Full Answer
How do you calculate the second derivative?
Jun 25, 2020 · The second derivative is the rate of change of the rate of change of a point at a graph (the "slope of the slope" if you will). This can be used to find the acceleration of an object (velocity is given by first derivative).
What does second derivative represent?
Its derivative is f' (x) = 3x2. The derivative of 3x 2 is 6x. So the second derivative of f (x) is 6x: f'' (x) = 6x. A derivative can also be shown as dy dx. and the second derivative shown as d2y dx2.
How to do second derivative?
The second derivative is acceleration or how fast velocity changes. 🔗 Graphically, the first derivative gives the slope of the graph at a point. The second derivative tells whether the curve is concave up or concave down at that point. If the second derivative is positive at a point, the graph is bending upwards at that point.
What is the second derivative rule?
1. If the first derivative f' is positive (+) , then the function f is increasing () . 2. If the first derivative f' is negative (-) , then the function f is decreasing ( ) . 3. If the second derivative f'' is positive (+) , then the function f is concave up () . 4. If the second derivative f'' is negative (-) , then the function f is concave down () . 5.

What does the 2nd derivative represent?
The second derivative measures the instantaneous rate of change of the first derivative. The sign of the second derivative tells us whether the slope of the tangent line to f is increasing or decreasing.
How do you find the first and second derivative of a graph?
1:444:08Given fx sketch the first and second derivative graph - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipYou know f of x equals x to the fourth. And then we do F prime of X. Well now relating that for XMoreYou know f of x equals x to the fourth. And then we do F prime of X. Well now relating that for X cubed. Right. So we're losing a curve we're losing a turning points and then if we did F double Prime.
How do you find the second derivative?
1:274:18How to find second derivative of a function 1 - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipTimes 2 that is 18x. And 2 minus 1 that is 1 so it is just 18x. Simple you know it is simple secondMoreTimes 2 that is 18x. And 2 minus 1 that is 1 so it is just 18x. Simple you know it is simple second derivative means derivative of the function.
How do you tell if a graph is a derivative of another graph?
Derivative Graph Rules The top graph is the original function, f(x), and the bottom graph is the derivative, f'(x). What do you notice about each pair? If the slope of f(x) is negative, then the graph of f'(x) will be below the x-axis. If the slope of f(x) is positive, then the graph of f'(x) will be above the x-axis.Jul 25, 2021
What is the second derivative of a graph?
On the graph of a function, the second derivative corresponds to the curvature or concavity of the graph. The graph of a function with a positive second derivative is upwardly concave, while the graph of a function with a negative second derivative curves in the opposite way.
What happens when the second derivative of a function changes sign?
If the second derivative of a function changes sign, the graph of the function will switch from concave down to concave up, or vice versa. A point where this occurs is called an inflection point. Assuming the second derivative is continuous, it must take a value of zero at any inflection point, although not every point where the second derivative is zero is necessarily a point of inflection.
GRAPHING OF FUNCTIONS USING FIRST AND SECOND DERIVATIVES
The following problems illustrate detailed graphing of functions of one variable using the first and second derivatives. Problems range in difficulty from average to challenging.
Click HERE to return to the original list of various types of calculus problems
Your comments and suggestions are welcome. Please e-mail any correspondence to Duane Kouba by clicking on the following address :
Overview
- The second derivativeof a function f(x) is the derivative of the derivative of f(x). In other notation: 1. f(x) is the original function 2. f’(x) is the derivative of f’(x) 3. f’’(x) is the second derivative of f(x) and the first derivative of f’(x) Remember that the derivative of a function tells us the slope of the tangent line at a given point. That is, the first derivative of a function tells us how the function is …
Relation to the graph
Second derivative power rule
Notation
Alternative notation
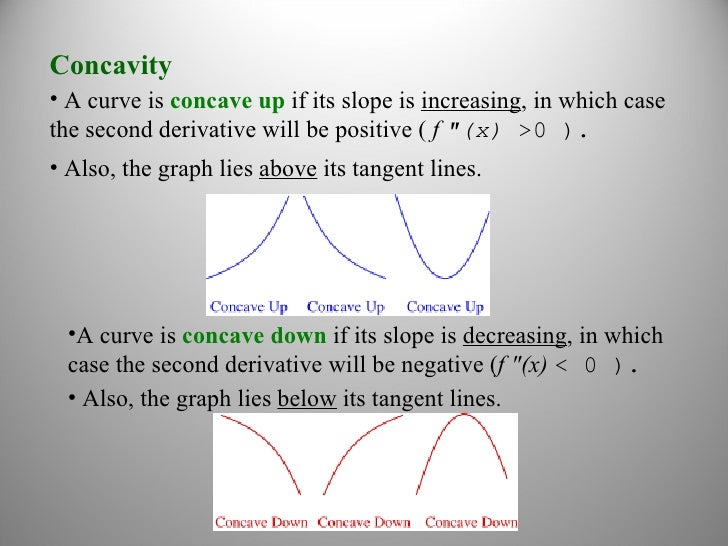
The second derivative of a function f can be used to determine the concavity of the graph of f. A function whose second derivative is positive will be concave up (also referred to as convex), meaning that the tangent line will lie below the graph of the function. Similarly, a function whose second derivative is negative will be concave down (also simply called concave), and its tangent lines will lie above the graph of the function.
Example
The power rule for the first derivative, if applied twice, will produce the second derivative power rule as follows:
Limit
The second derivative of a function is usually denoted . That is:
When using Leibniz's notation for derivatives, the second derivative of a dependent variable y with respect to an independent variable x is written
This notation is derived from the following formula:
Quadratic approximation
As the previous section notes, the standard Leibniz notation for the second derivative is . However, this form is not algebraically manipulable. That is, although it is formed looking like a fraction of differentials, the fraction cannot be split apart into pieces, the terms cannot be cancelled, etc. However, this limitation can be remedied by using an alternative formula for the second derivative. This one is derived from applying the quotient ruleto the first derivative. Doing this yields the for…