Explore
When the pancreas is young, the surface of the pancreas is relatively smooth. As it ages the earliest signs of volume loss is development of a nodular shape of the surface. Thus the shape deformity reflects an involutional process and assessment of the shape gives insight into the size and approximate age of the gland.
What does the shape of the pancreas reveal about its age?
Anatomy of the pancreas. The pancreas is an elongated, tapered organ located across the back of the belly, behind the stomach. The right side of the organ—called the head—is the widest part of the organ and lies in the curve of the duodenum, the first division of the small intestine. The tapered left side extends slightly upward—called the body...
What is the anatomy of the pancreas?
In general as we view the pancreas in the transverse plain, the neck is marked by point where the globular head thins out into the more rectangular shaped neck. Like the neck of most structures its overall size is less than the head and the body which it connects. It can however be short and fat or long and thin.
What is the shape of the pancreas neck?
The narrow end of the pancreas, called the tail, extends to the left side of the body. Diabetes, type 1: The body’s immune system attacks and destroys the pancreas’ insulin-producing cells.
What is the narrow end of the pancreas called?

What is a pancreas shaped like?
The pancreas is a leaf shaped organ tucked under the liver, close to the gallbladder, stomach and bowel. It is part of both the digestive and endocrine systems. The pancreas lies across your body just behind your stomach.
Is pancreas J shaped?
The pancreas, named for the Greek words pan (all) and kreas (flesh), is a 12-15–cm long J-shaped (like a hockey stick), soft, lobulated, retroperitoneal organ. It lies transversely, although a bit obliquely, on the posterior abdominal wall behind the stomach, across the lumbar (L1-2) spine (see the image below).
What is the Colour of pancreas?
The pancreas is a elongated organ, light tan or pinkish in color, that lies in close proximity to the duodenum.
What is the size of a normal pancreas?
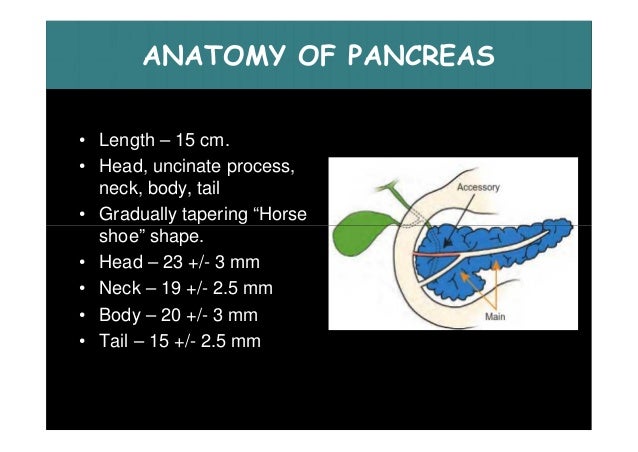
The size of the normal pancreas was found to be up to 3.0 cm for the head, 2.5 cm for the neck and body, and 2.0 cm for the tail.
What is another word for pancreas?
n. duct gland, exocrine gland, exocrine.
What type of muscle is the pancreas?
Smooth muscle fibers are located in walls of hollow visceral organs (such as the liver, pancreas, and intestines), except the heart, appear spindle-shaped, and are also under involuntary control.
What is the weight of pancreas?
Thirty cadaver pancreas specimens were dissected and carefully measured. The weights were recorded and averaged 91.8 g (range: 40.9 to 182 g).
Can u live without a pancreas?
It's possible to live without a pancreas. But when the entire pancreas is removed, people are left without the cells that make insulin and other hormones that help maintain safe blood sugar levels. These people develop diabetes, which can be hard to manage because they are totally dependent on insulin shots.
Which is the largest gland in human body?
LiverLiver is the largest gland in human body.
How thick is the pancreas?
Pancreatic neck thickness varied between 6 and 11 mm, and pancreatic tail thickness was defined between 10 and 20 mm. In the current study, the median pancreatic head thickness varied between 15 and 18 mm. Siegel et al. measured mean pancreatic body thickness as 6–11 mm.
What is the function of pancreas?
The pancreas performs two main functions: Exocrine function: Produces substances (enzymes) that help with digestion. Endocrine function: Sends out hormones that control the amount of sugar in your bloodstream.
How do I check my pancreas?
What tests do health care professionals use to diagnose pancreatitis?Blood tests. ... Stool tests. ... Ultrasound. ... Computed tomography (CT) scan. ... Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP). ... Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS link). ... Pancreatic Function Test (PFT).
What is the histology of the pancreas?
The structure of the pancreas is dominated by the fact that it is a dual function organ with both exocrine and endocrine cell types. The vast bulk of the pancreas is composed of exocrine tissue, and secretions from those cells flow into a series ducts for ultimate delivery into the duodenum.
Why is the pancreas referred to as an exo endocrine gland?
Endocrine glands are those glands which release their secretions directly into the blood which carries it to the target sites. Endocrine glands mainly secrete hormones. Since pancreas secretes both digestive juices and hormones and has exocrine and endocrine parts, it is known as an exo- endocrine gland.
Can u live without a pancreas?
It's possible to live without a pancreas. But when the entire pancreas is removed, people are left without the cells that make insulin and other hormones that help maintain safe blood sugar levels. These people develop diabetes, which can be hard to manage because they are totally dependent on insulin shots.
What are the early signs of pancreas problems?
SymptomsUpper abdominal pain.Abdominal pain that radiates to your back.Tenderness when touching the abdomen.Fever.Rapid pulse.Nausea.Vomiting.
Where is the pancreas located?
The pancreas is about 6 inches long and sits across the back of the abdomen, behind the stomach. The head of the pancreas is on the right side of the abdomen and is connected to the duodenum (the first section of the small intestine) through a small tube called the pancreatic duct. The narrow end of the pancreas, called the tail, ...
How to tell if you have pancreatitis?
Physical examination: By pressing on the center of the belly, a doctor might check for masse s or abdominal pain. They can also look for other signs of pancreas conditions. Pancreatic pain often radiates to the back.
What is a pseudocyst in the pancreas?
Pancreatic pseudocyst: After a bout of pancreatitis, a fluid-filled cavity called a pseudo cyst can form. Pseudocysts may resolve spontaneously, or they may need surgical drainage. Islet cell tumor: The hormone-producing cells of the pancreas multiply abnormally, creating a benign or cancerous tumor.
How to treat pancreas?
Pancreas Treatments. Insulin: Injecting insulin under the skin causes body tissues to absorb glucose, lowering blood sugar. Insulin can be created in a lab or purified from animal sources. Pseudocyst drainage: A pseudocyst can be drained by inserting a tube or needle through the skin into the pseudocyst.
What is the procedure to remove pancreas tissue?
Pancreas biopsy: Either using a needle through the skin or a surgical procedure, a small piece of pancreas tissue is removed to look for cancer or other conditions. Endoscopic u ltrasound: A probe is placed on the belly, and harmless sound waves create images by reflecting off the pancreas and other organs.
What is the genetic disorder that affects the lungs and pancreas?
Cystic fibrosis: A genetic disorder that affects multiple body systems, usually including the lungs and the pancreas. Digestive problems and diabetes often result. Pancreatic cancer: The pancreas has many different types of cells, each of which can give rise to a different type of tumor.
What does an abdominal ultrasound show?
Abdominal ultrasound: An abdominal ultrasound can detect gallstonesthat might block the outflow of fluid from the pancreas. It also can show an abscess or a pancreatic pseudocyst.
What are the two types of glands in the pancreas?
The pancreas is made up of 2 types of glands: Exocrine. The exocrine gland secretes digestive enzymes. These enzymes are secreted into a network of ducts that join the main pancreatic duct. This runs the length of the pancreas. Endocrine.
What are the functions of the pancreas?
Functions of the pancreas. The pancreas has digestive and hormonal functions: The enzymes secreted by the exocrine gland in the pancreas help break down carbohydrates, fats, proteins, and acids in the duodenum. These enzymes travel down the pancreatic duct into the bile duct in an inactive form.
Which hormones are secreted by the endocrine gland in the pancreas?
The main hormones secreted by the endocrine gland in the pancreas are insulin and glucagon, which regulate the level of glucose in the blood, and somatostatin, which prevents the release of insulin and glucagon.
Where do enzymes travel?
These enzymes travel down the pancreatic duct into the bile duct in an inactive form. When they enter the duodenum, they are activated. The exocrine tissue also secretes a bicarbonate to neutralize stomach acid in the duodenum. This is the first section of the small intestine.
Which side of the pancreas is the widest?
The right side of the organ—called the head—is the widest part of the organ and lies in the curve of the duodenum, the first division of the small intestine. The tapered left side extends slightly upward—called the body of the pancreas—and ends near the spleen—called the tail. The pancreas is made up of 2 types of glands:
What is the body part of the pancreas called?
It is shaped like a flat pear and is surrounded by the stomach, small intestine, liver, spleen and gallbladder. The wide end of the pancreas on the right side of the body is called the head. The middle sections are the neck and body. The thin end of the pancreas on the left side of the body is called the tail.
Which part of the pancreas is uncinate?
The uncinate process is the part of the gland that bends backwards and underneath the head of the pancreas. Two very important blood vessels, the superior mesenteric artery and superior mesenteric vein, cross behind the neck of the pancreas and in front of the uncinate process. The pancreas is both an exocrine gland and endocrine gland ...
What are the two hormones that are produced by the pancreas?
The two main pancreatic hormones are insulin and glucagon. Islet cells are endocrine cells within the pancreas that produce and secrete insulin and glucagon into the bloodstream. Insulin lowers blood sugar levels while glucagon raises blood sugar levels.
What is the name of the disease that starts when abnormal cells in the pancreas grow out of control and form?
Pancreatic cancer begins when abnormal cells in the pancreas grow out of control and form a tumor. The symptoms associated with pancreatic cancer are often vague, similar to symptoms caused by other conditions and may not be present in early stages of the disease.
What are the two main pancreatic hormones?
They are usually made in one part of the body and carried through the blood to take action on another part of the body. The two main pancreatic hormones are insulin and glucagon.
Is Pancan a substitute for medical advice?
Information provided by the Pancreatic Cancer Action Network, Inc. (“ PanCAN”) is not a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, treatment or other health care services. PanCAN may provide information to you about physicians, products, services, clinical trials or treatments related to pancreatic cancer, but PanCAN does not recommend ...
What is the pancreas?
The pancreas is a long flattened gland that has two functions: it is a vital part of the digestive system and a critical controller of blood sugar levels.
How to find the pancreas?
To visualize the position of the pancreas, try this: Touch your right thumb and right "pinkie" fingers together, keeping the other three fingers together and straight. Then, place your hand in the center of your belly just below your lower ribs with your fingers pointing to your left.
Why does pancreatic cancer cause jaundice?
This helps us understand why some people with pancreatic cancer develop jaundice, an abnormal yellowing of the skin and eyes. Pancreatic cancers in the head of the pancreas can block the bile duct, which blocks the bile from flowing out of the liver. The bile backs up and causes jaundice.
What is the yellow fluid in the pancreas?
Bile & Jaundice. Bile is a greenish-yellow fluid that aids in the digestion of fats in food. Bile is important to understand because the flow of bile (the green arrow in the illustration) is often blocked by pancreatic cancers and/or altered during surgery for pancreatic cancer.
What causes the brown arrow in the pancreas?
The flow of pancreatic fluid (the brown arrow in the illustration) is often blocked by tumors of the pancreas and/or altered by pancreatic surgery.
Where does bile go in the body?
Bile is produced by the liver and travels through the bile ducts to the gallbladder, where it is stored. The bile duct then passes through the pancreas on its way to the intestine. This helps us understand why some people with pancreatic cancer develop jaundice, an abnormal yellowing of the skin and eyes.
What is the thin section of the gland between the head and the body of the pancreas?
Neck - The neck is the thin section of the gland between the head and the body of the pancreas. Body - The body is the middle part of the pancreas between the neck and the tail. The superior mesenteric artery and vein run behind this part of the pancreas. Tail - The tail is the thin tip of the pancreas in the left side of the abdomen, ...
Overview
The pancreas is an organ in the back of your abdomen (belly). It is part of your digestive system.
Function
An exocrine gland runs the length of your pancreas. It produces enzymes that help to break down food (digestion). Your pancreas releases the following enzymes:
Anatomy
Your pancreas sits behind your stomach and in front of your spine. Your gallbladder, liver and spleen surround your pancreas.
Care
Maintaining a healthy weight. Regular exercise and avoiding weight gain can help prevent Type 2 diabetes and gallstones that can cause pancreatitis.
Frequently Asked Questions
If you have symptoms that don’t go away or keep coming back, you should talk to a healthcare provider. Signs of pancreas problems may include:
What is the neck of the pancreas?
The neck of the pancreas usually merges imperceptibly with the body and head. In general as we view the pancreas in the transverse plain, the neck is marked by point where the globular head thins out into the more rectangular shaped neck. Like the neck of most structures its overall size is less than the head and the body which it connects. It can however be short and fat or long and thin. Its stated range of A-P dimension is .8-2.5cms while its lenth is in the 1.5-2cms range
What is the most superior part of the pancreas?
This series of six images show a normal pancreas from superior to inferior. The tail being the most superior first comes into view, and then the body, head and finally the uncinate process. The duct is seen as a faint lucency in c. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 38031c01 code pancreas normal code pancreas normal anatomy
What is diffuse enlargement of the gland on the CT scan through the abdomen?
This diffuse enlargement of the gland on the CT scan through the abdomen is secondary to enlarged pancreatic lymph nodes in this patient with metatstattic Merkel cell tumor. Note the enlarged venous collateral anterior to the pancreas, the focal filling defect in the splenic vein both suggesting the occlusion or high grade stenosis of the splenic vein. 22322 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
What is the red arrow on the pancreas?
There are two normal narrowings that may be seen. The first (red arrow) is the normal constriction of the pancreatic duct sphincter. The second is sometimes seen in the neck at the junction of the dorsal and ventral components of the duct (black arrow). 41394size002b04L Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
Why is the pancreas thinning?
Diffuse thinning of the gland is more common than diffuse enlargement. Overall volume loss of the gland is usually caused by aging, chronic pancreatitis, or by an obstructed pancreatic duct. Diffuse enlargement of the gland may be caused by acute pancreatitis, lymphoma and and metastasis to the gland. Less common diseases such as von Hippel Lindau, hemangioma, Merckl cell tumor, sarcomas, and VIPOMAS are usually associated with unusual contour deformities and heterogeneous morphology of the gland. There is an unusual disease called pseudohypertrophy
Is the pancreas smooth or smooth?
When the pancreas is young, the surface of the pancreas is relatively smooth. As it ages the earliest signs of volume loss is development of a nodular shape of the surface. Thus the shape deformity reflects an involutional process and assessment of the shape gives insight into the size and approximate age of the gland.
How long is the pancreas?
Length 12-15 cm in length. In young patients, the body or the tail may be larger than the head, whereas in people over 40 the head assumes larger proportions than the body and tail. When the pancreas is young, the surface of the pancreas is relatively smooth. As it ages the earliest signs of volume loss is development of a nodular shape ...
Where is the pancreas located?
The head of the pancreas lies lateral to the neck, nestled in the C-loop of the duodenum. In this area it lies anterior to the inferior vena cava and right crus of the diaphragm. The inferomedial portion of the head is called the uncinate process, which varies greatly in size.
What is the color of the pancreas in a CT scan?
The CT scan through the abdomen in this case shows a dilated duct, atrophied pancreas (pink), and a stent in the CBD. In this case pancreatic carcinoma caused obstruction of the duct with secondary atrophy of the gland.. 16312c Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
What is the red arrow on the pancreas?
There are two normal narrowings that may be seen. The first (red arrow) is the normal constriction of the pancreatic duct sphincter. The second is sometimes seen in the neck at the junction of the dorsal and ventral components of the duct (black arrow). 41394size002b04L Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
Why is the pancreas thinning?
Diffuse thinning of the gland is more common than diffuse enlargement. Overall volume loss of the gland is usually caused by aging, chronic pancreatitis, or by an obstructed pancreatic duct. Diffuse enlargement of the gland may be caused by acute pancreatitis, lymphoma and and metastasis to the gland. Less common diseases such as von Hippel Lindau, hemangioma, Merckl cell tumor, sarcomas, and VIPOMAS are usually associated with unusual contour deformities and heterogeneous morphology of the gland. There is an unusual disease called pseudohypertrophy
What is diffuse enlargement of the gland on the CT scan through the abdomen?
This diffuse enlargement of the gland on the CT scan through the abdomen is secondary to enlarged pancreatic lymph nodes in this patient with metatstattic Merkel cell tumor. Note the enlarged venous collateral anterior to the pancreas, the focal filling defect in the splenic vein both suggesting the occlusion or high grade stenosis of the splenic vein. 22322 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
What is the most superior part of the pancreas?
This series of six images show a normal pancreas from superior to inferior. The tail being the most superior first comes into view, and then the body, head and finally the uncinate process. The duct is seen as a faint lucency in c. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 38031c01 code pancreas normal code pancreas normal anatomy
What is the pancreas made of?
The pancreas with surrounding vessels and organs. Almost all of the pancreas (95%) consists of exocrine tissue that produces pancreatic enzymes for digestion. The remaining tissue consists of endocrine cells called islets of Langerhans. These clusters of cells look like grapes and produce hormones that regulate blood sugar ...
Where is the pancreas located?
The pancreas is located behind the stomach in the upper left abdomen. It is surrounded by other organs including the small intestine, liver, and spleen. It is spongy, about six to ten inches long, and is shaped like a flat pear or a fish extended horizontally across the abdomen. The wide part, called the head of the pancreas, ...
What is the function of the pancreas?
The pancreas has two main functions: an exocrine function that helps in digestion and an endocrine function that regulates blood sugar.
What is the most common form of pancreatic cancer?
Pancreatic Cancer. The most common form of pancreatic cancer is pancreatic adenocarcinoma, an exocrine tumor arising from the cells lining the pancreatic duct. A far less common form, endocrine tumors, account for less than 5% of all pancreatic tumors and are sometimes referred to as neuroendocrine or islet cell tumors.
What are the diseases of the pancreas?
Diseases of the Pancreas. Disorders affecting the pancreas include pancreatitis, precancerous conditions such as PanIN and IPMN, and pancreatic cancer. Each disorder may exhibit different symptoms and requires different treatments.
What is the term for inflammation of the pancreas?
Pancreatitis. Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas that occurs when pancreatic enzyme secretions build up and begin to digest the organ itself. It can occur as acute painful attacks lasting a matter of days, or it may be a chronic condition that progresses over a period of years.
What is the number to the Pancreas Center?
Whether you need a diagnosis, treatment, or a second opinion, we have an entire team of experts ready to help. Call us at (212) 305-9467 or use our online form to get in touch today. Pancreatic Cancer Care Program.