
What type of agar does Staphylococcus epidermidis grow on?
Tryptic soy agar (TSA) On tryptic soy agar, S. epidermidis produces white raised, cohesive colonies of the size 1-2 mm in diameter. Some strains of S. epidermidis are also known to produce subtle violet, pinkish, or brownish pigment.
What type of microorganism is S epidermidis?
S. epidermidis is a very hardy microorganism, consisting of nonmotile, Gram-positive cocci, arranged in grape-like clusters. It forms white, raised, cohesive colonies about 1–2 mm in diameter after overnight incubation, and is not hemolytic on blood agar.
What is the difference between Staphylococcus aureus and S epidermidis?
Friedrich Julius Rosenbach distinguished S. epidermidis from S. aureus in 1884, initially naming S. epidermidis as S. albus. He chose aureus and albus since the bacteria formed yellow and white colonies, respectively. S. epidermidis is a very hardy microorganism, consisting of nonmotile, Gram-positive cocci, arranged in grape-like clusters.
Where is Staphylococcus epidermidis found in human skin?
S. epidermidis is the most familiar resident staphylococcal species on human skin in terms of population size. It is a ubiquitous inhabitant of human skin and mucous membranes that forms a part of the normal flora of skin in humans, predominantly found in the nasal passage and sweaty areas of the body like the armpits and the back.
Is Staphylococcus epidermidis gram or gram?
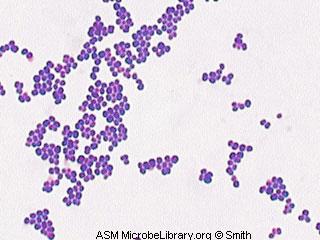
gram-positive cocci bacteriaStaphylococcus epidermidis is a coagulase-negative, gram-positive cocci bacteria that form clusters.
What is the size of staphylococci?
CHARACTERISTICS: Staphylococcus aureus are Gram-positive, catalase positive cocci belonging to the Staphylococcaceae family 1, 2. They are approximately 0.5-1.5 µm in diameter, nonmotile, non-spore-forming, facultative anaerobes (with the exception of S. aureus anaerobius) that usually form in clusters.
What is the shape of Staphylococcus epidermidis?
cocci-shapedStructure and Physiology This bacteria is a Gram-positive, cocci-shaped, facultative anaerobe. S. epidermidis is part of the human bacterial flora, mostly located on skin.
What is the shape and size of Staphylococcus?
Staphylococci are Gram-positive cocci about 0.5 – 1.0 μm in diameter. They grow in clusters, pairs and occasionally in short chains. The clusters arise because staphylococci divide in two planes.
How do you differentiate S. aureus and S. epidermidis?
Staphylococcus aureus forms a fairly large yellow colony on rich medium; S. epidermidis has a relatively small white colony. S. aureus is often hemolytic on blood agar; S.
What color is Staphylococcus epidermidis?
whiteSTAPHYLOCOCCI - BLOOD AGAR CULTURE aureus usually displays a light to golden yellow pigment, whereas S. epidermidis has a white pigment and S. saprophyticus either a bright yellow or white pigment.
Is Staph epidermidis bacilli or cocci?
Staphylococci are known as clustering Gram-positive cocci, nonmotile, non-spore forming facultatively anaerobic that classified in two main groups, coagulase-positive and coagulase-negative.
What is the margin of Staphylococcus epidermidis?
epidermidis are observed on NA. The colonies are mostly 1mm in diameter with an entire margin. The colonies have raised elevation and a dense center with transparent borders.
What is significant about Staphylococcus epidermidis?
S. epidermidis is currently the main pathogen in catheter-related bloodstream infections and early-onset neonatal sepsis and is also a frequent cause of prosthetic joint infections, prosthetic valve endocarditis, and other biomedical device-related infections (12,–15).
What is the size of a bacteria?
about 1 to 2 micronsMost common bacteria are about 1 to 2 microns in diameter and 5 to 10 microns long. A micron is one millionth of a meter, or 1/10,000th of a centimeter.
What is the typical size of bacteria?
Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and Caulobacter crescentus, the primary models for bacterial cell biology, are more or less typical in size, with individual cell volumes between ∼0.4–3 µm3 (or 0.4–3.0 femtoliters; femtoliter or fL is equal to 10−15 L).
What is the shape of Staphylococcus?
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria are pathogens to both man and other mammals. They are gram positive bacteria that are small round in shape (cocci) and occur as clusters appearing like a bunch of grapes on electron microscopy.
Is Staphylococcus a shape?
Staphylococci are spherical organisms that divide sequentially in three orthogonal planes over three consecutive division cycles1,2.
What is the shape of Staphylococcus aureus?
S. aureus cells are Gram-positive and appear in spherical shape. They are often in clusters resembling bunch of grapes when observed under light microscope after Gram staining.
How do you identify Staphylococcus?
Coagulase testing is the single most reliable method for identifying Staphylococcus aureus [9]. Coagulase production can be detected using either the slide coagulase test (SCT) or the tube coagulase test (TCT).
How do staphylococci grow?
S. aureus is a facultative anaerobe that grows by aerobic respiration or by fermentation, which yields principally lactic acid. The bacterium metabolizes glucose via the pentose phosphate pathway (Reizer et al., 1998).
What is the habitat of Staphylococcus epidermidis?
Habitat of Staphylococcus epidermidis. S. epidermidis is the predominant coagulase-negative Staphylococcus species found in the material of human origin. Humans are the only natural host for this organism. The physiological habitat of S. epidermidis is the skin and mucous membranes of humans and animals.
What is the habitat of S. epidermidis?
The physiological habitat of S. epidermidis is the skin and mucous membranes of humans and animals. The name ‘epidermidis’ indicates the habitat of the organism. S. epidermidis is the most familiar resident staphylococcal species on human skin in terms of population size.
What is the most frequently isolated species from human epithelia?
What is Staphylococcus epidermidis? Staphylococcus epidermidis is a Gram-positive bacterium belonging to the genus Staphylococcus and is the most frequently isolated species from human epithelia.
What are the biochemical properties of staphylococci?
Besides, other biochemical properties of staphylococci are useful for the differentiation of species, including the production of lactic acid when grown under anaerobic conditions.
What is the classification of a staph?
Classification of species of the genus Staphylococcus is based on various factors like the chemical properties of the cell wall, especially the amino acid composition and sequence of the interpeptide bridges of the peptidoglycan and teichoic acid composition.
Which microorganism retains the ability to adhere to host proteins in the skin specifically?
As a commensal microorganism, S. epidermidis retains the ability to adhere to host proteins in the skin specifically.
Is S. epidermidis a coagulase negative staphylococcus?
S. epidermidis belongs to the group of coagulase-negative staphylococci ( CoNS), which is different from coagulase-positive staphylococci such as S. aureus by lacking the enzyme coagulase.
Is Staphylococcus epidermidisis a gram positive or negative?
Staphylococcus epidermidisis a coagulase-negative, gram- positive cocci bacteria that form clusters. It is also a catalase-positive and facultative anaerobe. They are the most common coagulase-nega tive Staphylococcusspecies that live on the human skin. In its natural environments such as the human skin or mucosa, they are usually harmless.
Is staph a coagulase negative organism?
In its natural environments such as the human skin or mucosa, they are usually harmless. Many times, these coagulase-negative staph species invade the human body via prosthetic devices, at which point a small number of microbes travel down the prosthetic device to the bloodstream.
Is Staphylococcus epidermidis a cocci?
In its natural environments such</span> …. <span><i>Staphylococcus epidermidis</i> is a coagulase-negative, gram-positive cocci bacteria that form clusters. It is also a catalase-positive and facultative anaerobe.
Why is Staphylococcus epidermidisis a BAI?
Also extracellular polysaccharides production and biofilm formation increase the bacterial stability on different surfaces therefore the antibiotic penetration will be prevented [73].
What are the two groups of staph infections?
Staphylococci are known as clustering Gram-positive cocci, nonmotile, non-spore forming facultatively anaerobic that classified in two main groups, coagulase-positive and coagulase-negative. Staphylococcus epidermidiswith the highest percentage has the prominent role among coagulase-negative Staphylococci that is the most important reason of clinical infections. Due to various virulence factors and unique features, this microorganism is respected as a common cause of nosocomial infections. Because of potential ability in biofilm formation and colonization in different surfaces, also using of medical implant devices in immunocompromised and hospitalized patients the related infections have been increased. In recent decades the clinical importance and the emergence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidisstrains have created many challenges in the treatment process.
Which cocci produced white colonies on blood agar plates?
Rosenbach in 1884 named the Cocci which produced white colonies on blood agar plates as Staphylococcus albus, thereafter in 1891 Staphylococcus epidermidis albus, in 1908 Albococcus epidermidisand Staphylococcus epidermidisin 1916 were used by Welch et al. [2].
What is the virulence factor of S. epidermidisin?
Bap/Bhp: One more virulence factor of S. epidermidisin biofilm accumulation is Bap (biofilm associated protein) which is known as a surface adhesion protein that commonly found in S. epidermidisstrains, while in Staphylococcus aureusthe bovine mastitis isolates are the only strains that harbor the Bap [15].
Is staph a coagulase?
Sta phylococcus epi dermidiswhich is known as a coagulase-negative and Gram-positive Staphylococcus, is one of the five significant microorganisms that are located on human skin and mucosal surfaces with the ability of causing nosocomial infections due to the wide usage of medical implants and devices, hence until 1980 S. epidermidiswas considered as an opportunistic microorganism, while in accordance to various infections increasement such as cardiovascular, CNS shunts, joints, blood stream infections, etc. The mentioned bacteria is regarded as one of the main cause of nosocomial infections [7]. Later researches show that the activity of Staphylococcus epidermidislipase enzyme can produce various types of esters such as geranyl, unsaturated and medium-chain esters without organic solvents; therefore this ability can be considered as an advantage in the biotechnology field of studies [8]. Investigators proved that when S. epidermidishas been treated with n-propanol, propanol/ethanol/chlorhexidine and alcohols this bacterium is no more alive in biofilms. Five minutes incubation in hydrogen peroxide solution in comparison to povidine-iodine reduces the mass of live cells respectively. Subsequently hydrogen peroxide (3%) and also (5%) is one of the most effective method for removing the S. epidermidisaccumulation from surfaces by reducing the biofilms amount [9].
Is staph a coagulase negative organism?
Coagulase-negative Staphylococci particularly Staphylococcus epidermidisare the saprophytic microorganisms that isolated with high fre quency from the blood stream and the other various sources may cause the true invasive infections . Determining the differences between S. aureusand S. epidermidisinfections are valuable in discrimination of highly contaminated and true bacteremia infections, hence the rigorous and rapid diagnosis of the main cause of infection in clinical microbiology laboratories is exactly essential [45]. In past decades studies based on bacterial colony identification, microbiological culture medium, Gram staining, catalase test, coagulase and phosphatase activity, nitrate reductase, DNase, TNase, acid production from carbohydrates (D-trehalose, sucrose, maltose, D-mannitol, D-xylose), tolerance to 10–15% NaCl, hemolytic activity on 5% blood sheep (Table 1 (Tab. 1)), antibiotic sensitivity test to polymyxin B and novobiocin for detection of CoNs specially S. epidermidisisolates were more common [46], while some investigators in microbiological laboratories have identified Staphylococcus epidermidiswith high sensitivity and specificity by using complex medium containing trehalose, mannitol, phenol and phosphate in a single agar plate [47], [48]. Currently most of typical traditional methods as mentioned above are used for detection of Staphylococci species, for instance the tube coagulase test can directly detect this enzyme from blood samples but due to common culturing and prepared dilution methods the sensitivity range of the test is reported from 62 to 100% [48], [49]. Analysis of fatty acids is another diagnostic method for determining S. aureusisolates, while in coagulase-negative Staphylococci this kind of identification usually fails. However despite certain S. epidermidisstrains with phosphatase negative reaction are often misidentified with S. hominis[50]. Commercial kits almost known as the rapid and miniaturized systems methods for identification of S. epidermidissuch as: API Staph-Ident, API Staph-Trac, Sceptor Gram-Positive MIC/I, Vitek GPI Card and Minitek Gram-Positive System. Rapid molecular methods for example peptide nucleic acid (PNA), fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), etc. prepare results in less than 2 hours. It’s about more than one decade that the PNA FISH technique has been used in clinical labs, because of the limitation of PNA FISH [51], [52] additional alternative methods are being used. In QuickFISH method the coagulase-negative Staphylococci are determined in <30 minutes with blood culture containing tubes that specific probes are the advantage of this method. In many researches despite DNA hybridization and 16s rRNA analysis, ERIC and BOX-PCR have been used as a complementary methods [53].
What is the strain of MRSA?
One strain that is of great concern to humans is methi cillin-resistant S. aureus ( MRSA ), which is characterized by the presence of a single mutation that renders it resistant to methicillin, a semisynthetic penicillin used to treat staphylococcus infections that are resistant to mold-derived penicillin.
How many people died from MRSA in 2005?
In 2005 in the United States, deaths from MRSA (approximately 18,000) surpassed deaths from HIV/AIDS (approximately 17,000), underscoring the need for improved surveillance to prevent and control the spread of this potentially lethal organism.
What is the last line of defense against MRSA?
The treatment of MRSA infections with vancomycin, an antibiotic often considered as a last line of defense against MRSA, has led to the emergence of vancomycin-resistant S. aureus (VRSA), against which few agents are effective.
What is the term for a cell that aggregates in grapelike clusters?
The term staphylococcus, generally used for all the species, refers to the cells’ habit of aggregating in grapelike clusters. Staphylococci are microbiologically characterized as gram-positive (in young cultures), non-spore-forming, nonmotile, facultative anaerobes (not requiring oxygen).
When was S. aureus first isolated?
This strain of S. aureus was first isolated in the early 1960s, shortly after methicillin came into wide use as an antibiotic. Today methicillin is no longer used, but the strain of MRSA to which it gave rise is commonly found on the skin, in the nose, or in the blood or urine of humans.
Is S. aureus a pathogen?
While S. epidermidis is a mild pathogen, opportunistic only in people with lowered resistance, strains of S. aureus are major agents of wound infections, boil s, and other human skin infections and are one of the most common causes of food poisoning.
