What is the arrangement and cell morphology of Staphylococcus?
Staphylococcus: Streptococcus: 1: Arrangement: Grape-like clusters. A chain of round cells. 2: Division: Staphylococci divide in various directions (multiple axes). Division occurs in one linear direction (single axis). 3: Catalase Test: Positive (Catalase is an enzyme to converts hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen gas). Negative: 4 ...
What is the size of Staphylococcus aureus?
morphology of staphylococcus aureus. Shape – Round shape (cocci) Size – 1 micron (diameter) Arrangement of cells – Grape-like clusters; Motility – Non-motile; Flagella – Non-flagellated; Spores – Non-sporing; Capsule – present in some strains; Gram Staining reaction – Gram +ve; CULTURE REQUIREMENTS OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS
What is the shape and arrangement of S. aureus?
When viewed under the microscope, staphylococcus (e.g. S. aureus) will appear as small spherical bodies that form grape-like clusters which are purple or bluish in color. This is because their thick peptidoglycan allows them to retain the primary stain.
What are the diseases caused by Staphylococcus aureus?
Symptoms
- Skin infections. The most common type of staph infection is the boil, a pocket of pus that develops in a hair follicle or oil gland.
- Food poisoning. Staph bacteria are one of the most common causes of food poisoning. ...
- Bacteremia. ...
- Toxic shock syndrome. ...
- Septic arthritis. ...
- When to see a doctor. ...
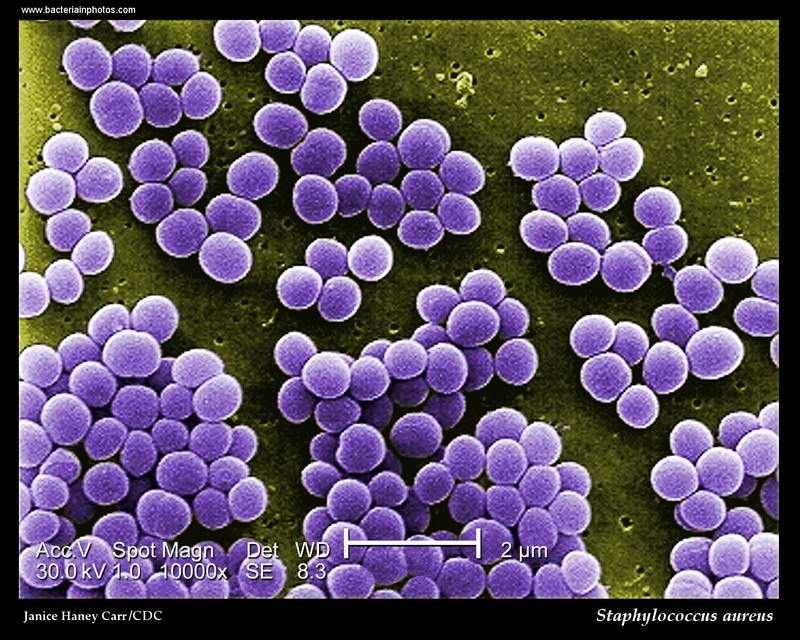
What is staphylococcus bacteria shape?
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria are pathogens to both man and other mammals. They are gram positive bacteria that are small round in shape (cocci) and occur as clusters appearing like a bunch of grapes on electron microscopy.
What is the shape of Staphylococcus aureus?
S. aureus cells are Gram-positive and appear in spherical shape. They are often in clusters resembling bunch of grapes when observed under light microscope after Gram staining.
What is the shape and size of Staphylococcus?
Staphylococci are Gram-positive cocci about 0.5 – 1.0 μm in diameter. They grow in clusters, pairs and occasionally in short chains. The clusters arise because staphylococci divide in two planes.
What does staphylococci look like?
Staph infection MRSA infections start out as small red bumps that can quickly turn into deep, painful abscesses. Staph skin infections, including MRSA , generally start as swollen, painful red bumps that might look like pimples or spider bites. The affected area might be: Warm to the touch.
What is the Colour of Staphylococcus?
STAPHYLOCOCCI - BLOOD AGAR CULTURE On blood agar, S. aureus usually displays a light to golden yellow pigment, whereas S. epidermidis has a white pigment and S. saprophyticus either a bright yellow or white pigment.
What are the characteristics of Staphylococcus?
Characteristics. Staphylococci are Gram-positive, nonspore forming, facultatively anaerobic, nonmotile, catalase-positive or negative, small, spherical bacteria from pairs to, grape-like clusters, from where the name Staphylococcus comes from (staphyle, meaning a bunch of grapes, and kokkos, meaning berry).
Which is a rod-shaped bacteria?
Bacilli are rod-shaped bacteria. Bacilli all divide in one plane producing a bacillus, streptobacillus, or coccobacillus arrangement (see Figure 2.1.
What is the general shape of bacteria?
There are three basic shapes of bacteria: coccus, bacillus, and spiral.
What are the basic shapes of bacteria?
Individual bacteria can assume one of three basic shapes: spherical (coccus), rodlike (bacillus), or curved (vibrio, spirillum, or spirochete).
How do you differentiate between Staphylococcus and streptococcus?
Staphylococci and Streptococci are grouped as Gram-positive cocci. Staphylococci form clumps, whereas Streptococci grow in chains. They can be discriminated by catalase test because Staphylococci have the capability to produce catalase [2].
How do you say staphylococci?
0:120:44How to Pronounce Staphylococci? (CORRECTLY) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipHow do you say it staphylococci you do want to stress on that fourth. Car syllable.MoreHow do you say it staphylococci you do want to stress on that fourth. Car syllable.
Where is Staphylococcus found?
Staphylococcus aureus is a bacterium that causes staphylococcal food poisoning, a form of gastroenteritis with rapid onset of symptoms. S. aureus is commonly found in the environment (soil, water and air) and is also found in the nose and on the skin of humans.
Is Staph aureus Gram-positive cocci?
Gram-positive cocci: Staphylococcus aureus is a gram-positive, catalase-positive, coagulase-positive cocci in clusters. S. aureus can cause inflammatory diseases, including skin infections, pneumonia, endocarditis, septic arthritis, osteomyelitis, and abscesses.
What is the size of Staphylococcus aureus?
approximately 0.5-1.5 µmCHARACTERISTICS: Staphylococcus aureus are Gram-positive, catalase positive cocci belonging to the Staphylococcaceae family 1, 2. They are approximately 0.5-1.5 µm in diameter, nonmotile, non-spore-forming, facultative anaerobes (with the exception of S. aureus anaerobius) that usually form in clusters.
What is the shape and arrangement of Streptococcus bacteria?
So far as the arrangement is concerned, it may Paired (diplo), Grape-like clusters (staphylo) or Chains (strepto). In shape they may principally be Rods (bacilli), Spheres (cocci), and Spirals (spirillum).
What does Staphylococcus look like under a microscope?
Staphylococcus aureus is a facultative anaerobe, Gram-positive, nonmotile, non-spore-forming coccus. When looking at this organism under a microscope it appears to be in clusters that look like grapes. The round colonies appear to be golden in color hence the origin of the name aureus in Latin means “golden.”
What is the role of GpsB in Staphylococcus aureus?
Based on various studies, this process in Staphylococcus aureus has been shown to be under the control of GpsB (an essential protein). Here, GpsB is suggested to interact with FtsZ (an important component of cell division machinery in bacteria) increasing its GTPase activity.
Why are staph bacteria so problematic?
This is one of the reasons Staphylococci species are very problematic in clinical settings where they infect medical devices and various surfaces etc.
What are some examples of staphyococcus?
Common examples of Staphylococcus bacteria include: Staphylococcus aureus. Staphylococcus epidermidis.
How do Staphylococcus aureus cells reproduce?
Reproduction and life cycle (Staphylococcus aureus) Like many other bacteria, Staphylococci bacteria divide through binary fission. While this process produces two daughter cells, they do remain attached to one another which eventually results in clustering.
What is the name of the bacteria that resembles grapes?
Unlike other cocci bacteria that may exist as single cells or in pairs etc, Staphylococcus occurs in clusters and thus resemble grape-like clusters. In these clusters, individual cells may vary in size.
What is the cell wall of bacteria?
Cell Wall. For the majority of bacteria, the cell is surrounded by a cell wall. This cell wall is composed of peptidoglycan and teichoic acid in Staphylococcus (which are also used to distinguish different Staphylococcus species).
What is the classification of Staphylococcus?
Classification of Staphylococcus. Domain: Bacteria - Single-celled prokaryotes widely distributed in every environment across the world. They exist as parasites or as free-living organisms with some of the species being beneficial to man. Phylum: Firmicutes - The phylum Firmicutes consists of many Gram-positive bacteria with a few species ...
What is the most pathogenic organism in the genus Staphylococcus?
Bacteria in the genus Staphylococcus are pathogens of man and other mammals. Traditionally they were divided into two groups on the basis of their ability to clot blood plasma (the coagulase reaction). The coagulase-positive staphylococci constitute the most pathogenic species S aureus.
What is NCBI bookshelf?
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Is coagulase a virulence factor?
Coagulase is a marker for S aureus but there is no direct evidence that it is a virulence factor. Also, some natural isolates of S aureus are defective in coagulase. Nevertheless, the term is still in widespread use among clinical microbiologists.
Which is the most pathogenic species?
The coagulase-positive staphylococci constitute the most pathogenic species S aureus. The coagulase-negative staphylococci (CNS) are now known to comprise over 30 other species. The CNS are common commensals of skin, although some species can cause infections.
What is the color of a staph?
Staphylococcus aureus is Gram-positive bacteria (stain purple by Gram stain) that are cocci-shaped and tend to be arranged in clusters that are described as “grape-like.” On media, these organisms can grow in up to 10% salt, and colonies are often golden or yellow (aureus means golden or yellow). These organisms can grow aerobically or anaerobically (facultative) and at temperatures between 18 C and 40 C. Typical biochemical identification tests include catalase positive (all pathogenic Staphylococcusspecies), coagulase positive (to distinguish Staphylococcus aureusfrom other Staphylococcusspecies), novobiocin sensitive (to distinguish from Staphylococcus saprophyticus), and mannitol fermentation positive (to distinguish from Staphylococcus epidermidis). [4][1] MRSA strains carry a mecgene on the bacterial chromosome, which is a component of the larger Staphylococcal chromosomal cassette mec(SCCmec) region, conferring resistance to multiple antibiotics depending on the SCCmectype.[2] The mecgene encodes the protein PBP-2a (penicillin-binding protein 2a). PBP-2a is a penicillin-binding protein (PBP), or essential bacterial cell wall enzyme that catalyzes the production of the peptidoglycan in the bacterial cell wall. PBP-2A has a lower affinity to bind to beta-lactams (and other penicillin-derived antibiotics) when compared to other PBPs, so PBP-2A continues to catalyze the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall even in the presence of many antibiotics. As a result, S. aureusstrains that synthesize PBP-2A can grow in the presence of many antibiotics, and these MRSA strains are resistant to many antibiotics. MRSA strains tend to be resistant to methicillin, nafcillin, oxacillin, and cephalosporins. [2][4]
What is Staphylococcus aureus?
Last Update: August 23, 2020. Continuing Education Activity. Staphylococcus aureus is a gram-positive bacteria that cause a wide variety of clinical diseases. Infections caused by this pathogen are common both in community-acquired and hospital-acquired settings. The treatment remains challenging due to the emergence of multi-drug resistant strains ...
What are the most common infections caused by S. aureus?
aureusare one the most common bacterial infections in humans and are the causative agents of multiple human infections, including bacteremia, infective endocarditis, skin and soft tissue infections (e.g., impetigo, folliculitis, furuncles, carbuncles, cellulitis, scalded skin syndrome, and others), osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, prosthetic device infections, pulmonary infections (e.g., pneumonia and empyema), gastroenteritis, meningitis, toxic shock syndrome, and urinary tract infections.[6] Depending on the strains involved and the site of infection, these bacteria can cause invasive infections and/or toxin-mediated diseases. [6][7] The pathophysiology varies greatly depending on the type of S. aureusinfection.[6] Mechanisms for evasion of the host immune response include the production of an antiphagocytic capsule, sequestering of host antibodies or antigen masking by Protein A, biofilm formation, intracellular survival, and blocking chemotaxis of leukocytes. [8][7] Binding of the bacteria to extracellular matrix proteins and fibronectin in infectious endocarditis is mediated by bacterial cell wall-associated proteins such as fibrinogen-binding proteins, clumping factors, and teichoic acids.[7] Also, Staphylococcal superantigens (TSST-1 or toxic shock syndrome toxin 1) are important virulence factors in infectious endocarditis, sepsis, as well as toxic shock syndrome. [9][10] Pneumonia infections are associated with the bacterial production of PVL (Panton-Valentine leukocidin), Protein A, and alpha-hemolysin, and infections are more common following influenza virus infection as well as a diagnosis of Cystic Fibrosis. Prosthetic device infections are often mediated by the ability of S. aureusstrains to form biofilms as well as communicate using quorum sensing in a bacterial cell density-dependent manner. [11]
How to prevent S. aureus infection?
Prevention of S. aureusinfections remains challenging. Despite many efforts, a routine vaccination for S. aureusinfections has remained elusive. As a result, efforts have relied on infection control methods such as hospital decontamination procedures, handwashing techniques, and MRSA transmission prevention guidelines. Topical antimicrobials such as mupirocin can be used to eliminate nasal colonization in some nasal carriers. However, usage is controversial.
How long does it take to treat S. aureus?
When prescribing antibiotics, one should limit the duration to no more than 7 to 10 days for most infections. The reason is that the empirical prescription of antibiotics has led to the development of resistant strains. Pharmacists should coordinate with the clinician to target antimicrobial therapy, and nursing can chart the progress so modification to the regimen can be made if treatment is ineffective. This kind of interprofessional coordination is necessary to treat such infections with precision.
How to diagnose S. aureus?
In many cases, routine cultures will reveal the diagnosis (i.e.,blood, sputum); however, RT-PCR (real-time PCR) for 16S rRNA genes may be necessary in some cases. Drug susceptibility testing often is required to guide treatment. If patient samples are collected for pathogen identification in the microbiology laboratory, caution must be exercised as the presence of S. aureusin the skin or mucous membrane does not necessarily indicate infection because these organisms are frequently members of the normal flora. [4]
Why should patients be educated about hand hygiene?
In addition, the patient should be educated by an interprofessional team of nurses and physicians about hand hygiene to help prevent transmission of infection to others.

Overview
Classification of Staphylococcus
- Domain: Bacteria - Single-celled prokaryoteswidely distributed in every environment across the world. They exist as parasites or as free-living organisms with some of the species being beneficial to man. Phylum: Firmicutes - The phylum Firmicutes consists of many Gram-positive bacteriawith a few species exhibiting Gram-negative properties. They also produce inactive spor…
Distribution and Ecology
- Members of the genus Staphylococcus are distributed worldwide and can be found wherever human beings and other warm-blooded animals exist. Early on, researchers noticed that Staphylococcus bacteria are often found in association with other organisms (particularly warm-blooded organisms). This led to the conclusion that mammalian skin acts as the major habitat o…
General Morphology and Cell Structure
- As the name suggests, Staphylococcus bacteria have a spherical shape (cocci). Unlike other cocci bacteria that may exist as single cells or in pairs etc, Staphylococcus occurs in clusters and thus resemble grape-like clusters. In these clusters, individual cells may vary in size. However, this variation has also been detected between different spec...
Cell Wall
- For the majority of bacteria, the cell is surrounded by a cell wall. This cell wall is composed of peptidoglycan and teichoic acid in Staphylococcus (which are also used to distinguish different Staphylococcus species). While peptidoglycan type L-Lys-GlY5-6 is found in several Staphylococci (Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus hycus, and Staphylococcus cohnii etc), the compositio…
Reproduction and Life Cycle
- Like many other bacteria, Staphylococci bacteria divide through binary fission. While this process produces two daughter cells, they do remain attached to one another which eventually results in clustering. Based on various studies, this process in Staphylococcus aureus has been shown to be under the control of GpsB (an essential protein). Here, GpsB is suggested to interact with Fts…
Nutritional Adaptations
- Staphylococci species have been shown to circulate between various nutrient-limiting environments including terrestrial habitats and host species among others. In the event of limited nutrients, they persist on given environs for a long time which allows them to survive until conditions improve. For instance, when Staphylococcus aureus are grown in a glucose-limiting …
Pathogenesis
- Although a good number of Staphylococci bacteria exist as commensals on various regions of the body, they can cause various infections some of which can be fatal if untreated. Depending on the conditions, these infections may be a result of a mechanical breach in the skin/mucosal barriers or as a result of toxins produced by the bacteria. Given that they frequently present on the skin a…
Culture and Microscopy
- Using culture media, it is possible to isolate and maintain pure cultures of a given organism. This also makes it possible to determine whether a given microorganismof interest is present in a sample. Blood agar is commonly used as a differential and enriched medium to culture Staphylococci bacteria. Here, blood is used as the enrichment ingredient for cultivating fastidiou…
Requirements
- Sample
- Glass slide
- Crystal violet
- Safranin