Skeletal muscle cells, a striated
Striated muscle tissue
Striated muscle tissue is a muscle tissue that features repeating functional units called sarcomeres. The presence of sarcomeres manifests as a series of bands visible along the muscle fibers, which is responsible for the striated appearance observed in microscopic images of t…
What are the 4 main functions of skeletal muscle?
- Support : It provides a framework to support the organs and tissues of the body.
- Protection: It protects our internal organs.
- Movement: It provides a framework for muscles to attach.
What are the cells in large skeletal muscles called?
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is a type of sarcoma made up of cells that normally develop into skeletal (voluntary) muscles. These are muscles that we control to move parts of our body. Well before birth, cells called rhabdomyoblasts (which will eventually form skeletal muscles) begin to form. These are the cells that can develop into RMS.
What to eat to build skeletal muscle?
Some high protein/lower calorie choices include:
- Almonds and pistachios – 13% protein = 6 grams per ounce of nuts
- Chicken breast – 80% protein = 53 grams of protein per cooked skinless breast
- Oats – 15% protein = 13 grams of protein in 1/2 cup of raw oats
- Greek Yogurt – 48% protein = 17 grams of protein in a 1 cup serving (do not get it with added sugar)
What are the different types of skeletal muscle?
You have:
- Skeletal muscles, such as your biceps, which are under voluntary control.
- Smooth muscles, such as those in your intestines, which are under involuntary nervous system control.
- Cardiac muscle, which is the involuntarily controlled muscle of your heart.
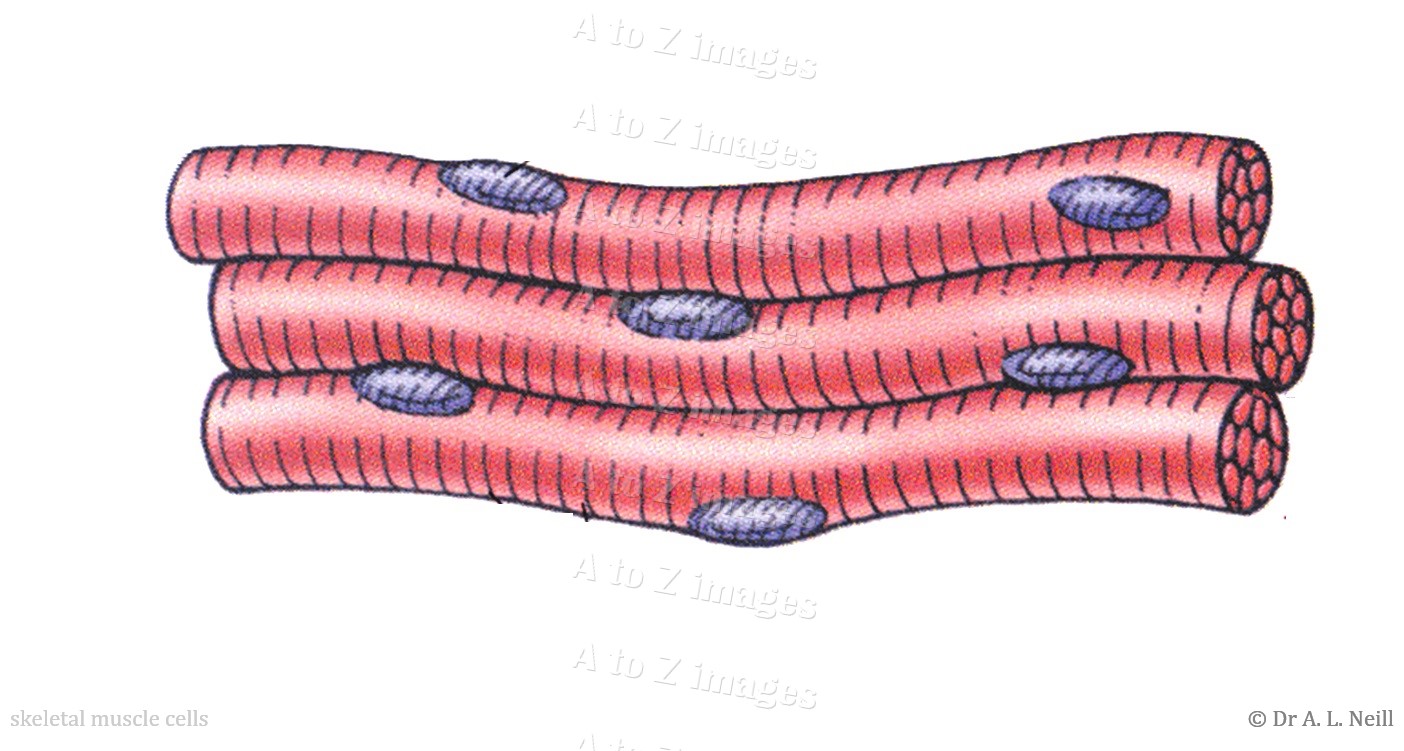
How big is a single muscle cell?
30 to 200 micrometresThey have a single nucleus and range from 30 to 200 micrometres in length. This is thousands of times shorter than skeletal muscle fibers. The diameter of their cells is also much smaller which removes the need for T-tubules found in striated muscle cells.
Are skeletal muscle cells short or long?
Skeletal muscle cells are long, cylindrical, and striated. They are multi-nucleated meaning that they have more than one nucleus.
What is the diameter of skeletal muscle?
Muscle fibers are typically large cells, some 20–100 μm in diameter and many centimeters long, with the longest fibers being about 12 cm. These cells are multinucleated, because they need many nuclei to govern protein synthesis and degradation.
Is skeletal muscle size and shape?
Skeletal muscles vary considerably in size, shape, and arrangement of fibers. They range from extremely tiny strands such as the stapedium muscle of the middle ear to large masses such as the muscles of the thigh. Some skeletal muscles are broad in shape and some narrow.
What is a skeletal muscle cell?
Skeletal muscle cells or fibers are highly elongated cells with a very elastic and resistant plasma membrane, called the sarcolemma. Fibers are characterized by the presence of numerous nuclei located at the periphery of the cell, hence muscle fibers are described as a syncytium.
What is the structure of a skeletal muscle cell?
Skeletal muscle fibers are long, multinucleated cells. The membrane of the cell is the sarcolemma; the cytoplasm of the cell is the sarcoplasm. The sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) is a form of endoplasmic reticulum. Muscle fibers are composed of myofibrils which are composed of sarcomeres linked in series.
How long is a muscle cell?
Skeletal muscle cells are responsible for practically all movements that are under voluntary control. These cells can be very large (2–3 cm long and 100 μm in diameter in an adult human) and are often referred to as muscle fibers because of their highly elongated shape.
How do you calculate skeletal muscle?
The most accurate way to calculate muscle mass percentage is to use magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). An MRI uses strong magnets to take an image of your muscles.
Is a myofibril a muscle cell?
A myofibril (also known as a muscle fibril or sarcostyle) is a basic rod-like organelle of a muscle cell. Skeletal muscles are composed of long, tubular cells known as muscle fibers, and these cells contain many chains of myofibrils. Each myofibril has a diameter of 1–2 micrometres.
What is skeletal muscle percentage?
According to Withings, normal ranges for muscle mass are: Ages 20-39: 75-89 percent for men, 63-75.5 percent for women. Ages 40-59: 73-86 percent for men, 62-73.5 percent for women. ages 60-79: 70-84 percent for men, 60-72.5 percent for women.
What percent of the body is skeletal muscle?
Skeletal muscle is one of the most dynamic and plastic tissues of the human body. In humans, skeletal muscle comprises approximately 40% of total body weight and contains 50-75% of all body proteins.
What do muscle cells look like?
Skeletal muscle fibers are cylindrical, multinucleated, striated, and under voluntary control. Smooth muscle cells are spindle shaped, have a single, centrally located nucleus, and lack striations.
Why are muscle cells long?
The muscle cell is long so it can contract and relax with other cells.
What is the shape of a skeletal muscle cell quizlet?
What type of contractile shape is the Skeletal Muscle cell? Elongated.
Are muscle cells long lived?
An average skeletal muscle cell's lifespan is 10 to 16 years.
Why skeletal muscle cells are extremely long cells when compared to other cells in the body?
Skeletal muscle cells are extremely long compared to other cells in the body because they are multinucleate cells made from the fusion of other cells. They have a complex structure contained within their length.
How many inches are in a skeletal muscle?
Skeletal muscles consist of flexible muscle fibers that range from less than half an inch to just over three inches in diameter. These fibers usually span the length of the muscle. The fibers contract (tighten), which allows the muscles to move bones so you can perform lots of different movements.
What percentage of your body is muscle?
Skeletal muscles comprise 30 to 40% of your total body mass. They’re the muscles that connect to your bones and allow you to perform a wide range of movements and functions. Skeletal muscles are voluntary, meaning you control how and when they work.
What are striated muscles?
Skeletal muscle fibers are red and white. They look striated, or striped, so they’re often called striated muscles. Cardiac muscles are also striated, but smooth muscles aren’t.
Why is it important to keep your muscles strong?
Skeletal muscles are the most common muscles in your body. You use them to move your bones, so they play a vital role in everyday activities. Skeletal muscle injuries or diseases can have a profound effect on your life. It’s important to keep your muscles as strong and healthy as possible.
What muscles do you use when you reach for a book?
Nerves in your somatic nervous system send signals to make them function. If you reach for a book on a shelf, you’re using skeletal muscles in your neck, arm and shoulder.
What are the muscles that make up the majority of the body?
The majority of the muscles in your body are skeletal muscles. They make up between 30 to 40% of your total body mass. Tendons (tough bands of connective tissue) attach skeletal muscle tissue to bones throughout your body. Your shoulder muscles, hamstring muscles and abdominal muscles are all examples of skeletal muscles.
How much muscle mass does a man have?
Although skeletal muscles typically make up roughly 35% of your body weight, this can vary from person to person. Men have about 36% more skeletal muscle mass than women. People who are tall or overweight also tend to have higher muscle mass. Muscle mass decreases with age in both men and women.
How long are skeletal muscles?
Skeletal muscles are attached to bones by tendons and can be as long as 30 cm, although they are usually 2 to 3 cm in length.
What are the different types of muscle cells?
There are 3 types of muscle cells in the human body; cardiac, skeletal, and smooth. Cardiac and skeletal myocytes are sometimes referred to as muscle fibers due to their long and fibrous shape. Cardiac muscle cells, or cardiomyocytes, are the muscle fibers comprise the myocardium, the middle muscular layer, of the heart.
What are the different types of myofilaments in sarcoplasm?
Sarcoplasm also contains many tubular protein structures called myofibrils, which are made up of myofilaments. There are 3 types of myofilament; thick, thin, and elastic . Thick myofilaments are made from myosin, a type of motor protein, whilst thin myofilaments are made from actin, another type of protein used by cells for structure. Elastic myofilaments are composed of a springy form of anchoring protein known as titin. Together these myofilaments work to create muscle contractions by allowing the myosin protein heads to walk along the actin filaments creating a sliding action. The basic unit of striated (striped) muscle is a sarcomere comprised of actin (light bands) and myosin (dark bands) filaments.
How do myofilaments work?
Together these myofilaments work to create muscle contractions by allowing the myosin protein heads to walk along the actin filaments creating a sliding action. The basic unit of striated (striped) muscle is a sarcomere comprised of actin (light bands) and myosin (dark bands) filaments.
How do smooth muscle cells contract?
As with cardiac and skeletal muscle cells, smooth muscle cells contract as a result of depolarization of the sarcolemma. In smooth muscle cells this is facilitated by gap junctions. Gap junctions are tunnels which allow impulses to be transmitted between them, so that depolarization can spread, causing the myocytes to contract together in unison.
What is the cytoplasm of muscle cells?
The anatomy of muscle cells differs from that of other body cells and biologists have applied specific terminology to different parts of these cells. The cell membrane of a muscle cell is known as the sarcolemma and the cytoplasm is called sarcoplasm. The sarcoplasm contains myoglobin, an oxygen storage site, as well as glycogen in the form of granules in the cytosol, which both provide an energy supply.
Why are skeletal muscle cells multi-nucleated?
They are multi-nucleated meaning that they have more than one nucleus. This is because they are formed from the fusion of embryonic myoblasts. Each nucleus regulates the metabolic requirements of the sarcoplasm around it.
What is the role of skeletal muscle?
Skeletal muscle is the most abundant tissue in the body comprising 40-50% of body mass in humans and playing a central role in maintaining metabolic health. Skeletal muscle protein undergoes rapid turnover, a process that is intricately regulated by the balance between the rates ...
Which muscle is the most abundant in the body?
Skeletal muscle is the most abundant tissue in the body comprising 40-50% of body mass in humans and playing a central role in maintaining metabolic health.
What is the process of skeletal muscle hypertrophy and regeneration?
The process of skeletal muscle hypertrophy and regeneration is an important adaptive response to both contractile activity (i.e., exercise) and nutrient availability (i.e., protein ingestion). Ageing and physical inactivity are two conditions associated with a loss of skeletal muscle protein (sarcopenia).
What is the most abundant tissue in the body?
Skeletal muscle is the most abundant tissue in the body comprising 40-50% of body mass in humans and playing a central role in maintaining metabolic health. Skeletal muscle protein undergoes rapid turnover, a process that is intricately regulated by the balance between the rates of protein synthesis and degradation.
What is the structure of skeletal muscle?
Skeletal Muscle Structure. Skeletal muscle is comprised of a series of muscle fibers made of muscle cells. These muscle cells are long and multinucleated. At the ends of each skeletal muscle a tendon connects the muscle to bone. This tendon connects directly to the epimysium, or collagenous outer covering of skeletal muscle.
What is skeletal muscle?
Skeletal Muscle Definition. Skeletal muscle is a specialized contractile tissue found in animals which functions to move an organism ’s body. Skeletal muscle is comprised from a series of bundles of muscle fibers, surrounded by protective membranes. This arrangement allows skeletal muscle to contract quickly and release quickly without subjecting ...
How does ATP work in skeletal muscle?
Energy from ATP is used to move one head, while the other is attached. When many hundreds or thousands of heads are involved, this quickly contracts the sarcomere up to 70% of its original length. As the nervous impulse hits each muscle fiber and muscle at the same time, the arm can lift in a fluid motion. As an added feedback measure, every skeletal muscle has special sensory cells which send feedback to the brain. These cells, called muscle spindles, have specialized proteins which can sense tension. When tension is received by the cell, the cell starts a nervous impulse and sends the signal through neurons to the brain.
What is the outer covering of skeletal muscle called?
This tendon connects directly to the epimysium, or collagenous outer covering of skeletal muscle. Underneath the epimysium, muscle fibers are grouped into bundles called fascicles. These fascicles are surrounded by another protective covering formed from collagen.
How are fascicles formed?
Each fascicle is formed from tens to hundreds of bundled muscle fibers. Each muscle fiber is formed from a chain of multinucleated muscle cells. These fibers are then protected by another layer called the endomysium as they are bundled into fascicles.
Which type of muscle tissue is found in most multicellular forms of life?
This arrangement allows skeletal muscle to contract quickly and release quickly without subjecting the individual fibers to too much friction. Skeletal muscle tissue can be found across the animal kingdom, in most multi-cellular forms of life.
Where are skeletal muscles found?
Many muscles are obscurely small or are sometimes grouped together with similar muscles. Skeletal muscle is found between bones, and uses tendons to connect the epimysium to the periosteum, or outer covering, of bone. Skeletal muscle is adapted and shaped in many different ways, which give rise to complex movements.
