
What kind of skeleton does bony fish have?
The skeleton of bony fishes is made of bone and cartilage. The vertebral column, cranium, jaw, ribs, and intramuscular bones make up a bony fish’s skeleton. Do bony fish have an exoskeleton? Fishes of this class are found in freshwater as well as marine water. Endoskeleton of these fishes are made up of bones, so these are called bony fishes.
Does a bony fish have a skeleton of bone?
There are over 20,000 species of fresh and salt water bony fish. All bony fish have skeletons made of bone. Most of them have a swim bladder or air-filled sac that helps them float. Bony fish are covered in scales and they have gills on the sides of their heads.
Does a bony fish have a backbone?
There are two types of fish that have vertebral columns: cartilaginous fish, which have a skeletal structure made of cartilage, and bony fish, who have actual bones. Nearly every fish has a backbone, with the only exception being the hagfish, which have something called a notochord.
Do bony fish have backbones?
They have a bony endoskeleton with a backbone and jaws; they breathe only with lungs; they have four limbs; their skin is covered with scales; they have amniotic eggs; they are ectothermic. What makes a bony fish a bony fish? Bony fish differ from fish like sharks and rays in the chondrichthyes class. Instead of cartilage, bony fish have bones.
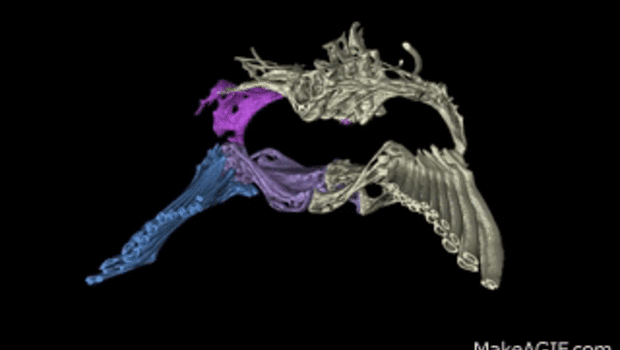
Do bony fish have a skeleton made of cartilage?
As the name suggests, “bony fish” have a skeleton composed of only bones while a cartilaginous fish has a skeleton made entirely of cartilage.
What is skeleton in fish?
A skeleton of fish is either made of bone or Cartilage. There are two different skeletal types: Exoskeleton- An outer shell of an organism. Endoskeleton- Inner shell of an organism.
What fish has a skeleton made of hard bone?
The lone fish has a skeleton of bone. The rays have a skeleton of cartilage, and so they are known as cartilaginous fish.
What makes a bony fish a bony fish?
Bony fishes share several distinguishing features: a skeleton of bone, scales, paired fins, one pair of gill openings, jaws, and paired nostrils. Osteichthyes includes the largest number of living species of all scientific classes of vertebrates, more than 28,000 species.
What is a skeleton made of?
The adult human skeleton is made up of 206 bones. These include the bones of the skull, spine (vertebrae), ribs, arms and legs. Bones are made of connective tissue reinforced with calcium and specialised bone cells. Most bones also contain bone marrow, where blood cells are made.
What is the animal skeleton made of?
The skeleton consists of both fused and individual bones supported and supplemented by ligaments, tendons, muscles and cartilage. It serves as a scaffold which supports organs, anchors muscles, and protects organs such as the brain, lungs, heart and spinal cord.
What type of skeleton do most fish have?
There are two different skeletal types: the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, and the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside the body. The skeleton of the fish is made of either cartilage (cartilaginous fishes) or bone (bony fishes).
How do you make a fish skeleton?
0:516:48Katie Hacker Creates a Wiggly Fish on Hands On Crafts for Kids (1801-2)YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipLike this one to cut. And just cut straight down. And all the way around your pattern then you'reMoreLike this one to cut. And just cut straight down. And all the way around your pattern then you're going to completely cut this out the head and the tail and then you can kind of rub.
Is fish an endoskeleton or exoskeleton?
Mammals, reptiles, birds, fish and amphibians are vertebrates with endoskeletons (skeletons inside their bodies). Their skeletons provide support and protection and help them to move. Insects, spiders and shellfish are some of the invertebrates that have exoskeletons.
Do bony fish have a bony skeleton?
The skeleton of bony fishes is made of bone and cartilage. The vertebral column, cranium, jaw, ribs, and intramuscular bones make up a bony fish's skeleton.
Do bony fish have calcium bones?
Bony fish (Osteichthyes) are distinguished from other fish species that have a cartilaginous skeleton (Chondrichthyes—sharks, rays and chimaeras, for example) by the presence of true bone—a mixture of calcium phosphates and carbonates—in their skeletons.
How are the skeletons of sharks different from the skeletons of bony fish?
Unlike fishes with bony skeletons, a shark's skeleton is made out of cartilage. This is a flexible but strong connective tissue that's also found throughout the human body, in places like the nose, ears, and in joints between bones.
What is the difference between a bony fish and a cartilaginous fish?
In simple terms, a bony fish (Osteichthyes ) is one whose skeleton is made of bone, while a cartilaginous fish (Chondrichthyes) has a skeleton made of soft, flexible cartilage. A third type of fish, including eels and hagfish, is the group known as Agnatha, or jawless fish. The cartilaginous fish include sharks , skates , and rays .
What are the two types of bony fish?
Species. Bony fish are considered to members of the class Osteichthyes, which is subdivided into two main types of bony fish: Ray-finned fishes, or Actinopterygii. Lobe-finned fishes, or Sarcopterygii, which includes the coelacanths and lungfishes. The subclass Sarcopterygii is made up of about 25,000 species, all characterized by the presence ...
How many species are in the Sarcopterygii subclass?
The subclass Sarcopterygii is made up of about 25,000 species, all characterized by the presence of enamel on their teeth. They have a central axis of bone that acts as a unique skeletal support for fins and limbs, and their upper jaws are fused with their skulls. Two major groups of fishes fit under the Sarcopterygii: the Ceratodontiformes ...
What are the two groups of fish that fit under the Sarcopterygii?
Two major groups of fishes fit under the Sarcopterygii: the Ceratodontiformes (or lungfishes) and the Coelacanthiformes (or coelacanths), once thought to be extinct. Actinopterygii includes 33,000 species in 453 families.
What are bony fish prey?
A bony fish's prey depends on the species but may include plankton, crustaceans ( e.g., crabs), invertebrates ( e.g., green sea urchins ), and even other fish. Some species of bony fish are virtual omnivores, eating all manner of animal and plant life.
How long does it take for a bony fish to mature?
Some bony fish are born sexually mature or become mature shortly after birth; most mature within the first one to five years. The main reproduction mechanism is external fertilization. During the spawning season, females release hundreds to thousands of eggs in the water, and males release sperm and fertilize the eggs.
When did cartilaginous fish diverge?
Bony fish and cartilaginous fish diverged into separate classes about 420 million years ago . Cartilaginous species are sometimes seen as more primitive, and for good reason. The evolutionary appearance of bony fish eventually led to land-dwelling vertebrates with bony skeletons.
What are bony fish made of?
Starting from the head, bony fish consist of solid hard bones called cranium. Cranium protects the brain from mechanical stresses. Osteichthyes have hinged jaws which aid them in feeding. But fishes like hagfish, lampreys are jawless fishes.
What are the two main skeletal systems of fish?
There are two different skeletal types: Exoskeleton- An outer shell of an organism. Endoskeleton- Inner shell of an organism. The main features of the fish skeletal system are it consists of the vertebral column, jaw, ribs, cranium and intramuscular bones.
What are the features of fish?
General features of fishes include fins, streamlines and scales and tails. But differences are highlighted under their skins. Hence classification is much easier based on the skeletal system. A variety of fishes is found in aquatic habitat some may be cartilaginous (Chondrichthyes) or bony fishes (Osteichthyes).
What are the ear plates of fish called?
Otoliths are unique characteristics of ear plates of bony fish which helps in steadiness. Gills are the pair of the respiratory organ of fish and some amphibians. There are three pairs of bones that aid gills. These pair of bones is called gill arches which are made of bony filaments. Fins are a vital part of fish.
What kingdom do fish belong to?
In the taxonomic hierarchy, fishes belong to the kingdom Animalia, phylum Chordata. They are in diverse groups which include jawless fish, armoured fish, cartilaginous fish, lobe-finned fishes and ray-finned fish and so on. Among these, most of them are ectothermic i.e. cold-blooded organisms.
What are the fins of fish?
Fins are a vital part of fish. They help with propulsion, steering, and stability. Paired fins take up the role of steering while caudal fins and dorsal fins help in propulsion and stability respectively. For more details on the skeletal system of fish and other species, visit BYJU’S. Respiration In Fish.
What are the two types of skeletons?
A skeleton of fish is either made of bone or Cartilage. There are two different skeletal types: 1 Exoskeleton- An outer shell of an organism. 2 Endoskeleton- Inner shell of an organism.
What is a fish skull made of?
fish (Sarcopterygii) (Actinopterygii are bony fish that have radiated fins made-up by. bony tissues. Their skull is mainly made of cartilaginous tissue. Moreover, they have two gill openings protected by an operculum, and the scales are overlapping and rudimentary.
What is a boney fish?
Bony fish are those vertebrate and gnathostomes fish (vertebrates characterized by having articulated jaws). They are endowed with an internal bone skeleton, hence their name. They are also known as Osteichthyes
What is a cartilaginous fish?
Cartilaginous fish, also known as chondrichthyes, are a class of fish characterized by having their skeleton made-up by cartilage and not by bone as occurs in bony fish. This group includes well-known marine animals such as: sharks, sawfish and rays.
How many pairs of gills are there in a fish?
In cartilaginous fish, the gills are exposed and not protected by any external skin. Most fish, whether bony or cartilaginous, have five pairs of gills.
Which is longer, cartilaginous or bony fish?
The intestine of cartilaginous fish is typically shorter than that of bony fish. However, it spirals internally to create a larger surface area that optimizes nutrient absorption. In the bony fish, the intestine is longer and has no spiral shape.
What is the mouth of a bony fish called?
The mouth of these animals is called the terminal mouth , which is capable of very accurate movements, thanks mainly to the articulated dermal bones by which it’s made-up.
Where are red blood cells produced in fish?
In bony fish, red blood cells are produced in the bone marrow, (the central part of the bone). This process is known as hemopoiesis. Cartilaginous fish lack bone marrow for hemopoiesis. Instead, these fish produce red blood cells in the spleen and thymus organs.
What is the largest group of fish that has an internal skeleton made from calcified bones?
Bony fish is the largest group of the fish that have an internal skeleton made from calcified bones. Bony fish belong to the class Osteichthyes. Teleost is another name that refers to bony fish. They are vertebrates, and presently they are some of the most abundant vertebrates on the planet.
What is the difference between a shark and a bony fish?
The key difference between sharks and bony fish is that the shark has an internal skeleton made from cartilages while bony fish has an internal skeleton made from calcified bones. Fish are one of the five vertebrate groups belonging to Kingdom Animalia. They are multicellular aquatic organisms.
What are the two groups of fish?
Sharks and bony fish are two fish groups. Sharks are cartilaginous fish. They have a cartilaginous skeleton. Bony fish have a skeleton made from calcified bones. Sharks and bony fish belong to the class Chondrichthyes and Osteichthyes respectively. This is the difference between sharks and bony fish.
What are the three main groups of fish?
Fish may have an internal skeleton made from bones or cartilages. There are three major groups of fish namely cartilaginous fish, Bony fish and lobe-finned fish.
What class is a shark?
Sharks are cartilaginous fish which have an internal skeleton made from cartilages. Sharks belong to class Chondrichthyes. Along with sharks, this group includes rays, skates and chimaeras as well. According to the fossil records, cartilaginous fish were more abundant in the past. Presently they are less abundant than bony fish.
How many species of bony fish are there?
Salmon, trout, lanternfish, cavefish, cods, anglerfish, tarpon, herrings, electric eels, etc. are few bony fish species. There are 63 bones in the bony fish skull. They have pleural ribs made from dermal bone. They lack eyelids. Hence, they are not able to protect their eyes like sharks.
Do sharks have pleural ribs?
And also sharks lack pleural ribs, unlike bony fish. Gill slits of a shark are visible, and there is no protective bony plate covering the gills. Sharks have eyelids that help to protect their eyes.

Skeletal System
- The skeleton of bony fishes is made of bone and cartilage. The vertebral column, cranium, jaw, ribs, and intramuscular bones make up a bony fish's skeleton. The skeleton of a bony fish gives structure, provides protection, assists in leverage, and (along with the spleen and the kidney) is a site of red blood cell production.
Muscular System
- The muscles of the tail and trunk consist of a series of muscle blocks called myotomes. The myotomes usually resemble a sideways letter "W". A connective tissue called myosepta separates the myotomes. A horizontal septum separates the myotomes into dorsal (top) myotomes and ventral (bottom) myotomes.
Nervous System
- The nervous system of fishes is poorly developed compared to that of other vertebrates. 1. The forebrain is responsible for the bony fish's ability to smell. Bony fishes that have an especially good sense of smell, such as eels, have an enlarged forebrain. 2. The midbrain processes vision, learning, and motor responses. Blind bony fishes, such as blind cavefishes in the family Amblyo…
Cardiovascular System
- A bony fish's heart has two chambers: an atrium and a ventricle. The venous side of the heart is preceded by an enlarged chamber called the sinus venosus. The arterial side of the heart is followed by a thickened muscular cavity called the bulbus arteriosus. 1. The sinus venosus receives oxygen-depleted blood from the body. A valve at the end of the sinus venosus opens int…
Digestive System
- The esophagus in bony fishes is short and expandable so that large objects can be swallowed. The esophagus walls are layered with muscle. Most species of bony fishes have a stomach. Usually the stomach is a bent muscular tube in a "U" or "V" shape. Gastric glands release substances that break down food to prepare it for digestion.
Respiratory System
- Water enters the gill chamber through a fish's mouth and exits through gill openings under the operculum. Blood flowing through the gill filaments absorbs oxygen from the water.
Swim Bladder
- Apparently the swim bladder originally developed in fish as an organ of respiration, as evidenced by the "lung" of the lungfishes. In modern bony fishes that possess a swim bladder, the organ serves principally in maintaining neutral buoyancy.
Description
Species
- Bony fish are considered to members of the class Osteichthyes, which is subdivided into two main types of bony fish: 1. Ray-finned fishes, or Actinopterygii 2. Lobe-finned fishes, or Sarcopterygii, which includes the coelacanthsand lungfishes. The subclass Sarcopterygii is made up of about 25,000 species, all characterized by the presence of enamel on their teeth. They hav…
Habitat and Distribution
- Bony fish can be found in waters all around the world, freshwater and saltwater both, unlike cartilagenous fish who are found only in salt waters. Marine bony fish live in all the oceans, from shallow to deep waters, and in both cold and warm temperatures. Their lifespans range from a few months to over 100 years. An extreme example of bony fish adaptation is the Antarctic icefi…
Diet and Behavior
- A bony fish's prey depends on the species but may include plankton, crustaceans (e.g., crabs), invertebrates (e.g., green sea urchins), and even other fish. Some species of bony fish are virtual omnivores, eating all manner of animal and plant life. Bony fish behavior varies greatly, depending on the species. Smaller bony fish swim in schools for protection. Some like the tuna swim conti…
Reproduction and Offspring
- Some bony fish are born sexually mature or become mature shortly after birth; most mature within the first one to five years. The main reproduction mechanism is external fertilization. During the spawning season, females release hundreds to thousands of eggs in the water, and males release sperm and fertilize the eggs. Not all bony fish do lay eggs: Some are live-bearing. Some are her…
Evolutionary History
- The first fish-like creatures appeared over 500 million years ago. Bony fish and cartilaginous fish diverged into separate classes about 420 million years ago. Cartilaginous species are sometimes seen as more primitive, and for good reason. The evolutionary appearance of bony fish eventually led to land-dwelling vertebrates with bony skeletons. And the gill structure of bony fish gill was …
Conservation Status
- Most bony fish species are classed as Least Concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), but there numerous species that are Vulnerable, Near Threatened, or Critically Threatened, such as Metriaclima koningsiof Africa.
Sources
- "Bony and Ray-Finned Fishes."Endangered Species International, 2011.
- Class Osteichthyes. The Biology Classroom of Mr. Pletsch. University of British Columbia, February 2, 2017.
- Hastings, Philip A., Harold Jack Walker, and Grantly R. Galland. "Fishes: A Guide to Their Diversity." Berkeley, University of California Press, 2014.
- "Bony and Ray-Finned Fishes."Endangered Species International, 2011.
- Class Osteichthyes. The Biology Classroom of Mr. Pletsch. University of British Columbia, February 2, 2017.
- Hastings, Philip A., Harold Jack Walker, and Grantly R. Galland. "Fishes: A Guide to Their Diversity." Berkeley, University of California Press, 2014.
- Konings, A. "Metriaclima ." The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species: e.T124556154A124556170, 2018. koningsi