What are tRNAs?
Transfer RNAs or tRNAs are molecules that act as temporary carriers of amino acids, bringing the appropriate amino acids to the ribosome based on the messenger RNA ( mRNA) nucleotide sequence. In this way, they act as the intermediaries between nucleotide and amino acid sequences.
What is the role of tRNA in translation?
During translation, each time an amino acid is added to the growing chain, a tRNA molecule forms base pairs with its complementary sequence on the messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule, ensuring that the appropriate amino acid is inserted into the protein. Transfer RNA is that key link between transcribing RNA and translating that RNA into protein.
What is the relationship between tRNA and mRNA?
They pair with mRNA in a complementary and antiparallel manner, and each tRNA can base pair with a stretch of three nucleotides on mRNA. These sets of three nucleotides on the mRNA are called codons and the corresponding sequence on the tRNA is called the anticodon.
How many types of tRNA are there?
A tRNA can be classified based on the amino acid it carries, giving rise to 20 different tRNAs. Alternatively, they can also be grouped based on their anticodon. There are 64 possible codons arising from a combination of four nucleotides. Of these, 3 are stop codons that signal the end of translation.
How do you find a tRNA sequence?
Each tRNA has a set of three bases on it known as an anti-codon. The anti-codon matches complementary bases in the mRNA sequence. To determine the overall anti-codon sequence that will match a strand of mRNA, simply retranscribe the RNA sequence; in other words, write out the complementary bases.
What is the base sequence of tRNA?
All tRNA molecules have the sequence pCpCpA at the 3' terminus. Roughly in the middle of the tRNA molecule is a sequence of three bases called the anticodon. These three bases are hydrogen bonded to a complementary sequence in an RNA molecule— called messenger RNA, mRNA— during protein synthesis.
What is sequence in 3 end of tRNA?
The CCA tail is a cytosine-cytosine-adenine sequence at the 3′ end of the tRNA molecule. The amino acid loaded onto the tRNA by aminoacyl tRNA synthetases, to form aminoacyl-tRNA, is covalently bonded to the 3′-hydroxyl group on the CCA tail.
How many tRNA sequences are there?
There are thought to be 31 different tRNAs, but these 20 synthetases are capable of "charging" all of them with the correct amino acid.
What is the tRNA anticodon sequence?
The tRNA anticodon is a sequence of three nucleotides that are the complement of the three nucleotides in the mRNA codon. The function of the anticodon is to help the tRNA find the appropriate amino acid that the mRNA codon specified.
Does tRNA use U or T?
Note that DNA contains thymine (T) but no uracil (U) and that both mRNA and tRNA contain U and not T.
What are the two functional ends of a tRNA?
One end of the tRNA binds to a specific amino acid (amino acid attachment site) and the other end has an anticodon that will bind to an mRNA codon. One end of the L shape has the anticodon, while the other has the attachment site for the amino acid.
What are tRNA made of?
To clarify, transfer RNA transfers amino acids, not RNA. The tRNA molecule is made of RNA and functions as a shuttle to get amino acids to the ribosome. The ribosome needs specific amino acids in a specific order to ensure that the correct protein is built.
How many tRNA are there for stop codon?
By analogy, we call them termination tRNAs: Ter-tRNA1 and Ter-tRNA2, respectively, even though they transport no amino acids, and suggest that they directly pair to stop codons.
Why are there 20 types of tRNA?
A tRNA can be classified based on the amino acid it carries, giving rise to 20 different tRNAs. Alternatively, they can also be grouped based on their anticodon. There are 64 possible codons arising from a combination of four nucleotides.
How many tRNA does each amino acid have?
Specialized tRNAs exist for each of the 20 amino acids needed for protein synthesis, and in many cases more than one tRNA for each amino acid is present. The 61 codons used to code amino acids can be read by many fewer than 61 distinct tRNAs.
How do you find the amino acid sequence from tRNA?
0:185:29The Genetic Code- how to translate mRNA - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThrough the process of transcription. This sequence of nucleotides in a gene is transcribed orMoreThrough the process of transcription. This sequence of nucleotides in a gene is transcribed or copied into an RNA form to make a molecule of messenger RNA in the process of translation translation
How do you transcribe mRNA to tRNA?
To translate messenger RNA, or mRNA, use an amino acid table to help you figure out the codon sequence in transfer DNA known as tRNA. Genes in DNA are like coded recipes for proteins. Cells transcribe these coded recipes onto an messenger mRNA transcript and export it out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm of the cell.
What bases would be found in the complementary tRNA anticodon?
At one end, the tRNA has an anticodon of 3'-UAC-5', and it binds to a codon in an mRNA that has a sequence of 5'-AUG-3' through complementary base pairing. The other end of the tRNA carries the amino acid methionine (Met), which is the the amino acid specified by the mRNA codon AUG.
What are mRNA and tRNA?
mRNA is short for messenger RNA. mRNA is formed during the transcription stop of protein synthesis when the enzyme RNA polymerase matches up mRNA n...
How is tRNA used in protein synthesis?
tRNA is used in the second step of protein synthesis: translation. During translation, the ribosome reads the mRNA code three bases at a time (cal...
Where is RNA transferred?
To clarify, transfer RNA transfers amino acids, not RNA. The tRNA molecule is made of RNA and functions as a shuttle to get amino acids to the rib...
Why is it called transfer RNA?
Transfer RNA is so named because it is responsible for transferring amino acids to the ribosome. Some amino acids are produced by the body, whereas...
What is transfer RNA?
Transfer RNA is that key link between transcribing RNA and translating that RNA into protein. The transfer RNA matches up via the anticodon to the specific codons in the messenger RNA, and that transfer RNA carries the amino acid that that codon encodes for.
What is tRNA in biology?
Transfer RNA (tRNA) Transfer RNA (tRNA) is a small RNA molecule that participates in protein synthesis. Each tRNA molecule has two important areas: a trinucleotide region called the anticodon and a region for attaching a specific amino acid. During translation, each time an amino acid is added to the growing chain, ...
What happens to amino acids in translation?
During translation, each time an amino acid is added to the growing chain, a tRNA molecule forms base pairs with its complementary sequence on the messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule, ensuring that the appropriate amino acid is inserted into the protein.
What are the tRNAs that are used in translation?
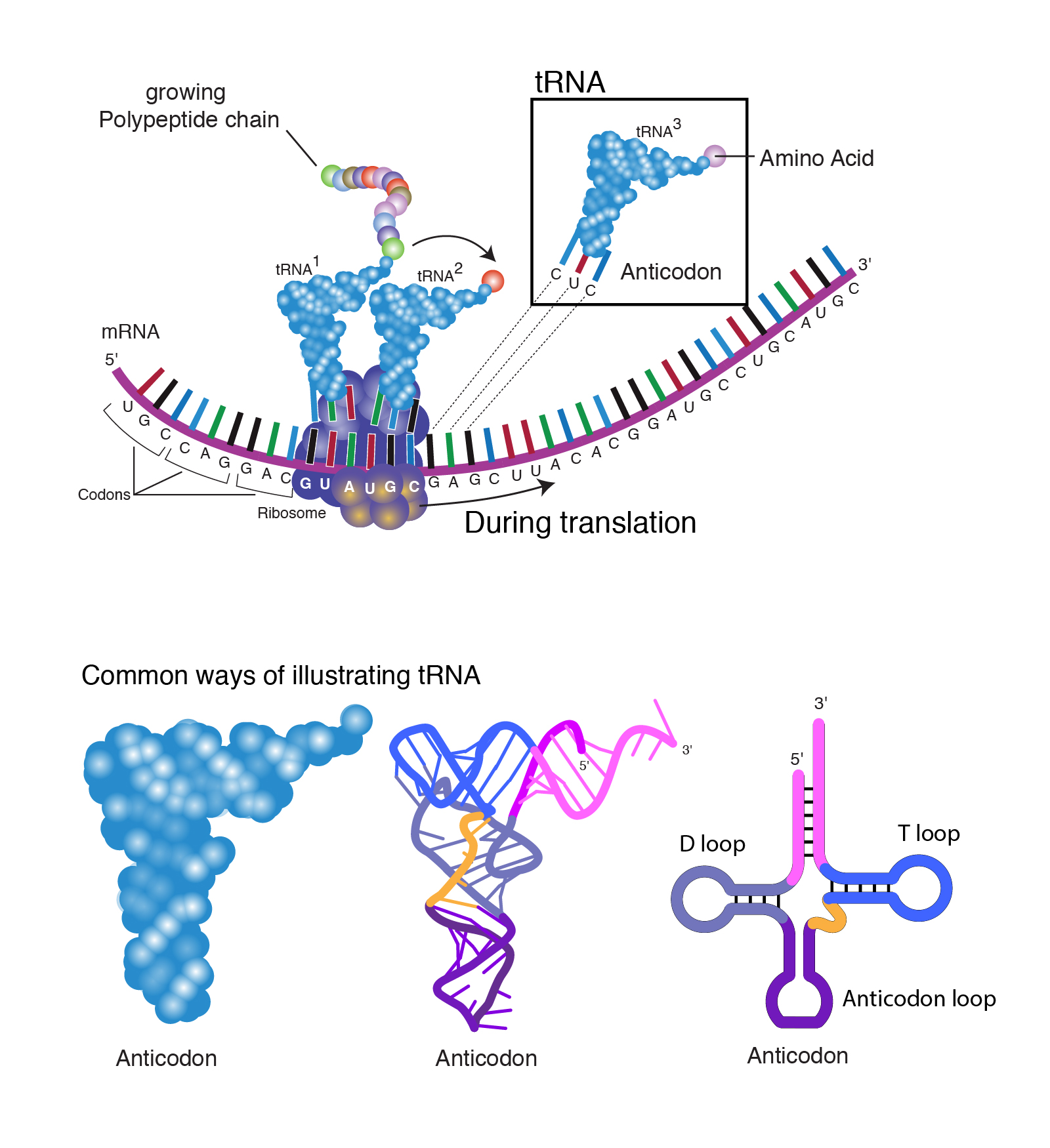
tRNAs are ribonucleic acids and therefore capable of forming hydrogen bonds with mRNA. Additionally, they can also form ester linkages with amino acids, and therefore, can physically bring mRNA and amino acids together during the process of translation. They pair with mRNA in a complementary and antiparallel manner, and each tRNA can base pair with a stretch of three nucleotides on mRNA. These sets of three nucleotides on the mRNA are called codons and the corresponding sequence on the tRNA is called the anticodon. Base pairing between the codon and anticodon brings specificity to the process of translation. On one end of the tRNA, an appropriate amino acid is attached to its 3’ hydroxyl group based on the anticodon and the ribosome catalyzes the formation of a peptide bond between this amino acid and the elongating polypeptide chain.
What is the secondary structure of tRNA?
The secondary structure of tRNA containing the acceptor region, D- and T-arms and the anticodon loop is said to resemble a cloverleaf. After the RNA folds into its tertiary structure, it is L-shaped, with the acceptor stem and T-arm forming an extended helix and the anticodon loop and D-arm similarly making another extended helix. These two helices align perpendicularly to each other in a way that brings the D-arm and T-arm into close proximity while the anticodon loop and the acceptor arm are positioned on opposite ends of the molecule.
How many nucleotides are in a tRNA?
Transfer RNAs are coded by a number of genes, and are usually short molecules, between 70-90 nucleotides (5 nm) in length. The two most important parts of a tRNA are its anticodon and the terminal 3’ hydroxyl group, which can form an ester linkage with an amino acid. However, there are other aspects to a tRNA’s structure such as the D-arm and T-arm, which contribute to its high level of specificity and efficiency. Only 1 in 10,000 amino acids are incorrectly attached to a tRNA, which is a remarkable number given the chemical similarities between many amino acids.
What is a tRNA?
tRNA Definition. Transfer RNAs or tRNAs are molecules that act as temporary carriers of amino acids, bringing the appropriate amino acids to the ribosome based on the messenger RNA ( mRNA) nucleotide sequence. In this way, they act as the intermediaries between nucleotide and amino acid sequences. tRNAs are ribonucleic acids ...
What are the 5 and 3 ends of tRNA?
This gives rise to the 5’ and 3’ ends of the RNA since all the other phosphate and hydroxyl groups are involved in phosphodiester bonds within the nucleic acid. RNA-Nucleobases. The last three bases on the 3’ end of tRNA are always CCA – two cytosines followed by one adenine base.
How many different types of tRNA are there?
Types of tRNA. A tRNA can be classified based on the amino acid it carries, giving rise to 20 different tRNAs. Alternatively, they can also be grouped based on their anticodon. There are 64 possible codons arising from a combination of four nucleotides. Of these, 3 are stop codons that signal the end of translation.
Why does tRNA bind to the nucleus?
The enzyme binds to many regions of the tRNA to ensure high specificity in the reaction and even proofreads its own reaction since many amino acids have similar structures. Mature tRNA then binds specific export factors that export it from the nucleus, using the RanGTP system.
What is the start codon in mRNA?
Our cells use a very smart strategy to solve this problem – the “start codon”. Because the translation only begins at the start codon (AUG) and continues in successive groups of three, the position of the start codon ensures that the mRNA is read in the correct frame (in the example above, in Frame 3).
What is the name of the mRNA molecule that Nirenberg discovered?
Nirenberg started with an mRNA molecule consisting only of the nucleotide uracil (called poly-U). When he added poly-U mRNA to the cell-free system, he found that the polypeptides made consisted exclusively of the amino acid – Phenylalanine (Phe). Nirenberg concluded that UUU might code for phenylalanine. Using the same approach, he discovered that triplet CCC codes for Proline (Pro).
What is the relationship between amino acids and codons called?
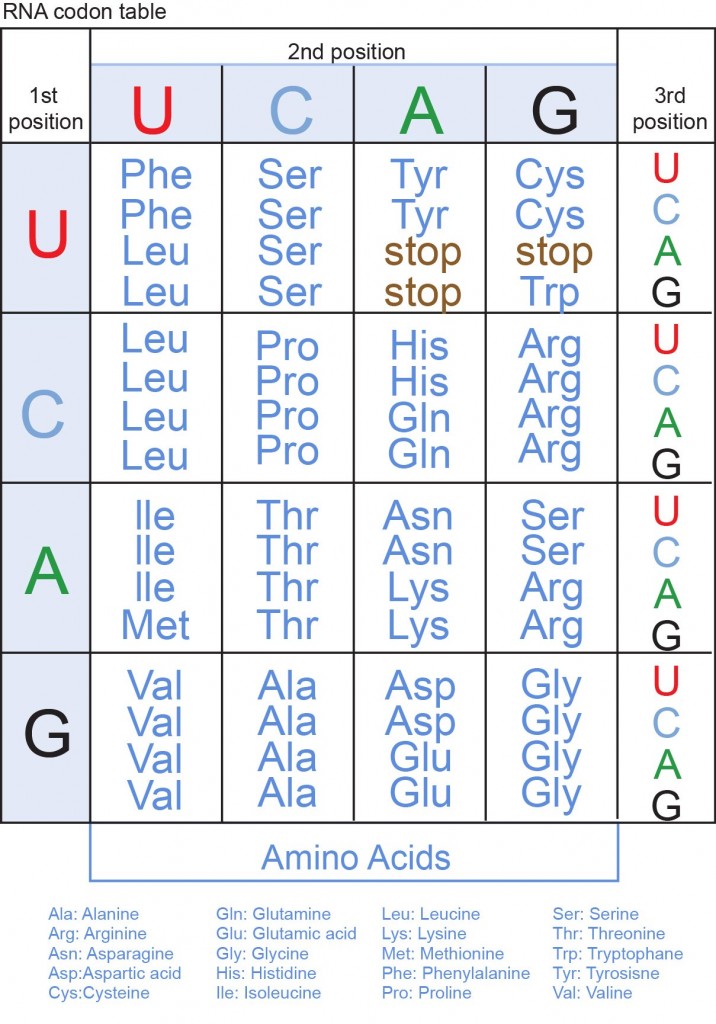
The full set of relationships between codons and amino acids (or stop signals) is called the genetic code . The genetic code is often summarized in a codon chart (or codon table), where codons are translated to amino acids.
What is the order of the protein translation?
mRNA codons are read from 5′ end to 3′ end, and its order specifies the order of amino acids in a protein from N-terminus to C-terminus.
Why are codons used in natural selection?
Codon usage biases could be the consequence of natural selection (tRNA abundance ). For laboratories to produce certain proteins in a large quantity, researchers may perform “codon optimization” to resynthesize genes in such a way that their codons are more appropriate for the desired expression host (i.e., making human proteins in E coli. bacteria).
What did Nirenberg do in a test tube?
Nirenberg did so in a test tube of cytoplasm from burst E. coli bacteria, which contains all the ingredients needed for translation.
How many stop codons are there in a protein?
Three “ Stop ” codons mark the end of a protein and terminate the translation.

tRNA Definition
tRNA Structure and Function
- Transfer RNAs are coded by a number of genes, and are usually short molecules, between 70-90 nucleotides (5 nm) in length. The two most important parts of a tRNA are its anticodon and the terminal 3’ hydroxyl group, which can form an ester linkage with an amino acid. However, there are other aspects to a tRNA’s structure such as the D-arm and T-arm, which contribute to its high lev…
Types of tRNA
- A tRNA can be classified based on the amino acid it carries, giving rise to 20 different tRNAs. Alternatively, they can also be grouped based on their anticodon. There are 64 possible codons arising from a combination of four nucleotides. Of these, 3 are stop codons that signal the end of translation. This gives rise to a situation where one amino acid is represented by multiple codon…
tRNA Interaction with Ribosome
- The ribosome contains three important regions – the P (peptidyl) site containing the growing polypeptide, the A (acceptor) site that receives a new charged tRNA and the E (exit) site through which a deacylated tRNA leaves the ribosome. These sites span both the subunits of the ribosome and are denoted as P/P or A/A sites with the first letter referring to the site on the smal…
Related Biology Terms
- Antiparallel– Parallel but running in opposite directions, such as the two sugar-phosphate backbones of a DNA molecule.
- Complementarity – The property of nitrogenous bases in nucleic acids to form specific and stable hydrogen bonds with other nitrogen bases. For instance, the interaction between adenine and thyminei...
- Antiparallel– Parallel but running in opposite directions, such as the two sugar-phosphate backbones of a DNA molecule.
- Complementarity – The property of nitrogenous bases in nucleic acids to form specific and stable hydrogen bonds with other nitrogen bases. For instance, the interaction between adenine and thyminei...
- Introns– Parts of an RNA molecule that are removed post-transcriptionally.
- Transcription– The process of generating an RNA molecule from a DNA template.
Quiz
- 1. Which of these is a structure found on tRNAs? A. Anticodon loop B. Codons C. AATS D.All of the above 2. Which of these modified residues are found on tRNAs? A. Pseudouridine B. Thymidine C. Cytidine D.All of the above 3. Which of these modified bases is derived from adenine? A. Adenosine B. Inosine C. Cytidine D.All of the above