S1 affects the hips and groin area. S2 affects the back of the thighs.
Can you damage the sacrum?
Damaging either the S1, S2, S3, S4, or S5 vertebrae should leave the patient fairly functional with some issues controlling bowel and bladder function. Patients with injuries to the sacrum typically live very normal lives. Some assistance may be needed for these patients, but most do well on their own.
Is sacral nerve injury a concern for men?
Sexual function is a concern, especially in men who experience sacral spinal nerve injuries. Men’s fertility may be affected with lumbar and/or sacral nerve injuries while a woman’s fertility is typically not affected.
Where is the sacral chakra located?
The sacral chakra is believed to be located below the navel, where the perineum is. It’s said to govern the sex organs and the kidneys, though this isn’t supported by scientific research. It’s associated with the water element and portrayed as a vibrant orange color.
What blocks the sacral chakra?
Certain attitudes or experiences are believed by some to play a role in blocking the sacral chakra.
How to restore sacral chakra balance?
If you want to restore balance to your sacral chakra, Covington and Konst suggest a few practices, including: meditation and yoga . affirmations. essential oils.
How to tell if you have an overactive sacral chakra?
Signs of an overactive sacral chakra. “With [overactivity in] this chakra, in particular, you exhibit being consumed by and drowning in emotions, being emotionally tempestuous, and using escapism to avoid life,” says Covington says. According to Covington, signs of an overactive sacral chakra can include:
Who is the goddess of sacral chakra?
Some believe this chakra is governed by Parvati, the Hindu goddess of fidelity, fertility, and power. “The Sanskrit name [for the sacral chakra] is Svadhisthana,” says certified chakra and crystal healer Laura Konst. “The symbol of the sacral chakra is a moon crescent, which represents the relationship between the tides of water and the phases ...
What is the purpose of chakras?
enhances creative expression. improves sexual intimacy. increases intuition. Though there’s no scientific evidence to support the existence of the chakras, they’re part of religious and spiritual belief systems around the globe, including Buddhism and Hinduism.
What is a sacral dimple?
Sacral dimples are small clefts at the base of the spine. They are relatively common in newborn babies and do not usually indicate problems.
Where are sacral dimples found?
It is found in the small of the back, near the tailbone, which is also known as the sacrum. It is a congenital condition, meaning a person is born with it. Sacral dimples are sometimes known as pilonidal dimples. Often, they will be discovered when a doctor first examines an infant.
What does it mean when you have a large sacral dimple?
Sometimes large or deep sacral dimples are a sign of a birth defect involving the spinal cord or the spinal bones. The most common of these is spina bifida occulta, when there is a small irregularity in one of the vertebrae.
How common are sacral dimples?
Sacral dimples are relatively common in healthy, newborn babies and do not normally signal a concern. They are seen in around 2-4 percent of births, although the cause of them is unknown.
What is spinal cord fixation?
This is a fixation of the spinal cord that limits a person’s movement. In a child, this can mean increased tension on the spinal cord as they grow, which can lead to several neurological problems. In most cases, the individual will experience problems in childhood, but they may not appear until adulthood.
When is the first ultrasound done for sacral dimple?
It is usually carried out within 3 or 4 months after the child is born.
Do sacral dimples have risk factors?
Minor sacral dimples have no known risk factors.
Where is the sacral curve located?
Your sacral curve, located at the base of your spine.
What is the top of the sacrum called?
The top of the sacrum bone is called the sacral base and it is not horizontal. Rather, it tilts. The degree of sacral base tilts vary in individuals; they can be, relatively speaking, steep or flat, or places in between.
What is the lumbar segment?
A "segment" is basically an intervertebral joint which consists of an upper spinal bone and a lower spinal bone with a disc in between.
What is the sacrum joint?
The sacrum is a triangular bone that is wedged in between the two hip bones in back to help stabilize the column, and to ease the load on your spine as it transfers down to your lower body.
What determines the degree of curve in the lumbar, thoracic and cervical areas?
As the base of support for the spine, then, this sacral angle determines, at least in part, the degree of curve in the lumbar, thoracic and cervical areas. In other words, starting at the foundation, which, again is the top of the sacrum, and going up the spine, one angle influences another.
What are the four regions of the spine?
Quick Spinal Anatomy Review. The spine has four main curves. They are categorized in terms of regions, which are: Cervical, or neck. Thoracic, or upper and mid-back area. Lumbar, which is your low back, and, Your sacral curve, located at the base of your spine.
Which bone determines the degree of each spinal curve located above it?
Because your whole spine sits on top of that lowest sacrum bone, the angle of the top of the sacrum determines the degree of each of the spinal curves located above it. This includes the lumbar, thoracic and cervical curves.
How to treat a sacral spine?
Treatment for chordoma in the sacral spine. If the chordoma affects the lower portion of the spine (sacrum), treatment options may include: Surgery. The goal of surgery for a sacral spine cancer is to remove all of the cancer and some of the healthy tissue that surrounds it. Surgery may be difficult to perform because the cancer is ...
What is the best treatment for skull base chordoma?
Radiation therapy. Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams, such as X-rays or protons, to kill cancer cells. Radiation therapy is often recommended after surgery for skull base chordoma to kill any cancer cells that might remain. If surgery isn't an option, radiation therapy may be recommended instead.

Bony Landmarks
- Base
The top part of the sacrum, lying just below the spinal base, is referred to as the base of the scarum. It is the widest portion of the bone. The first one of the five fused sacral vertebrae, S1, is located here. The S1 vertebra is the biggest one, having concave superior articular facets that pr… - Apex
It is the pointy part of the sacrum, directing downwards. The fifth sacral vertebra lies in this most inferior segment of the bone. The apex projects posteriorly to increase the size of the pelvic cavity. This region features an oval facet for articulation with the coccyx.
Articulations
- Lumbosacral joint: The base of the sacrum articulates with the fifth lumbar vertebrae (L5) superiorly via the L5/S1 intervertebral disc, forming this amphiarthrodial joint.
- Sacrococcygeal joint: Here, the apex of the bone articulates with the base of the coccyx, to form another amphiarthrodial joint.
- Sacroiliac joint: The sacral ala laterally articulates with the ilium of the pelvis, forming this sy…
- Lumbosacral joint: The base of the sacrum articulates with the fifth lumbar vertebrae (L5) superiorly via the L5/S1 intervertebral disc, forming this amphiarthrodial joint.
- Sacrococcygeal joint: Here, the apex of the bone articulates with the base of the coccyx, to form another amphiarthrodial joint.
- Sacroiliac joint: The sacral ala laterally articulates with the ilium of the pelvis, forming this synovial joint.
Anatomical Variations of The Sacrum
- Sometimes, the sacrum shows some anatomical variation, including variation in the number of vertebrae, its surface and curvature. 1. The most common anatomical variation of the bone is the variation in the number of sacral vertebrae. Commonly sacrum has five fused vertebrae, but four or six sacral vertebrae have also been documented. 2. Another anomaly of the sacrum is relate…
Sacrum in Females vs. in Males
- Sacrum is sexually dimorphic, meaning it has a slightly different appearance in females and males. The sacrum is wider in females than males. It is also more backwardly curved in females, increasing the size of the pelvic cavity. This wider pelvic cavity in females aids in enduring pregnancy, offers more space for the developing fetus, and houses reproductive organs. Severa…
Injuries to The Sacral Spine
Symptoms
- Patients with injuries to the sacral nerve roots may experience: 1. Lack of control of bowels or bladder 2. Lower back pain 3. Leg pain, which may radiate down the back of the leg(s) 4. Sensory issues in the groin and buttocks area
Causes
- The most common causes of spinal cord injuries to the sacrum are: 1. Motor vehicle accidents 2. Trauma 3. Falls 4. Birth defects 5. Degeneration 6. Osteoporosis
Treatment
- Current treatments available for spinal cord patients with sacrum injuries are: 1. Drugs:Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) drugs are used in treating spinal cord and nerve root injuries. The quicker these drugs are initiated after injury, the better the result for the patient by reducing inflammation around the spinal cord. 2. Surgery:Surgical decompression of the nerves and fusio…
Additional Information
- Damaging either the S1, S2, S3, S4, or S5 vertebrae should leave the patient fairly functional with some issues controlling bowel and bladder function. Patients with injuries to the sacrum typically live very normal lives. Some assistance may be needed for these patients, but most do well on their own.