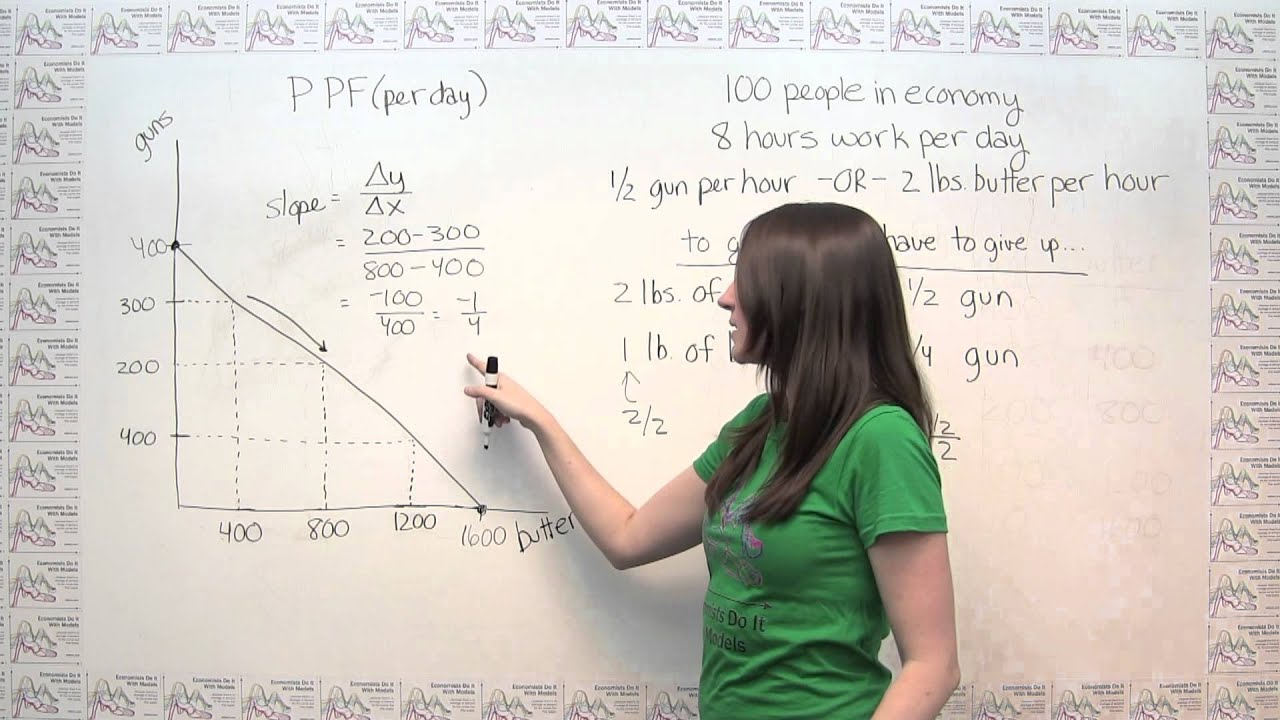
Is the slope of the production possibilities frontier positive or negative?
downward slopingThe production possibilities frontier is downward sloping: producing more of one good requires producing less of others. The production of a good has an opportunity cost. As time passes, the production possibilities frontier shifts outward due to the accumulation of inputs and technological progress.
Why is the slope of PPF negative?
Answer and Explanation: PPF is drawn on the assumption of fixed resources as well as technology. PPF has a negative or inverse slope that signifies that one of the two goods available needs to be sacrificed if the economy decides to increase the production of one of the goods.
What does the slope of the PPC tell us?
A production possibilities curve shows the combinations of two goods an economy is capable of producing. The downward slope of the production possibilities curve is an implication of scarcity. The bowed-out shape of the production possibilities curve results from allocating resources based on comparative advantage.
Why does PPF get steeper?
More generally, as society produces more and more of some good or service, the cost of production grows larger and larger relative to the cost of producing other goods or services. Thus, the slope of a PPF starts flat and becomes increasingly steeper.
Why is the PPF concave to the origin?
PPF is concave to origin because of the increasing marginal opportunity costs. That is more and more units of one commodity are sacrificed to gain an additional unit of another commodity. Due to this increasing marginal cost, PPF becomes more and more steep, thus the curve bends outwards and becomes concave to origin.
Why is the opportunity cost of production possibility frontier also called its slope?
Opportunity cost means the loss of the next best alternative available while choosing the one. The slope of the production possibilities frontier is equal to the opportunity cost of the good on the horizontal axis because it measures how much of good Y is given up for an increase in a unit of good X.
What may cause a PPF to shrink?
An inward shift of a PPF A PPF will shift inwards when an economy has suffered a loss or exhaustion of some of its scarce resources. This reduces an economy's productive potential.
What does it mean when the frontier shifts outward?
If there is an increase in land, labor or capital OR technology then the frontier will shift outwards. A shift out means that more of both products can be produced.
How can the Production-Possibilities Frontier be Shifted?
If the total amount of production factors like labor or capital increases, then the economy is able to produce more goods at any point along the frontier.
What are changes in the slope of the PPF?
Changes in the slope of the PPF are mainly linked to the production costs of the goods in the economy. Taking Economy A as an example, suppose that the total labor and capital inputs required to manufacture goods are summarized by the variable k. The 1-to-1 trade-off would only hold if carrots and potatoes both had the same k value, say 100 in the current economic conditions.
What would happen if the cost of producing 1 potato increased to 200?
Suppose that the cost of producing 1 potato increases to k= 200, and the cost of producing 1 carrot remains constant. In such a scenario, the trade-off would change, as producing 1 potato would require the economy to forego the production of 2 carrots.
How many units can an economy produce if it devotes all resources to producing potatoes?
We also see that if Economy A devotes all resources to producing potatoes, it would be able to produce 500 units. However, if we suppose that the economy sees profitability in both goods and wants to produce both, we encounter the idea of trade-off.
What are the three key performance indicators?
Governments and economists usually refer to three main key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess the strength of a nation's labor force. and capital are scarce. Therefore, there is only a finite amount of any one good that can be produced, and the scarce resources must be carefully allocated to the production of many goods.
What happens to the economy when the total amount of production factors like labor or capital increases?
If the total amount of production factors like labor or capital increases, then the economy is able to produce more goods at any point along the frontier. Conversely, during times of high unemployment and limited money supply, the frontier will retreat inwards and the total amount of goods that can be produced will decrease. ...
Can PPF shifts occur in real life?
Inward shifts in the PPF that are linked to regressions in technology could theoretically occur, but as technology has proven to generally continually improve over time, such a scenario is fairly unlikely to materialize in real life.
What is the production possibility frontier?
The production possibility frontier (PPF) is a visual representation used to illustrate the maximum possible output combinations of two separate products that can be produced using the same amount of limited resources.
How does the production possibility curve shift?
Businesses and economies can shift the production possibility curve outwards with certain improvements. For example, if a company develops a new technology that can speed up making cheese, the output would also increase. This increase in production will shift the curve outwards as long as the other production factors remain constant.
Why use the production possibility curve?
Businesses and economies will utilize the production possibility curve to improve efficiency.
What does shift in production possibility mean?
Shifts in the production possibility curve can symbolize either economic expansion or contraction. Different types of economies will require distinct approaches to determine the production possibility frontier. For example, in a market economy, supply and demand forces will determine the number of goods that should be produced.
What do curve points represent?
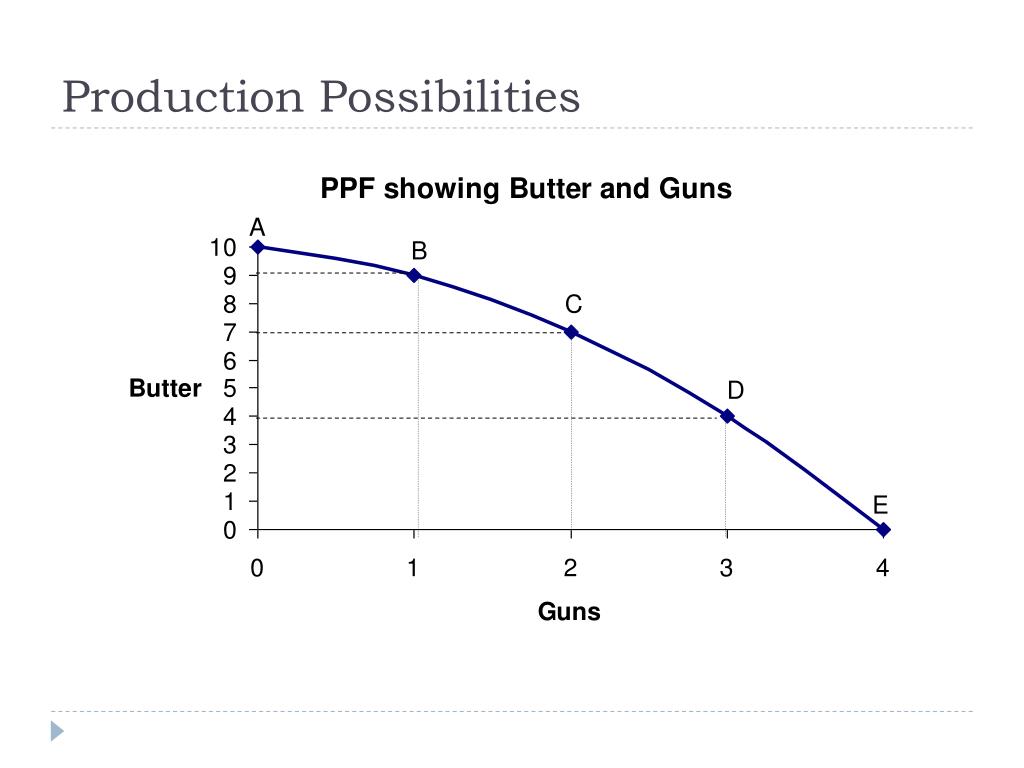
The curve points will represent various production levels that are most efficient for the economy, given the limited availability of resources.
What is the idea of a manufacturing combination?
The idea is to achieve production levels that will land on the production possibility curve, representing an efficient manufacturing combination. If the manufacturing combination falls within the curve, you are not using all of the resources available to you, and the manufacturing combination is regarded as inefficient.
How does an outward shift in production possibilities happen?
All economies want to see an outward shift in the production possibilities curve. This can only happen by generating more demand for either or both products. If demand increases, the production levels will need to be shifted as well to reflect those changes. Economies can also experience inward shifts in the graphical representation where the country may be experiencing a recession that caused a decrease in the demand and production for goods.
How is the production possibilities frontier constructed?
The production possibilities frontier is constructed by plotting all of the possible combinations of output that an economy can produce. In this example, let's say the economy can produce:
What happens to the production possibilities frontier?
If technology changes in an economy, the production possibilities frontier changes accordingly. In the example above, an advance in gun-making technology makes the economy better at producing guns. This means that, for any given level of butter production, the economy will be able to produce more guns than it did before. This is represented by the vertical arrows between the two curves. Thus, the production possibilities frontier shifts out along the vertical, or guns, axis.
What does the magnitude of the slope of the PPF mean?
Therefore, the magnitude, or absolute value, of the slope of the PPF represents how many guns must be given up in order to produce one more pound of butter between any 2 points on the curve on average.
What is a PPF curve?
The production possibilities frontier (PPF for short, also referred to as production possibilities curve) is a simple way to show these production tradeoffs graphically. Here is a guide to graphing a PPF and how to analyze it.
Why does the slope of the PPF increase?
Because of this, the magnitude of the slope of the PPF increases, meaning the slope gets steeper, as we move down and to the right along the curve.
What would happen if the economy was instead to experience an advance in butter-making technology?
If the economy were instead to experience an advance in butter-making technology, the production possibilities frontier would shift out along the horizontal axis, meaning that for any given level of gun production, the economy can produce more butter than it could before. Similarly, if technology were to decrease rather than advance, the production possibilities frontier would shift inward rather than outward.
What would happen if an economy instead faced a constant opportunity cost of one producing one of the goods?
If an economy instead faces a constant opportunity cost of one producing one of the goods, the production possibilities frontier would be represented by a straight line. This makes intuitive sense as straight lines have a constant slope.
What are the learning objectives of the production possibilities frontier?
Explain the production possibilities frontier. Just as individuals cannot have everything they want and must instead make choices, society as a whole cannot have everything it might want, either. Economists use a model called the production possibilities frontier (PPF) to explain the constraints society faces in deciding ...
What is the difference between a production possibilities frontier and a budget constraint?
A production possibilities frontier shows the possible combinations of goods and services that a society can produce with its limited resources. The first difference between a budget constraint and a production possibilities frontier is that the PPF, because it’s looking at societal choice, is going to have much larger numbers on the axes than those on an individual’s budget constraint.
What is the difference between a budget constraint and a production possibilities curve?
The most important difference between the two graphs, though, is that a budget constraint is a straight line, while a production possibilities curve is typically bowed outwards, i.e. concave towards the origin. The reason for this difference is pretty simple: the slope of a budget line is defined as the ratio of the prices of the two goods or services. No matter how many of each good or service a consumer buys, the prices stay the same. By contrast, the slope of a PPF is the cost to society of producing one good or service relative to the other good or service. When society reallocates resources from one product to another, the relative costs change, which means the slope of the PPF does also. Let’s dig into this.
What is the PPF model?
Economists use a model called the production possibilities frontier (PP F) to explain the constraints society faces in deciding what to produce . As you read this section, you will see parallels between individual choice and societal choice.
What would happen if we started at the other end of the PPF?
If we started at the other end of the PPF at point F and moved to point D, we would be moving doctors from teaching to healthcare with the result that the gain in healthcare would be large while the loss in education would be small (the same logic we used above). In short, the slope of the PPF from point F to D would be steep, and the opportunity cost of education in terms of healthcare would be high.
What happens to the slope of a PPF?
Thus, the slope of a PPF starts flat and becomes increasingly steeper. In the real world, of course, we have more than two goods and services, and we have more resources than just labor, but the general rule still holds.
What is the fifth lesson of the frontier?
For this reason, the frontier is usually drawn as a curved line that is concave to the origin. This curved line illustrates our fifth and final lesson. Lesson 5, the law of increasing opportunity cost. As you increase the production of one good, the opportunity cost to produce the additional good will increase.
How Does The production-possibilities Frontier Work?
How Can The Slope of The production-possibilities Frontier Change?
- Changes in the slope of the PPF are mainly linked to the production costs of the goods in the economy. Taking Economy A as an example, suppose that the total labor and capital inputs required to manufacture goods are summarized by the variable k. The 1-to-1 trade-off would only hold if carrots and potatoes both had the same k value, say 100 in the ...
How Can The production-possibilities Frontier Be Shifted?
- Outward or inward shifts in the PPF can be driven by changes in the total amount of available production factors or by advancements in technology. If the total amount of production factors like labor or capital increases, then the economy is able to produce more goods at any point along the frontier. Conversely, during times of high unemployment and limited money supply, the fronti…
More Resources
- CFI offers the Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)®certification program for those looking to take their careers to the next level. To learn more about related topics, check out the following CFI resources: 1. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) 2. Market Economy 3. Pigou Effect 4. Supply and Demand
How Does Production Possibility Frontier Work?
Production Possibility Frontier Example
- Let us understand the definition and aspects of the production possibility frontier at a deeper level with an example. Suppose an economy produces only two commodities, sugar and coffee. The production possibility diagram will show as a graph the most efficient output levels for the two goods. The curve points will represent various production levels that are most efficient for the e…
How Does Production Possibility Frontier Affect The Economy?
- A country can use this financial modelFinancial ModelFinancial modeling refers to the use of excel-based models to reflect a company's projected financial performance. Such models represent the financial situation by taking into account risks and future assumptions, which are critical for making significant decisions in the future, such as raising capital or valuing a busines…
Recommended Articles
- This article has been a guide to Production Possibility Frontier. Here, we discuss how it works, along with an example. You may learn more about financing from the following articles – 1. Supply Curve 2. Demand Curve 3. Lorenz Curve