What are some characteristics of Spirogyra?
Vegetative Structure of Spirogyra
- Cells are green-coloured, un-branched filamentous and cylindrical shaped.
- Basal differentiation is absent in free-floating species.
- In sedentary species, basal differentiation may occur in the form of an attachment organ, called holdfast or haptera.
- The cell walls have three distinct layers, and they are striated.
Is spirogyra a protozoan or an algae?
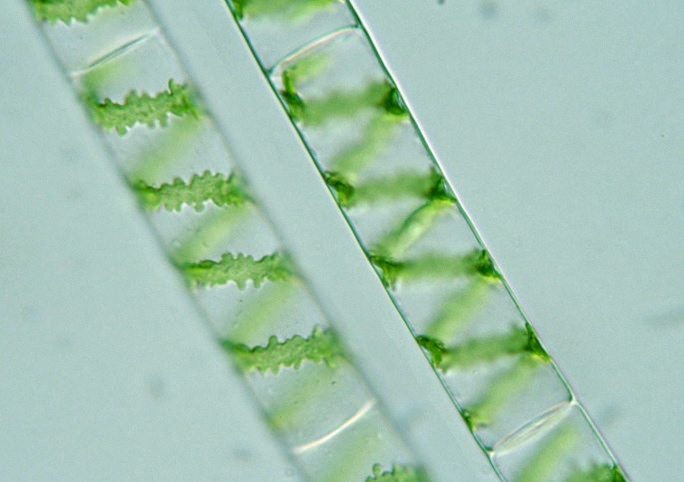
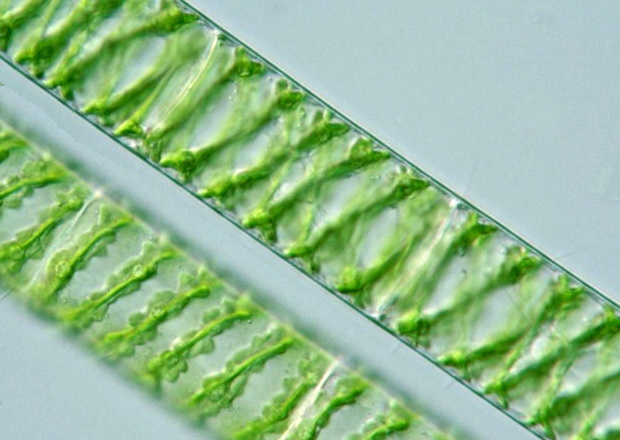
Spirogyra is a filamentous green algae of the, named for the helical or spiral arrangement of the chloroplasts.It is commonly found in freshwater areas. Spirogyra measures approximately 10 to 100μm in width and may stretch centimeters long. This particular algal species, commonly
Is Spirogyra included in algae or simple plants?
Spirogyra 1 Spirogyra Spirogyra is a member of the Algae. These are simple plants ranging from single-celled organisms (Chlamydomonas, Euglena) to complex seaweeds.They contain chlorophyll and make their food by photosynthesis. Spirogyra is a filamentous alga. Its cells form long, thin strands that, in vast numbers, contribute to the familiar green, slimy ‘blanket weed’ in ponds.
What group does Spirogyra belong to?
Spirogyra (common names include water silk, mermaid's tresses, and blanket weed) is a filamentous charophyte green alga of the order Zygnematales, named for the helical or spiral arrangement of the chloroplasts that is characteristic of the genus. It is commonly found in freshwater habitats, and there are more than 400 species of Spirogyra in the world. ...
What is the species name for Spirogyra?
SpirogyraWater silk / Scientific name
How many species of Spirogyra are there?
380 speciesThe genus Spirogyra is abundant in freshwater habitats worldwide, and comprises approximately 380 species.
How many species of Spirogyra is from India?
A total 12 species of Spirogyra Link was recorded from brackish water of Indian Sundarbans and its adjoining areas. Spirogyra dubia and Spirogyra ternata are found in the present study which was reported earlier.
What group does Spirogyra belong to?
algaeThallophyta of the plant kingdom includes algae. They have an undifferentiated body, reproduce by spores, are found in aquatic habitat and lack vascular tissues. Spirogyra, Chlamydomonas belong to this division.
What are 5 characteristics of Spirogyra?
Spirogyra Characteristics Each chloroplast houses several pyrenoids. Their bodies are characterized by multicellular filaments, which are present underneath a mucilaginous sheath. Pectin and cellulose can be found on the cell walls of such algae. Reproduction occurs asexually, sexually and vegetatively.
Is Spirogyra a plant or fungi?
Spirogyra is an example of Algae. It is a unicellular, flagellate algae, found in stagnant water and damp soil.It is a non-flowering plant and belongs to the group algae of Thallophyta.
Why Spirogyra is called algae?
The filamentous algae genus Spirogyra owes its name to the characteristic spiral shape of the chloroplasts possessed by its members. Sometimes alternatively known as water-silk, mermaid's tresses, or pond scum, a large presence of the unbranched algae often indicates the nutrient enrichment of freshwater bodies.
Who is known as father of algae?
Mandayam Osuri Parthasarathy Iyengar (15 December 1886–10 December 1963) was a prominent Indian botanist and phycologist who researched the structure, cytology, reproduction and taxonomy of algae. He is known as the "father of Indian phycology" or "father of algology in India".
Who discovered Spirogyra?
Indian species of spirogyra in which Prof Iyengar discovered class 11 biology CBSE.
Is a Spirogyra an algae?
Filamentous algae (Spirogyra, Cladophora, and many other varieties) Common names: Pond scum, water net, frog spittle, moss.
How many species of Spirogyra have been recorded to form Aplanospores?
We induced conjugation or aplanospore formation under controlled laboratory conditions in 15 of the 52 strains, which allowed us to identify 13 species. Two of the thirteen species were assignable to a related but taxonomically uncertain genus, Temnogyra, based on the unique characteristics of sexual reproduction.
How many species of Volvox are there?
20 speciesVolvox, genus of some 20 species of freshwater green algae (division Chlorophyta) found worldwide. Volvox form spherical or oval hollow colonies that contain some 500 to 60,000 cells embedded in a gelatinous wall and that are often just visible with the naked eye.
Who is known as father of algae?
Mandayam Osuri Parthasarathy Iyengar (15 December 1886–10 December 1963) was a prominent Indian botanist and phycologist who researched the structure, cytology, reproduction and taxonomy of algae. He is known as the "father of Indian phycology" or "father of algology in India".
How is Spirogyra named?
The filamentous algae genus Spirogyra owes its name to the characteristic spiral shape of the chloroplasts possessed by its members. Sometimes alternatively known as water-silk, mermaid's tresses, or pond scum, a large presence of the unbranched algae often indicates the nutrient enrichment of freshwater bodies.
How Are Spirogyra Classified?
Animals are most broadly classified by the Domain. The classification system can further be broken down into (in order) by Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, and Species. Spirogyra are a genus comprised of over 400 species.
What Are the Types Spirogyra?
Species of Spirogyra can be incredibly difficult to define. This is because their defining characteristics are based mostly on sexual reproduction. To properly identify a species of Spirogyra, the reproductive process must be identified in one or more of its stages. Wild-sampled spores can help identify different species.
How Do Spirogyra Produce Energy?
Spirogyra do not eat in a traditional sense. Instead, Spirogyra undergoes photosynthesis to harness energy from the sunlight and turn it into usable chemical energy. Photosynthesis can be separated into two categories: oxygenic and anoxygenic. Oxygenic photosynthesis is the most common amongst Spirogyra.
Where Do Spirogyra Live?
Spirogyras are found in freshwater environments like shallow ponds, ditches, and at the edges of lakes. They are generally free-floating and can be found in large mats of other Spirogyra.
How Do Spirogyra Reproduce?
Spirogyras can reproduce in three different ways: vegetatively, asexually, and sexually. Vegetative reproduction occurs through fragmentation. Asexual reproduction occurs through three different asexual spores. Sexual reproduction occurs through conjugation by the zygospore.
What is the order of zygnematales?
Order: Zygnematales – Also known as the conjugates, this order consists of 18 genera with over 600 species. The Spirogyra are amongst the best-known members of this order. Spirogyras are typically used as examples in Biology classes to best describe this order and green algae as a whole. Almost all species live in freshwater and are commonly called ‘pond scum’ since they collect in filamentous mats within water that collects on just about everything that it touches. Zygnematales have plastids which are unique membrane-bound organelles that are responsible for manufacturing food. Members of the Zygnematales produce either asexually by fragmentation or sexually by conjugation.
What is the name of the algae that has helical shape?
Spirogyra are a threadlike microscopic genus of green alga that are known for their helical shape of chloroplasts. These DNA-resembling algae are found in freshwater environments with over 400 species known in existence today. They can range anywhere from 10 to 100 micrometers wide and several centimeters long and are typically found in freshwater ...
How do spirogyra reproduce?
Spirogyra species can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Asexual, or vegetative, reproduction occurs by simple fragmentation of the filaments. Sexual reproduction occurs by a process known as conjugation, in which cells of two filaments lying side by side are joined by outgrowths called conjugation tubes.
What is conjugation in spirogyra?
Conjugation, a form of sexual reproduction in Spirogyra. The conjugation tubes between the two algal filaments allow the contents of one cell to fuse with those of the other, forming a zygote. The characteristic spiral chloroplasts are clearly visible.
What is the structure of the filaments of algae?
Each cell of the filaments features a large central vacuole, within which the nucleus is suspended by fine strands of cytoplasm. The chloroplasts form a spiral around the vacuole and have specialized bodies known as pyrenoidsthat store starch. The cell wallconsists of an inner layer of celluloseand an outer layer of pectin, which is responsible for the slippery texture of the algae.
What are the bodies of the chloroplasts?
The chloroplasts form a spiral around the vacuole and have specialized bodies known as pyrenoids that store starch. The cell wall consists of an inner layer of cellulose and an outer layer of pectin, which is responsible for the slippery texture of the algae. Spirogyra species can reproduce both sexually and asexually.
What is green algae?
green algae. Green algae, members of the division Chlorophyta, comprising between 9,000 and 12,000 species. The photosynthetic pigments (chlorophylls a and b, carotene, and xanthophyll) are in the same proportions as those in higher plants.
What is an encyclopedia editor?
Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree. ...
Where do spirogyras live?
spirogyra, (genus Spirogyra), any member of a genusof some 400 species of free-floating green algae(division Chlorophyta) found in freshwater environmentsaround the world. Named for their beautiful spiral chloroplasts, spirogyras are filamentous algaethat consist of thin unbranched chains of cylindrical cells. They can form masses that float near the surface of streams and ponds, buoyed by oxygenbubbles released during photosynthesis. They are commonly used in laboratory demonstrations.
What is the name of the structure formed by two filaments of spirogyra?
In scalariform conjugation, two filaments of Spirogyra come together and lie side by side. The structure formed looks like a ladder and thus it is named as scalariform conjugation or H-shape conjugation. Tube-like structure develops from each cell of the two filaments lying together.
What is the name of the gametes that fail to fuse during sexual reproduction?
Zygospores are also known as parthenos pores. These are the gametes, that failed to fuse during sexual reproduction and develop into a new filament asexually. Sexual reproduction in Spirogyra is isogamous which means that male and female gametes of same size fuse together in the sexual reproduction.
Why is spirogyra classified as chlorophyll?
When there is enough sunlight and warmth they produce large amounts of oxygen, which get stored as bubbles between the tangled filaments. (image will be uploaded soon) Spirogyra is classified under Chlorophyta due to the presence of chlorophyll. The genus contains around 400 species.
What is lateral conjugation?
In lateral conjugation, adjacent cells of a Spirogyra sp work as male and female gametes. Conjugation tubes are formed between cells of the same filament. Lateral conjugation is of two types:
What is asexual reproduction?
Asexual reproduction can be found in few species of Spirogyra. Asexual reproduction is carried out by the formation of azygospores, akinetes or aplanospores. Formation of aplanospores occurs under unfavourable conditions. The protoplast shrinks and forms a wall around it. This results in the formation of aplanospores.
How many chloroplasts are there in a cell?
In each cell, there is a nucleus, cytoplasm, a large central vacuole and spiral chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are ribbon-shaped and arranged spirally. There may be 1-16 chloroplasts present in a cell. Chloroplast contains many pyrenoids in a row. Pyrenoids store starch and protein.
What do aquatic organisms eat?
They increase the level of oxygen in their habitat. Many aquatic organisms feed on them. Each cell of the filaments features a large central vacuole, within which the nucleus is suspended by fine strands of cytoplasm. The chloroplasts form a spiral around the vacuole.
What is the name of the spores that develop into a new filament?
Akinetes and aplanospores are non-motile spores, which develop into a new filament under favourable conditions after the decay of the parent filament
How do aplanospores form?
Formation of aplanospores occurs under unfavourable conditions. The protoplast shrinks and forms a wall around it. This results in the formation of aplanospores
How many species of spirogyra are there?
There are around 400 species of Spirogyra found. The genus Spirogyra is named after the unique spiral chloroplast present in the cells of algae. Spirogyra are photosynthetic and contribute substantially to the total carbon dioxide fixation carried out. They increase the level of oxygen in their habitat.
What is a spirogyra?
Spirogyra are free-floating green algae present in freshwater habitats such as ponds, lakes, etc. Spirogyra are commonly known as “water silk or pond silk”. They have a filamentous and unbranched vegetative structure. There are around 400 species of Spirogyra found. The genus Spirogyra is named after the unique spiral chloroplast present in ...
Why is the spirogyra slimy?
Structure of Spirogyra. They are present as a slimy mass due to the presence of mucilage sheath around the filament. The cell wall is made up of two layers, inner cellulose and outer pectose. The slimy mucilage sheath is due to the dissolution of pectose in water.
Which canal is formed by the cell having male gamete and joins the adjacent cell having female gamete?
Indirect lateral conjugation: The conjugation canal is formed by the cell having male gamete and joins the adjacent cell having female gamete
Why are cells slimy?
They are present as a slimy mass due to the presence of mucilage sheath around the filament. The cell wall is made up of two layers, inner cellulose and outer pectose. The slimy mucilage sheath is due to the dissolution of pectose in water. In each cell, there is a nucleus, cytoplasm, a large central vacuole and spiral chloroplasts.
What are the different types of zygospores?
We recognised three types of zygospores or aplanospores (Types Z1–Z3; Supplementary Fig. S3 ). In the first type, the zygospores and aplanospores were ovoid in shape (resembling a watermelon) 4, and the mesospores were single- or double-layered (Type Z1). In the second type, the zygospore was ellipsoidal (resembling an American football) 4 and the mesospores were single-layered (Type Z2). In the third type, the zygospore was lenticular (a compressed spheroid) and the mesospores were single- or double- layered (Type Z3).
How many species of zygospores are there?
Twelve species formed zygospores and one species formed aplanospores. Nine of the twelve species that formed zygospores developed conjugation tubes from both male and female gametangia. The other three of the twelve that formed zygospores produced conjugation tubes from only the male gametangia; two of these three underwent unequal division of the mother gametangial cell to form one small and one large daughter cell, which developed into sterile and gametangial cells, respectively. We classified the observed modes of zygospore and aplanospore formation into five categories: Types C1–C5 (Supplementary Fig. S2 ).
How much of the species of spirogyra have been subjected to reliable taxonomic and?
Less than 10% of the species of Spirogyra -like algae have been subjected to reliable taxonomic and phylogenetic analyses 9, 11. Laboratory cultivation to induce sexual reproduction is a promising approach for the development of a modern taxonomic system for Spirogyra and its relatives.
What class is spirogyra link?
Spirogyra Link (Zygnemataceae, Zygnematales) is a genus in the Class Zygnematophyceae (Conjugatophyceae), which is a component member of the Infrakingdom Streptophyta 1, 2. Spirogyra has long been included in high school biology curricula. The genus is widely distributed in freshwater habitats including flowing water, ...
Which clade has a transverse wall?
Clade I contained all species with replicate transverse walls (type V3; e.g. S. dentireticulata chiA101 [JPS003], S. hopeiensis biw0302 [JPS004], and S. semiornata chiA304 [JPS014]), and several strains with plane transverse walls (type V1; e.g. S. longata chiA305 [JPS005] and kit0201 [JPS006]) (Figs 1 and 6 ). Vegetative cells of all of the identified species in this clade were relatively narrow (20–32 μm wide) with one chloroplast per cell 4, 11. Sexual reproduction and zygospore types were diverse (Types C3, C5, Z1 and Z2; Table 1 ).
How many strains are there in RBCl?
The 122 isolated strains were classifiable into 52 rbcL -types by differences in rbcL sequences; thus, we selected 52 strains with different rbcL sequences for further study (JPS001–JPS052; Supplementary Table S1 ). We attempted to induce conjugation in these strains.
Where were spirogyra algae collected?
Samples containing filaments of Spirogyra -like algae were collected from ponds or paddy fields in Japan (Supplementary Table S1 ). Clones were established from fragmented filaments using a pipette-washing procedure 17. The clones were grown in 100 mL of Closterium (C) medium 18 in glass vessels (50 mm × 95 mm) held at 20 °C under a 14:10 hour light/dark cycle. We established cultures of 122 new strains of Spirogyra -like algae from 26 localities in Japan (Supplementary Table S1 ).
What are the cells that contract and lose water called?
For this purpose, some cells of the filament contract, lose water, and form thick walls of cellulose and pectin. These spores are called akinetes that can form new filaments during favorable conditions. The process of formation of aplanospores is similar to that of akinetes, but the former have thinner walls.
How do conjugation tubes form?
In lateral conjugation, the contents of adjacent cells act like male and female gametes. So the adjacent cells of the same filament develop conjugation tubes. There are two types of lateral conjugation – direct and indirect. The style of conjugation canal formation differs in these two methods. In direct lateral conjugation, conjugation canals develop when the end walls of the adjacent cells lose contact with their middle lamella. In other words, the adjacent cells fuse through the middle lamella. In case of indirect lateral conjugation, the cells that act like male gametes form separate conjugation canals that connect with their adjacent cells, which act like female gametes. In both cases, the male gametes enter their adjacent cells and fuse with the female gametes. After conjugation, alternate cells of the same filament have zygotes and others will be empty.
How does spirogyra reproduce?
In scalariform conjugation, two filaments come together and lie side by side. The mucilage of the cell walls holds them together. The cells of each filament develop small tube-like structures that fuse together to form conjugation canals. The male gametes of one filament travel through these canals and fuse with the female gametes in the other filament, to form zygotes, which are oval or circular. After conjugation, one filament becomes empty, and the other has zygotes. Once the zygotes are released, the parent filaments die. The zygotes wait for favorable conditions to germinate.
What are the parts of a spirogyra?
Spirogyra – Parts and Structure. Spirogyra has long, unbranched filaments with cylindrical cells that are connected end to end. The cell wall is made up of an outer layer of pectin and an inner layer of cellulose. The inner surface of the cell wall is lined with a thin layer of cytoplasm. The spiraled ribbon-shaped chloroplasts are embedded in this ...
What happens to the male and female gametes after conjugation?
After conjugation, alternate cells of the same filament have zygotes and others will be empty . Spirogyra is commonly found in clean water and it produces food through the process of photosynthesis.
Why do pond silk filaments shine?
Spirogyra is also known as pond silk, as its filaments shine like silk due to the presence of mucilage. The outer cell wall has pectin which dissolves continuously, thereby producing the mucilage. Spirogyra filaments are slippery and float in large masses.
How many micrometers are in a spirogyra?
The cells are long and thin, and each spirogyra filament measures between 10 to 100 micrometer in width. Sometimes, these filaments develop root-like structures for attaching themselves to ...
What Are Spirogyras?
Frog spittle, mermaid hair and pond scum are a few of the nicknames for an interesting type of freshwater algae called spirogyra. What is spirogyra? Spirogyra characteristics include their filamentous shape, which means long and thin. Typical spirogyras are 10-100 micrometers in width and several centimeters in length.
Spirogyra Cells: Are Spirogyra Unicellular or Multicellular?
The cellular makeup is another unique spirogyra characteristic. Are spirogyra unicellular or multicellular? The most comprehensive answer is both. Spirogyra are unicellular organisms that connect to form multicellular filaments.
Spirogyra Locomotion
How do spirogyra move? As spirogyra filaments congregate near the surface of their freshwater source, they form sheets or mats. They line up very close and parallel without actually, physically attaching to each other. Access to sunlight is essential for spirogyra, since they make their own food via the process of photosynthesis.