
What are the characteristics of sclerenchyma?
(1) The cells are heavily thickened with lignified walls, simple pits and small lumen. (2) The cells are dead without protoplasm. (3) The cell walls with very low water content. (4) Their shapes and sizes vary. The sclerenchyma give rigidity and mechanical strength to plant organs.
What are the two types of cell walls in sclerenchyma?
Sclerenchyma cells possess two types of cell walls: primary and secondary walls. The secondary wall is very thick and highly lignified (15%–35%) and imparts a great rigidity and hardness to the cell and tissue. There are two main types of sclerenchyma cells: fibers and sclereids.
What is collenchyma and sclerenchyma made of?
Collenchyma is made up of unevenly thickened cell wall with more thickenings at the corners and composed of pectin and other substances. Sclerenchyma is made up of a thick and rigid cell wall composed of lignin and other substances.
Where is sclerenchyma found in xylem?
In the component of the xylem, xylem fiber is non-living sclerenchyma cells and they lose their protoplast at their maturity. In the xylem tissue, sclerenchyma cells are found in between the tracheids and the xylem vessels. 2. Is Sclerenchyma living or dead?
What is the shape of sclerenchyma Class 9?
Sclereids are short, isodiametric or irregular in shape. Their characteristics are: They may be spherical, oval or cylindrical. They are often dead and have highly thickened cell walls.
What are the sclerenchyma cells?
Sclerenchyma is a plant tissue providing mechanical stiffness and strength. Fibres and sclereids are the main types of sclerenchyma cells. Most sclerenchyma cells show intrusive growth. The cell walls of sclerenchyma have thickened secondary layers made from cellulose, hemicelluloses and lignin.
What are the characteristics of sclerenchyma cells?
Mature sclerenchyma cells are usually dead cells that have heavily thickened secondary walls containing lignin. The cells are rigid and nonstretchable and are usually found in nongrowing regions of plant bodies, such as the bark or mature stems.
What is the shape of the Collenchyma?
Collenchyma Characteristics The cells are mostly elongated, spherical, oval or polygonal in shape. Cells are alive at maturity. They contain a primary cell wall. The primary cell wall is unevenly thickened and mostly thickened at the corners.
What is sclerenchyma simple?
Definition of sclerenchyma : a protective or supporting tissue in higher plants composed of cells with walls thickened and often lignified.
Is sclerenchyma a simple tissue?
Sclerenchyma is a simple permanent tissue with thick secondary lignified cell walls.
What are the structure of sclerenchyma?
Sclerenchyma tissue, when mature, is composed of dead cells that have heavily thickened walls containing lignin and a high cellulose content (60%–80%), and serves the function of providing structural support in plants. Sclerenchyma cells possess two types of cell walls: primary and secondary walls.
How do you say sclerenchyma?
0:051:01How To Say Sclerenchyma - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipEs clarísima es clarísima es club íntimo es clave íntima. Esq la víctima es clarísima.MoreEs clarísima es clarísima es club íntimo es clave íntima. Esq la víctima es clarísima.
Does sclerenchyma have cell wall?
Sclerenchyma tissues are mainly composed of dead cells. They have a heavily thickened wall. The composition of lignin and high cellulose content (60 to 80 percent). It also serves the function of providing structural support in plants.
What is the difference between collenchyma and sclerenchyma?
Collenchyma cells consist of unevenly thick cell walls. They contain vacuolated protoplasts and are absent in monocots. Sclerenchyma cells are dead cells at their maturity, containing the thickest cell walls. They are specialized cells found in mature parts of the plant body.
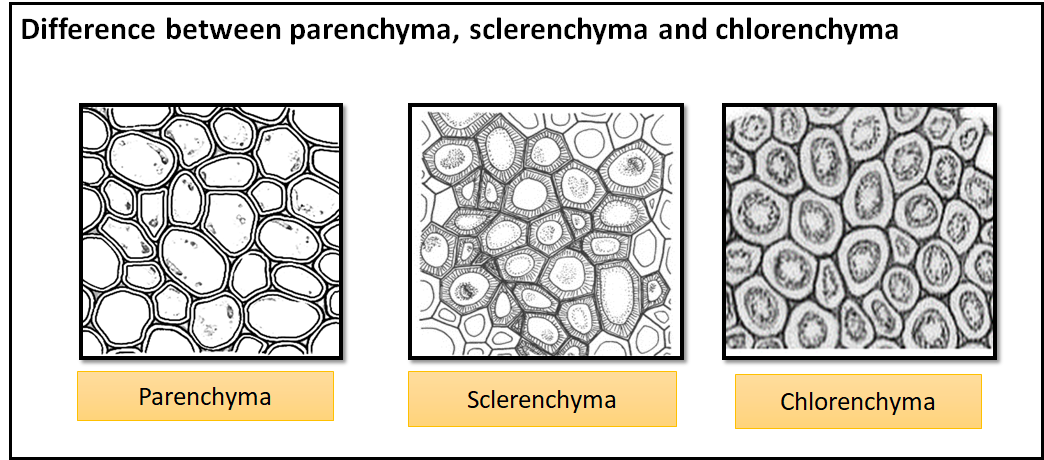
What is the difference between parenchyma and sclerenchyma?
Sclerenchyma is a type of permanent tissue....ParenchymaSclerenchymaCells are usually loosely packed with large intercellular spaces.There are no intercellular spaces between the cells.Stores nutrients and water in stems and rootsProvides strength to the parts of the plant.3 more rows
What is difference between parenchyma collenchyma and sclerenchyma?
The main difference between parenchyma collenchyma and sclerenchyma is that parenchyma cells are involved in photosynthesis, storage, and secretion, while collenchyma cells are involved in support and transportation of nutrients and sclerenchyma cells are involved in the support, protection, and transportation of water ...
What is the main function of sclerenchyma?
This tissue provides mechanical strength to the stem.
What is collenchyma and sclerenchyma?
Collenchyma cells are the least common plant cell type. They have a primary cell wall and provide support in herbaceous or temporary organs such as petioles and leaves. Sclerenchyma cells have a lignified and strong secondary cell wall and are usually dead at maturity.
What are collenchyma cells?
Collenchyma cells are elongated, living cells that occur especially in peripheral positions in leaves and stems of eudicotyledons where they provide mechanical support while they are still growing [1,2,3]. At maturity, the cell walls are thick and usually non-lignified, with the thickening often unevenly distributed.
Why are sclerenchyma cells so hard?
Sclerenchyma tissue possesses long, narrow cells with thickened walls. They possess secondary walls made of lignin. Lignin is a chemical substance, which acts as cement and hardens them.
What are the main functions of sclerenchyma?
Sclerenchyma tissue functions mainly to add structural support to a plant. It strengthens and allows the parts of a plant to maintain their shape a...
Why is sclerenchyma important for a plant?
Sclerenchyma cells are important as structural, strengthening, and support tissues. These tough cells help a plant maintain its position, shape, an...
What is the example of sclerenchyma?
Because sclerenchyma is a type of cellular tissue that results from dying parenchyma cells, examples are often seen in maturing trees. The young gr...
What is a sclerenchyma?
Sclerenchyma, in plants, support tissue composed of any of various kinds of hard woody cells. Mature sclerenchyma cells are usually dead and have thick secondary cell walls. They are commonly found as fibers or sclereids in nongrowing regions of plant bodies, such as in seed coats, bark, or vascular bundles. Sclerenchyma, in plants, support tissue ...
Where are mature sclerenchyma cells found?
The cells are rigid and nonstretchable and are usually found in nongrowing regions of plant bodies, such as the barkor mature stems. Sclerenchyma is one of the three types of ground, or fundamental, tissue in plants;
What are the two types of sclereids?
Sclerenchyma cells occur in many different shapes and sizes, but two main types occur: fibres and sclereids. ground tissue. The three types of ground, or fundamental, tissue in plants. Parenchyma tissue is composed of thin-walled cells and makes up the photosynthetic tissue in leaves, the pulp of fruits, and the endosperm of many seeds.
What type of cell is found in nuts?
The hard shells of many nuts contain sclereids, which are a type of sclerenchyma cell.
Where are sclerids found?
Sclereidsare extremely variable in shape and are present in various tissues of the plant, such as the periderm, cortex, pith, xylem, and phloem. They also occur in leaves and fruits and constitutethe hard shell of nutsand the outer hard coat of many seeds. Sometimes known as stone cells, sclereids are also responsible for the gritty texture of pearsand guavas.
What are the three types of ground tissue in plants?
The three types of ground, or fundamental, tissue in plants. Parenchyma tissue is composed of thin-walled cells and makes up the photosynthetic tissue in leaves, the pulp of fruits, and the endosperm of many seeds. Collenchyma cells mainly form supporting tissue and have irregular cell walls. They are found mainly in the cortex of stems and in leaves. The major function of sclerenchyma is support. Unlike collenchyma, mature cells of this tissue are generally dead and have thick walls containing lignin. Their size, shape, and structure vary greatly.
Sclerenchyma Cells
Imagine the process of a seed growing into a plant. After germination, a small sprout starts to poke its way through the soil. With adequate light, water, and nutrients, the plant begins to grow more and more, getting a little bit taller with each passing day. As it grows, it must overcome the challenges imposed on it by gravity.
Sclerenchyma Function
Plant tissues can be grouped into different types based on their function and structure. Three common classifications include sclerenchyma, parenchyma, and collenchyma tissue. Parenchyma cells are the most abundant and compose the majority of plant tissue.
Sclerenchyma Type: Fibers
There are two main types of sclerenchyma tissue. Sclerenchyma fibers are a type of sclerenchyma cell that is highly versatile, often found in nearly all parts of the plant. Examples of locations with sclerenchyma tissue include:
What is a sclerenchyma?
Sclerenchyma. Sclerenchyma is a tissue with two interrelated cell types: sclerenchyma fibers, or just fibers, and sclereids or stone cells. From: Encyclopedia of Applied Plant Sciences (Second Edition), 2017. Download as PDF. About this page.
What makes a sclerenchyma cell strong?
Sclerenchyma cells have thickened lignified walls, which make them strong and waterproof. They are commonly classified into support types and conducting forms.
Which monomers are involved in the formation of lignin?
Besides the classical p -hydroxyphenyl, guaiacyl and syringyl monomers, other molecules may participate in the formation of the lignin polymer, the so-called non-canonical subunits. These include ferulates, hydroxycinnamaldehydes (coniferaldehyde and sinapaldehyde), dihydrocinnamyl alcohols, and variously acylated monolignols ( Ralph et al., 2004, 2008; Sederoff et al., 1999 ), the presence and quantity of which is usually related to different taxa.
What are the conducting types of sclerenchyma?
The conducting types of sclerenchyma are the tracheids and vessel elements of the xylem, the tracheary elements of plants.
How do bundle sheaths form?
The bundle sheath may form bundle sheath extensions by spreading to the epidermis, especially in grass leaves. Sclereids are roughly isodiametric, and clumps of these “stone cells” (brachysclereids) give the Bartlett pear ( Pyrus communis) its distinctive grittiness.
How many nuclei are in a cell?
Up to 25–30 nuclei can be observed within one cell. Although bast fibers constitute around 6–7% of the total cell number seen in a stem cross-section, they contribute 30% of the stem's dry mass owing to the enormous development of their cell walls.
Which cell wall contains the most lignin?
The amount and composition of lignin also varies in the cell wall itself. It has been reported that the middle lamella has a greater quantity of lignin than the primary and secondary cell wall. In angiosperms, the middle lamella contains 50–70% lignin, while the secondary cell wall contains 20% lignin.
Where are sclerenchyma found?
Sclerenchyma tissues are located in several areas. E.g. Sclereids are found in the shells of nuts, stones of fruits and fibres are abundant ly found in the inner bark, wood, leaf veins, etc.
What is the function of sclerenchyma?
The main function of sclerenchyma is to provide mechanical support and strength to the plants.
What is a sclerid?
Sclereids are short, isodiametric or irregular in shape. Their characteristics are:
How many types of sclereids are there?
There are six types of sclereids found. They are:
What is a type of permanent tissue found in plants?
Sclerenchyma is a type of permanent tissue found in plants. Permanent tissues lose the power of cell division. They attain a definite shape, size and function. Sclerenchyma is a type of simple permanent tissue. Simple tissues are made up of a group of uniform cells having similar structures and perform the same function.
Why is the secondary cell wall thickened?
The secondary cell wall is highly thickened and has pits to allow the exchange of substances.
Where are osteosclereids found?
Osteosclereids – They are also called bone cells. They have rounded ends and are found in leaves and seed coats. It forms the hypodermal layer of many seeds, fruits and leaves of some xerophytes.
How many types of sclerenchyma are there?
Depending on the nature, there are 3 types of sclerenchyma fibres, which are as follows :
Where does sclerenchyma come from?
Origin : They originate from all the three types of meristematic tissues like protoderm, procambium and ground meristem. They may also be formed from the fusiform initials of cambium.
How many different sclereids are there?
Depending on the nature, structure and form of cell walls, five different sclereids are found, which are : (i) Macrosclereids: Elongated rod shaped sclereids forming a palisade like layer n the epidermis of seed coat e.g. pea and pulses.
What is the permanent tissue consisting of evenly thick-walled dead cells called?
The permanent simple tissue consisting of evenly thick-walled dead cells are named sclerenchyma. They are very hard and heavily lignified in nature.
What is the structure of fibers?
Structure of Fibres : (i) Fibres are elongated with tapering ends, (ii) They normally occur in a group. (iii) They are very long, narrow and with pointed ends, the length may be upto 55 cm. (iv) The lumen is very thin due to uniformly thickened, lignified walls. (v) The T.S. of the fibreslook angular.
Where does sclerenchyma originate?
Sclerenchyma originates from protoderm pro-cambium and ground meristem.
What is the cell wall of a collenchyma?
Collenchyma cells’ cell wall is made up of pectin and hemicelluloses. Collenchyma cells have little space between cells. Collenchyma consists of living cells at maturity. Collenchyma cells make up the epidermal layers. Collenchyma cells originate from pro-cambium like cells in the ground meristem.
What is Parenchyma?
Parenchyma is a tissue composed of living cells, usually having only thin primary cell walls and varying widely by morphology and metabolism. Parenchyma in the primary plant body often occurs as a continuous mass, such as in the cortex or pith of stems, roots, mesophyll and flesh of fruits. The common characteristic of all parenchyma cells is that they are living at maturity and capable of cell division, making them plays an important role in wound healing and tissue regeneration.
What is the name of the tissue that forms cylinders?
Collenchyma may form cylinders or occur as discrete strands and is one of the three ground or fundamental, tissues in plants, together with parenchyma (living thin-walled tissue) and sclerenchyma (dead supportive tissue with thick cell walls).
What is the difference between parenchyma and collenchyma?
Parenchyma is a tissue composed of living cells , usually having only thin primary cell walls and varying widely by morphology and metabolism. Collenchymas are plant tissues that consist of living elongated cells with unevenly thickened walls and acts as support especially in areas of primary growth.
What is collenchyma tissue?
Collenchyma is a tissue composed of elongated cells with irregular thick cell walls that provide support and structure. These cells are often found under epidermis or the outer layer of cells in young stems and in leaf veins. In plants with secondary growth, the collenchyma tissue is only temporarily functional and becomes crushed as woody tissue develops.
What is the cell wall of a plant called?
What You Need To Know About Parenchyma. Parenchyma cells are thin-walled cells that make up the inside of non-woody plant structures including stems, roots and leaves. Parenchyma is made up of cells having very thin cell wall that is uniformly thickened. Parenchyma cells are found in every soft part of the plant like leaves, fruits, bark, flowers, ...
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/sclerenchyma_cells-5a7e05e5ff1b780037b2ced8.jpg)
Sclerenchyma Characteristics
- It is a supportive tissue and is usually made up of dead cells with highly thickened lignified walls. It is mostly present in the mature parts of the plant. 1. It is made up of long and narrow cells. 2. Cells are usually dead without protoplasts. 3. The cell wall is thick and lignified with a few or numerous pits. 4. They possess both primary and s...
Types of Sclerenchyma
- Sclerenchyma is classified into two types based on their structure, origin and development. They are sclereids and fibres.
Sclereids
- Sclereids are short, isodiametric or irregular in shape. Their characteristics are: 1. They may be spherical, oval or cylindrical. 2. They are often dead and have highly thickened cell walls. 3. Sclereids have very narrow cavities and are hard and inflexible. 4. They have more pits than fibres. 5. They are commonly found in soft tissues, e.g. cortex, phloem, the pulp of fleshy fruits, f…
Fibres
- Fibres are elongated, needle-like pointed sclerenchyma cells. Their important characteristics are: 1. They are long and tapered at the end. 2. They are the longest cells found in higher plants. They can be as long as 1-8 mm in length. 3. They are often found in groups or clumps or patches. 4. They are often dead at maturity and lack a nucleus and cytoplasm. 5. They contain thick second…
Sclerenchyma Function
- The main function of sclerenchyma is to provide mechanical support and strength to the plants. 1. They provide structural support to the plant organs. 2. They form protective coverings around nuts and seeds. 3. They are also a part of vascular bundles and form conductive tissues. 4. The xylem vessels and tracheids are sclerenchymatous cells. 5. They form the hypodermis of some xeroph…