Is slime layer gram negative bacteria?
It can be found in both gram positive and gram negative bacteria. When the amorphous secretion of a capsule diffuses into the surrounding medium and becomes loose, it is called a slime layer.
What is the slime layer composed of?
A slime layer in bacteria is an easily removable (e.g. by centrifugation), unorganized layer of extracellular material that surrounds bacteria cells. Specifically, this consists mostly of exopolysaccharides, glycoproteins, and glycolipids. Therefore, the slime layer is considered as a subset of glycocalyx.
What is slime in biofilm?
Biofilms contain bacteria and fungi that have grown and multiplied on a surface. To grow, bacteria and fungi require water and a source of food. If both are present on the surface then the organisms will grow and multiply to produce a grey/black jelly-like (slime) growth or produce a pink/red staining.
Is S layer the same as slime layer?
The difference is that the S-layer is more organized. The slime layer is a mixture of various chemicals, including glycoproteins and glycolipids. The surface layer, or S-layer, is often instead made of proteins. Unlike the slime layer, the S-layer is carefully made to protect the surface and therefore it adheres more.
What is the slime layer called?
glycocalyxCapsule. Capsule or slime layer is used to describe glycocalyx which is a thin, high molecular weight secretory substance present in many bacteria external to cell wall (Fig. 7.6). It is composed of polysaccharide, polypeptide, or both.
What is the slime layer of a cell called?
glycocalyxA glycocalyx is considered a slime layer when the glycoprotein molecules are loosely associated with the cell wall. Bacteria that are covered with this loose shield are protected from dehydration and loss of nutrients.
What is a slime layer in bacteria?
The slime layer is an easily removed, diffuse, unorganized layer of extracellular material which surrounds the bacterial cell. It is usually composed of polysaccharides and it may serve to trap nutrients, to aid in cell motility, to bind cells together or to adhere to smooth surfaces.
What is the importance of slime layer in bacterial cell?
The slime layer's job is to protect bacteria cells from environmental threats including antibiotics and desiccation. Bacteria can adhere to smooth surfaces like prosthetic implants and catheters, as well as other smooth surfaces like Petri dishes, due to the slime layer.
What bacteria causes slime?
It's likely that this slime is caused by iron bacteria or related slime forming bacteria such as sulfur bacteria. Iron bacteria use dissolved iron or manganese in groundwater to grow, producing a bacterial slime along the way.
Do Gram-negative bacteria have glycocalyx?
The bacterial glycocalyx has been defined as polysaccharide components lying outside the outer membrane of gram-negative cells or the peptidoglycan layer of gram-positive cells (Costerton et al.
Where are slime layers found?
Many bacterial cells secrete some extracellular material in the form of a capsule or a slime layer. A slime layer is loosely associated with the bacterium and can be easily washed off, whereas a capsule is attached tightly to the bacterium and has definite boundaries.
What is the difference between capsule and slime layer?
The main difference between capsule and slime layer is that capsule is a thick glycocalyx layer that is tightly bound to the cell, defining boundaries of the cell whereas slime layer is a thin glycocalyx layer that is loosely bound to the cell.
Are slime layers made of polysaccharides?
The slime layer, which surrounds the bacterial cell, is an easily removable, diffuse, disorganized coating of extracellular material. It is made up mostly of polysaccharides and can be used to trap nutrients, enhance cell motility, bind cells together, or attach to smooth surfaces.
Where are slime layers found?
Many bacterial cells secrete some extracellular material in the form of a capsule or a slime layer. A slime layer is loosely associated with the bacterium and can be easily washed off, whereas a capsule is attached tightly to the bacterium and has definite boundaries.
What is the function of the slime capsule?
Function. The slime capsule can protect the bacteria from some toxic chemicals. The slime capsule is a defense against a phagocyte engulfing the bacteria.
What biological molecules can make up the bacterial capsule or slime layer?
Lab Test 1 Part 2QuestionAnswerwhat biological molecules can make up the bacterial capsule or slime layerCapsules are composed of polysaccharides or proteins.55 more rows
1. What are the Functions of Bacteria Capsules and Slime Layers?
A slime layer is a non-rigid matrix that can be easily deformed and cannot keep India Ink out. Many cells and their outer barriers make up biofilms...
2. What is the Composition of the Slime Layer?
A slime layer in bacteria is an unorganized layer of extracellular material that covers bacteria cells and is easily removed (e.g. by centrifugatio...
3. Is Glycocalyx Present in All Bacteria?
The glycocalyx is a viscous outer layer of fibres that spreads from the bacterium that is secreted by all bacteria. A capsule is a large, tightly b...
4. What are the functions of the capsule?
Following are the functions of capsule:Prevent Desiccation and Drying of the Cell: capsular polysaccharide binds a large amount of water, making th...
5. What are the key points about capsules?
Following are some points about capsules:A capsule is a 0.2m thick viscous layer that is securely connected to the cell wall of capsulated bacteria...
6. What is the slime layer and does it protect against phagocytosis?
The slime layer, which surrounds the bacterial cell, is an easily removable, diffuse, disorganized coating of extracellular material. It is made up...
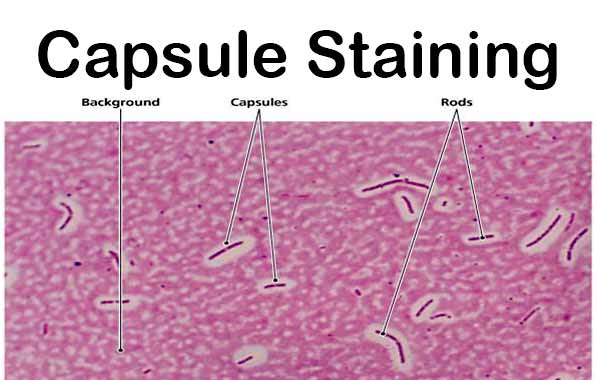
7. Where are capsules found and what is capsule stain?
Capsules are found just outside of gram-positive bacteria's murein (peptidoglycan) layer and gram-negative bacteria's outer membrane (lipopolysacch...
8. Where can I find notes on capsules and slimes?
Vedantu provides notes and questions on capsules and slimes. Professional educators produce content in such a way that it is easily understood and...
How do antibiotics reduce virulence?
Because of the abundance of so many bacteria that are increasing their resistance to antimicrobial agents such as antibiotics (these products inhibit cell growth or just kill the cell), there is new research coming out about new drugs that reduce virulence factors in some bacteria. Anti-virulent drugs reduce the pathogenic properties in bacteria, allowing the host to attack said bacteria, or allows antimicrobial agents to work. Staphylococcus aureus is a pathogenic bacteria that causes several human infections with a plethora of virulence factors such as: biofilm formation, quorum sensing, and exotoxins to name a few. Researchers took a look at Myricetin (Myr) as a multi-anti-virulence agent against S.areus and how it specifically impacts biofilm formation. After regular dosing it was found that biofilm formation decreased and the number of adhered cells on their specified media decreased without killing the cells. Myr is promising when surfaces are coated in the material, non-coated surfaces show a thick biofilm formation with a large quantity of cellular adherence; the coated material showed minimal cell clusters that were weakly adhered.
Why is slime not a biofilm?
Because a slime layer is loose and flowing, it does not aide the cell in its rigidity. While biofilms can be composed of slime layer producing bacteria, it is not typically not their main composition. Rather, a biofilm is made up of an array of microorganisms that come together to form a cohesive biofilm.
Why is slime overproduced?
While consisting mostly of polysaccharides, a slime layer may be over produced such that in a time of famine the cell can rely on the slime layer as extra food storage to survive. In addition, a slime layer may be produced in ground dwelling prokaryotes to prevent unnecessary drying due to annual temperature and humidity shifts.
How long does it take for slime to form?
Slime layers are amorphous and inconsistent in thickness, being produced in various quantities depending upon the cell type and environment. These layers present themselves as strands hanging extracellularly and forming net-like structures between cells that were 1-4μm apart. Researchers suggested that a cell will slow formation of the slime layer after around 9 days of growth, perhaps due to slower metabolic activity.
What is the slime layer?
A slime layer in bacteria is an easily removable (e.g. by centrifugation ), unorganized layer of extracellular material that surrounds bacteria cells. Specifically, this consists mostly of exopolysaccharides, glycoproteins, and glycolipids. Therefore, the slime layer is considered as a subset of glycocalyx .
What is the purpose of slime layer?
Cellular function. The function of the slime layer is to protect the bacteria cells from environmental dangers such as antibiotics and desiccation. The slime layer allows bacteria to adhere to smooth surfaces such as prosthetic implants and catheters, as well as other smooth surfaces like petri-dishes. Researchers found that the cells adhered ...
Why is concrete a problem?
A problem with concrete structures is the damage they receive during weather shifts, because if its porous nature there is an amount of water that can expand or contract the concrete depending on the environment. This damage makes these structures susceptible to sulfate attacks.
What is the slime layer in a Gram positive?
The capsule, which can be present in both gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, is distinct from the second lipid membrane, the bacterial outer membrane, which only exists in gram-negative bacteria and contains lipopolysaccharides and lipoproteins. A slime layer is created when the amorphous viscid secretion (that makes up the capsule) ...
Why does slime layer slow down?
Researchers believe that after 9 days of development, a cell's formation of the slime layer will slow, possibly due to slower metabolic activity. A bacterial capsule is similar to a slime layer, but it is more rigid. In comparison to their slime layer counterparts, capsules are more structured and difficult to extract.
What is the difference between a slime layer and a capsule?
A slime layer is loosely attached to the bacterium and can be washed away, while a capsule is firmly attached to the bacterium and has distinct boundaries.
What is the term for the slime layer?
The glycocalyx is a term that refers to both the capsule and the slime layer.
What is the capsule in bacteria?
The capsule is a polysaccharide film that extends beyond the cell envelope and is thus considered part of the bacterial cell's outer envelope. It's a well-organized layer that's difficult to remove and can cause a variety of diseases. The capsule, which can be present in both gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, ...
Why is the capsule considered a virulence factor?
The capsule is referred to as a virulence factor because it increases bacteria's capacity to cause disease (e.g. prevents phagocytosis). The capsule will protect cells from eukaryotic cells like macrophages engulfing them. n u m b e r s i x Phagocytosis can involve the presence of a capsule-specific antibody.
Which layer of the glycocalyx is most commonly found in bacteria?
As a result, the slime layer is assumed to be a branch of the glycocalyx. Although slime layers and capsules are most commonly found in bacteria, archaea may also have these structures. This structure and role knowledge are also transferable to these microorganisms.
