How does semi conservative replication work?
Semi-conservative replication. Semi-conservative replication is the mechanism by which DNA replicates in cells. The double stranded DNA unwinds, hydrogen bonds are broken between the two strands by the enzyme DNA helicase. One of the strands is used as a template to form a second complementary strand. The exposed bases on the single-stranded ...
What is the significance of semi-conservative DNA replication?
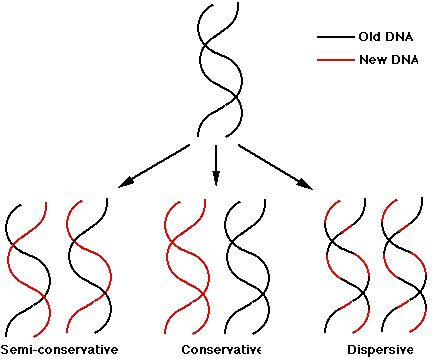
Semi-conservative replication. In this model, the two strands of DNA unwind from each other, and each acts as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand. ... Conservative replication. ... Dispersive replication. ...
What is semiconservation replication?
The semiconservative replication of DNA strands is the means by which the replication of DNA occurs in the cells. In the process of semiconservative replication, the double strands of a cell's DNA unwind because the hydrogen bonds present between both the strands are broken by the DNA helicase enzyme.
What are the 5 steps of DNA replication in order?
What are the steps of DNA replication in order quizlet?
- Starts at? DNA Replication begins at the Origin of Replication.
- Unwinds. …
- Holds strands. …
- Two types of strands added 3′ to 5′ …
- RNA Primer. …
- Add bases. …
- Fix mistakes, remove RNA Primer. …
What is the semiconservative model of replication quizlet?
Semiconservative DNA replication means that: each strand of a double-stranded DNA molecule is replicated differently. each daughter DNA molecule is composed of one original strand and one new strand. the cell can proofread its newly synthesized DNA only part of the time.
Why is DNA replication called the semi-conservative model?
Semiconservative replication is so named because one of the strands of DNA in each of the two copies of DNA is ancient and conserved while the other is newly produced at the moment of replication.
What does semi conservative replication mean simple definition?
Semi-conservative replication means that during DNA replication, the two strands of nucleotides separate. Both strands then form the template for free nucleotides to bind to to create the two identical daughter strands. Hence each daughter strand has half of the DNA from the original strand and half newly-formed DNA.
What does Semiconservative mean in simple terms?
Semi conservative literally means "Half conserved". In case of DNA , it is used for DNA replication in which one strand of DNA is conserved while other is not. Also primary structure of DNA duplex is conserved but secondary structure is disrupted.
How is semiconservative DNA replication measured?
The rate of semiconservative DNA replication in a living cell was first measured as the rate of the T4 phage DNA strand elongation in phage-infected E. coli. During the period of exponential DNA increase at 37 °C, the rate of strand elongation was 749 nucleotides per second. The mutation rate per base pair per round of replication during phage T4 DNA synthesis is 2.4 × 10−8. Thus, semiconservative DNA replication is both rapid and accurate.
What enzymes are involved in semiconservative replication?
For semiconservative replication to occur, the DNA double-helix needs to be separated so the new template strand can be bound to the complementary base pairs. Topoisomerase is the enzyme that aids in the unzipping and recombination of the double-helix. Specifically, topoisomerase prevents the double-helix from supercoiling, or becoming too tightly wound. Three topoisomerase enzymes are involved in this process: Type IA Topoisomerase , Type IB Topoisomerase , and Type II Topoisomerase. Type I Topoisomerase unwinds double stranded DNA while Type II Topoisomerase breaks the hydrogen bonds linking the complementary base pairs of DNA.
Why is semiconservative replication important?
It is fast, accurate, and allows for easy repair of DNA. It is also responsible for phenotypic diversity in a few prokaryotic species. The process of creating a newly synthesized strand from the template strand allows for the old strand to be methylated at a separate time from the new strand. This allows repair enzymes to proofread the new strand and correct any mutations or errors.
What are the two types of replication?
Semiconservative replication derives its name from the fact that this mechanism of transcription was one of three models originally proposed for DNA replication : 1 Semiconservative replication would produce two copies that each contained one of the original strands of DNA and one new strand. Semiconservative replication is beneficial to DNA repair. During replication, the new strand of DNA adjusts to the modifications made on the template strand. 2 Conservative replication would leave the two original template DNA strands together in a double helix and would produce a copy composed of two new strands containing all of the new DNA base pairs. 3 Dispersive replication would produce two copies of the DNA, both containing distinct regions of DNA composed of either both original strands or both new strands. The strands of DNA were originally thought to be broken at every tenth base pair to add the new DNA template. Eventually, all new DNA would make up the double helix after many generations of replication.
How many copies of DNA would be produced by semiconservative replication?
Semiconservative replication derives its name from the fact that this mechanism of transcription was one of three models originally proposed for DNA replication : Semiconservative replication would produce two copies that each contained one of the original strands of DNA and one new strand.
Why is DNA replication semi-conservative?
This process is known as semi-conservative replication because two copies of the original DNA molecule are produced. Each copy contains one original strand and one newly-synthesized strand.
What would happen if conservative replication was done?
Conservative replication would leave the two original template DNA strands together in a double helix and would produce a copy composed of two new strands containing all of the new DNA base pairs.
What is the term for the formation of two identical copies of the original double stranded molecule?
This results in the formation of two identical copies of the original double stranded molecule. This is called semiconservative replication. This term captures the idea that each round of DNA replication produces hybrid molecules each of which contains one old strand and one newly synthesized strand.
Who proposed the semiconservative DNA replication pattern?
The pattern of Semiconservative DNA replication was proposed in a 1953 paper by Watson and Crick.
Can you add videos to your watch history?
Videos you watch may be added to the TV's watch history and influence TV recommendations. To avoid this, cancel and sign in to YouTube on your computer.
What is DNA Replication?
DNA Replication is the process by which a cell copies its DNA prior to cell division.
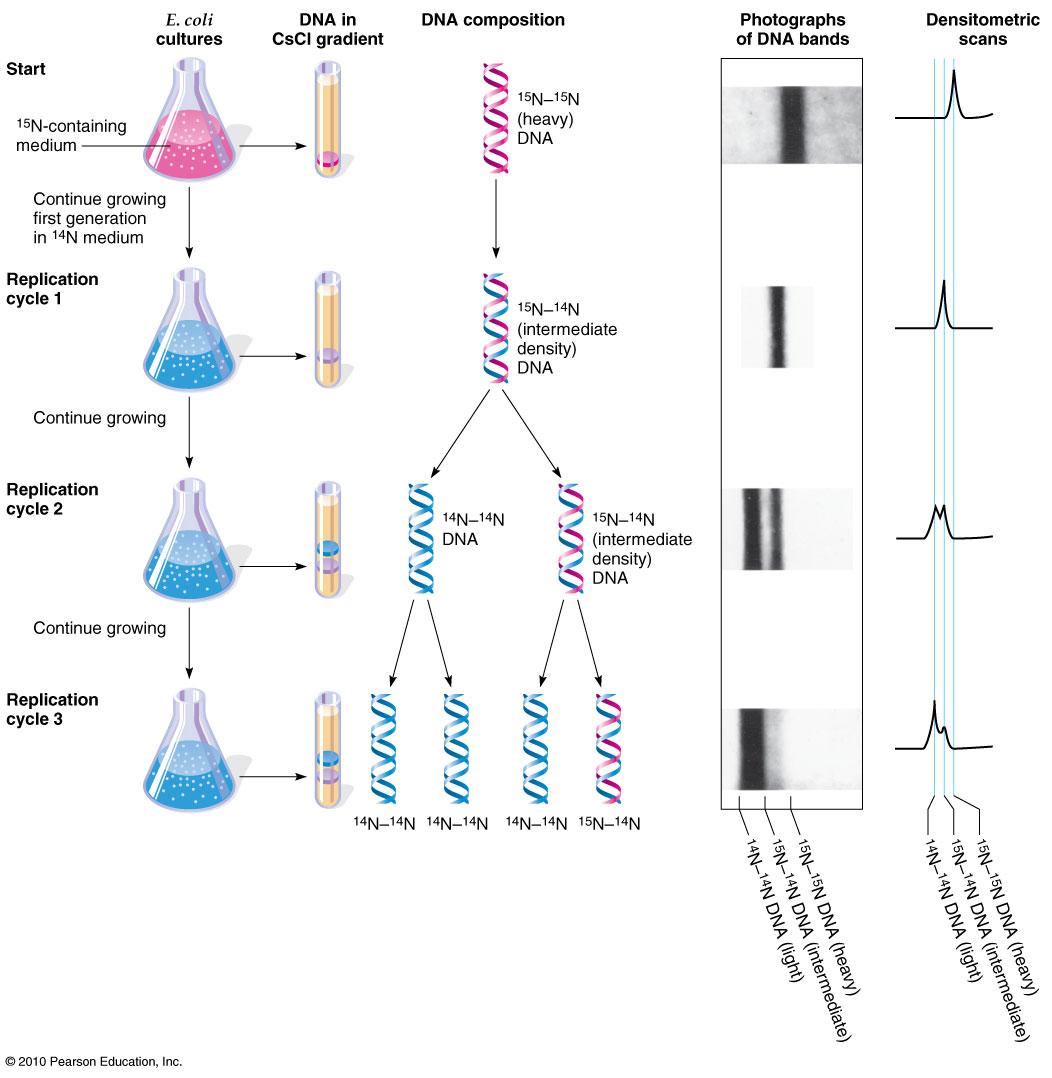
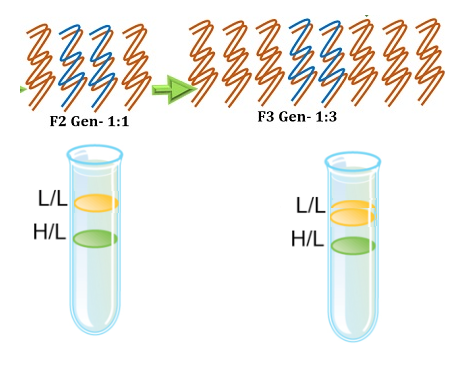
What is the intermediate band in DNA replication?
The intermediate band told Meselson and Stahl that the DNA molecules made in the first round of replication were a hybrid of light and heavy DNA. This result fits with the dispersive and semi-conservative models, but not with the conservative model (two distinct bands would appear). Thus, this mode may be rejected.
What is the nitrogen in E. coli?
Meselson and Stahl grew E. coli cells for many generations in a medium in which the heavy isotope of nitrogen, 15 N, had been substituted for the normal, light isotope, 14 N. As we all know that the purine and pyrimidine bases in DNA contain nitrogen. Thus, the cells grown on 15 N rich medium will have a greater DNA density than the cells grown on 14 N containing medium. A “heavy” isotope of nitrogen, 15N contains one more neutron than the naturally occurring 14N isotope; thus, molecules containing 15N are denser than those containing 14N.
What is the conservative model of DNA replication?
A conservative mechanism of replication proposes the entire double-stranded DNA molecule serves as a template for a whole new DNA molecule, and the original DNA molecule will remain fully conserve during replication. Thus, the new cell has one completely new double-helix and one completely old double-helix.
What is the role of nucleotide strands in DNA?
In this model, the nucleotide strands unwind and each serves as a template for a new DNA molecule. This means that every double helix in the new generation of an organism consists of one complete “old” strand and one complete “new” strand wrapped around each other.
How does dispersive replication work?
In dispersive replication, both nucleotide strands break down into fragments. These broken fragments serve as templates for the synthesis of new DNA fragments. Then somehow, they reassemble into two complete DNA molecules. In this model, each resulting DNA molecule is interspersed with fragments of old and new DNA. As a result, none of the original molecules is conserved.
How to separate DNA molecules?
They, then, separate the different density molecules by using the equilibrium density-gradient centrifugation technique. This method separates molecules such as DNA into bands by spinning them at high speeds in the presence of another molecule, such as cesium chloride, that forms a density gradient from the top to the bottom of the spinning tube. Molecules of DNA will reach equilibrium when their density equals the density of the gradient medium. In this case, 15 N-DNA will reach this point at a position closer to the bottom of the tube than will 14 N-DNA.