What stain do you use to stain spores?
The most commonly used spore staining is Schaeffer-Fulton Method. Dorner method is an alternative method that utilizes nigrosin as the counterstain. Malachite green is a primary stain that stains vegetative cells easily but not spores due to their impervious coats, which will not take the primary stain easily.
What is the difference between Dorner stain and spore stain?
In practice, the spore stain uses two different reagents. An alternative method known as the Dorner method is widely published and utilizes nigrosin as the counterstain. To prepare an endospore stain of bacterial cells and demonstrate endospores in the stained preparation. To differentiate between vegetative cells and endospores.
What is endospore staining?
Endospore staining is a differential staining technique that selectively stains the spores and makes them distinguishable from the vegetative part of the cells. Endospores are produced by a few genera of Gram-positive bacilli such as Bacillus and Clostridium, in response to adverse environmental conditions.
What color are endospores in Schaeffer Fulton stain?
Result Interpretation of Schaeffer–Fulton Stain Endospores: Endospores/ free spores are bright green. Vegetative Cells: They are brownish red to pink. Negative control: Absence of spores

What is endospore staining?
Last updated on June 21st, 2021. Endospore staining is a differential staining technique that selectively stains the spores and makes them distinguishable from the vegetative part of the cells. Endospores are produced by a few genera of Gram-positive bacilli such as Bacillus and Clostridium, in response to adverse environmental conditions.
How to stain endospores?
Prepare smears of organisms to be tested for the presence of endospores on a clean microscope slide and air dry it. Heat fix the smear. Place a small piece of blotting paper (absorbent paper) over the smear and place the slide (smear side up) on a wire gauze on a ring stand.
What is the most widely used stain technique for endospores?
Schaeffer-Fulton stain technique. It is the most widely used technique for endospore staining. The technique was first described by Alice B. Schaeffer and MacDonald Fulton in the 1930s. The method utilizes malachite green as the primary stain and safranin as counterstain.
What is the principle of Dorner's method for staining endospores?
Principle of Dorner’s method for staining endospores. Carbol fuchsin when applied to a heat-fixed slide and heated, softens the structure of the bacterial spores and the basic fuchsin, get into the spores. When decolorized with acid alcohol color washes off the vegetative cells and makes them colorless.
What happens when you decolorize with acid alcohol?
When decolorized with acid alcohol color washes off the vegetative cells and makes them colorless. Since the counterstain nigrosin is negatively charged, bacterial cells don’t easily take up the counterstain. Therefore, vegetative cells appear colorless, endospores stain red, and the background is black.
What color should a cell be when it is visualized under microscopy?
When visualized under microscopy the cells should have three characteristics: the vegetative cells should appear pink/red (i.e. the color of counterstain), the vegetative cells that contain endospores should stain pink while the spores should be seen as green ellipses within the cells.
How to remove secondary stain from slide?
Rinse both sides of the slide to remove the secondary stain and blot the slide/ air dry.
What is the primary stain for spores?
Malachite green is a primary stain that stains vegetative cells easily but not spores due to their impervious coats, which will not take the primary stain easily. For further penetration, heat is applied. In this preparation, both the vegetative cell and spore will appear green. Washing with tap water removes the primary stain of vegetative cells (colorless) but leaving the spores stained. Safranin is the counterstain that stains vegetative cells and that will absorb the counterstain and appear red. The spores retain the green of the primary stain.
What is the most common method of staining spores?
Schaeffer-Fulton is the most common staining method of spores.
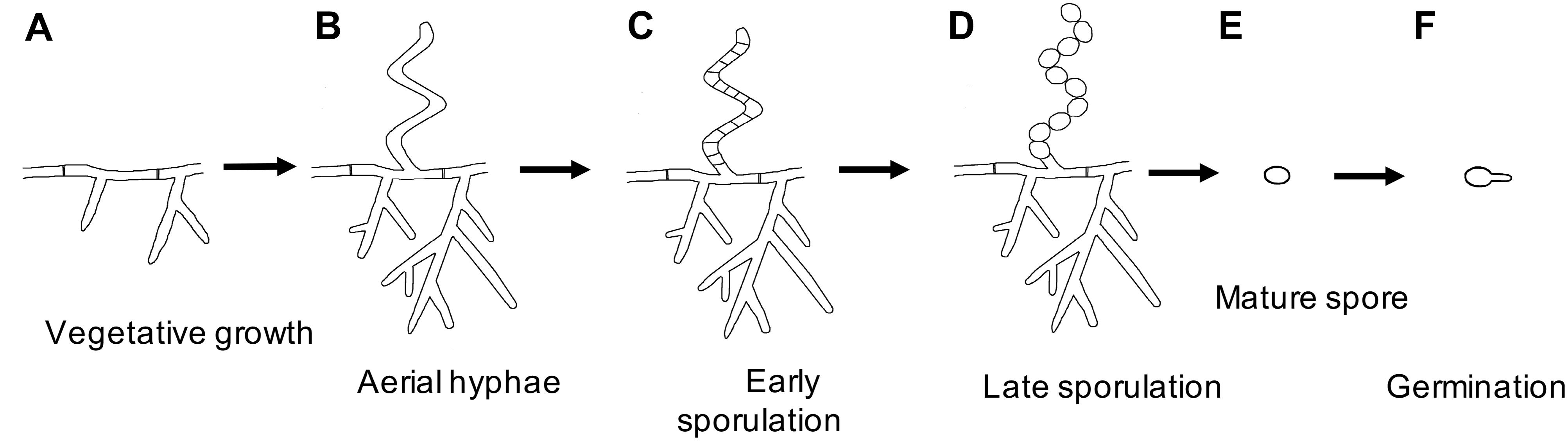
How do spores form?
Spore formation involves a change in enzyme activity and morphology. The spore may be positioned at the end (terminal) of the bacterium or centrally (median). It may be round, oval, or elongate. Endospores being dense and thick-walled, are able to withstand dehydration, heat, cold, and the action of disinfectants. A spore is unable to multiply but when conditions for vegetative growth return, it is able to produce a bacterial cell that is capable of reproducing. Spores of Bacillus species are dormant and extremely resistant to many environmental stresses including, heat, desiccation, radiation, and a variety of toxic chemicals. As a consequence, spores can survive for extremely long periods, certainly hundreds of years and perhaps much longer. Spore resistance is due to a variety of factors, including the outer spore coats and the relative impermeability of the spore’s inner membrane. There are also novel features of the spore’s central region or core, the site of spore DNA, which plays a major role in spore resistance. The spore stain applies to show endospores in the stained preparation that does not only assist the organism is sporulated or not but also to differentiate between vegetative cells and endospores. The most commonly used spore staining is Schaeffer-Fulton Method. Dorner method is an alternative method that utilizes nigrosin as the counterstain.
What is the endospore made of?
The endospore is made of DNA, ribosomes, and large amounts of dipicolinic acid . Dipicolinic acid is a spore-specific chemical that emerges to assist in the ability of endospores to maintain dormancy and thus save from ultraviolet radiation, desiccation, high temperature, extreme freezing, and chemical disinfectants.
What color are vegetative cells?
Vegetative Cells: They are brownish red to pink.
How long are endospores viable?
spores remaining viable over 10,000 years, and revival of spores millions of years old has been maintained.
What is the primary stain for spores?
Malachite green is a primary stain that stains vegetative cells easily but not spores due to their impervious coats, which will not take the primary stain easily. For further penetration, heat is applied. In this preparation, both the vegetative cell and spore will appear green. Washing with tap water removes the primary stain of vegetative cells (colorless) but leaving the spores stained. Safranin is the counterstain that stains vegetative cells and that will absorb the counterstain and appear red. The spores retain the green of the primary stain.
What is the most common method of staining spores?
Schaeffer-Fulton is the most common staining method of spores.
How do spores form?
Spore formation involves a change in enzyme activity and morphology. The spore may be positioned at the end (terminal) of the bacterium or centrally (median). It may be round, oval, or elongate. Endospores being dense and thick-walled, are able to withstand dehydration, heat, cold, and the action of disinfectants. A spore is unable to multiply but when conditions for vegetative growth return, it is able to produce a bacterial cell that is capable of reproducing. Spores of Bacillus species are dormant and extremely resistant to many environmental stresses including, heat, desiccation, radiation, and a variety of toxic chemicals. As a consequence, spores can survive for extremely long periods, certainly hundreds of years and perhaps much longer. Spore resistance is due to a variety of factors, including the outer spore coats and the relative impermeability of the spore’s inner membrane. There are also novel features of the spore’s central region or core, the site of spore DNA, which plays a major role in spore resistance. The spore stain applies to show endospores in the stained preparation that does not only assist the organism is sporulated or not but also to differentiate between vegetative cells and endospores. The most commonly used spore staining is Schaeffer-Fulton Method. Dorner method is an alternative method that utilizes nigrosin as the counterstain.
What is the endospore made of?
The endospore is made of DNA, ribosomes, and large amounts of dipicolinic acid . Dipicolinic acid is a spore-specific chemical that emerges to assist in the ability of endospores to maintain dormancy and thus save from ultraviolet radiation, desiccation, high temperature, extreme freezing, and chemical disinfectants.
How long are endospores viable?
spores remaining viable over 10,000 years, and revival of spores millions of years old has been maintained.
What color are vegetative cells?
Vegetative Cells: They are brownish red to pink.
How long to steam malachite green?
Cover smear with malachite green and place on top of a beaker of water sitting on a warm hot plate, allowing the preparation to steam for 2 to 3 minutes. Note: Do not allow the stain to evaporate; refill the stain as needed. Check the stain from boiling by adjusting the hot plate temperature.