Wave velocity is sometimes also called the propagation velocity or propagation speed, because the disturbance propagates from one location to another. Many people think that water waves push water from one direction to another.
What is a wave?
A wave is a disturbance in a medium that carries energy without a net movement of particles. It may take the form of elastic deformation, a variati...
Define frequency of a wave.
Frequency of a wave is the number of waves passing a point in a certain time. The unit of frequency is hertz (Hz) which is equal to one wave per se...
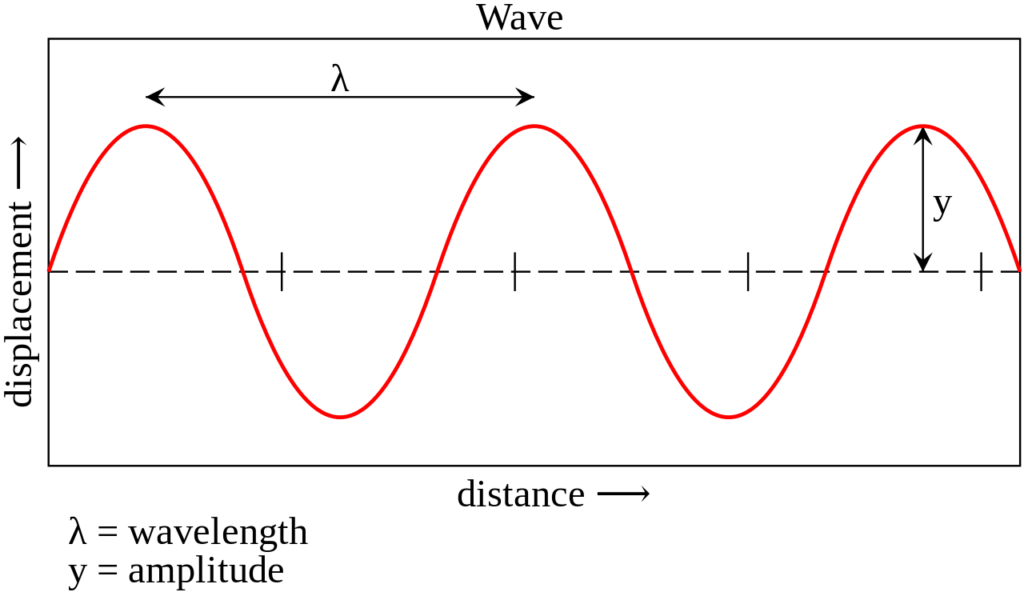
Define amplitude of a wave.
Amplitude is the maximum displacement from the neutral position. This represents the energy of the wave. Greater amplitude carries greater energy.
What are electromagnetic waves?
Electromagnetic waves are the disturbance that does not need any object medium for propagation and can easily travel through the vacuum. They are p...
Give some examples of electromagnetic waves.
Radio signals, light rays, x-rays, and cosmic rays are some of the examples of electromagnetic waves.
What happens when a wave bounces off a person's hand?
The wave will reflect or bounce off the person's hand. When a wave undergoes reflection, it remains within the medium and merely reverses its direction of travel. In the case of a slinky wave, the disturbance can be seen traveling back to the original end.
What is the difference between a wave and a medium?
One theme of this unit has been that "a wave is a disturbance moving through a medium." There are two distinct objects in this phrase - the "wave" and the "medium." The medium could be water, air, or a slinky. These media are distinguished by their properties - the material they are made of and the physical properties of that material such as the density, the temperature, the elasticity, etc. Such physical properties describe the material itself, not the wave. On the other hand, waves are distinguished from each other by their properties - amplitude, wavelength, frequency, etc. These properties describe the wave, not the material through which the wave is moving. The lesson of the lab activity described above is that wave speed depends upon the medium through which the wave is moving. Only an alteration in the properties of the medium will cause a change in the speed.
Why is the speed of the waves in rows 6-8 different than the speed of the wave in rows 1-5?
The obvious cause of this difference is the alteration of the tension of the rope. The speed of the waves was significantly higher at higher tensions. Waves travel through tighter ropes at higher speeds.
How does a slinky wave travel?
A slinky wave that travels to the end of a slinky and back has doubled its distance. That is, by reflecting back to the original location, the wave has traveled a distance that is equal to twice the length of the slinky. Reflection phenomena are commonly observed with sound waves.
What is the behavior of waves at the end of a medium?
One behavior that waves undergo at the end of a medium is reflection. The wave will reflect or bounce off the person's hand.
What happens when you let out a holler?
Reflection phenomena are commonly observed with sound waves. When you let out a holler within a canyon, you often hear the echo of the holler. The sound wave travels through the medium (air in this case), reflects off the canyon wall and returns to its origin (you). The result is that you hear the echo (the reflected sound wave) of your holler. A classic physics problem goes like this:
What is the wave equation?
The Wave Equation. A wave is a disturbance that moves along a medium from one end to the other. If one watches an ocean wave moving along the medium (the ocean water), one can observe that the crest of the wave is moving from one location to another over a given interval of time. The crest is observed to cover distance.
What is the unit of time for a wave?
Period – The period of a wave is the time for a particle on a medium to make one complete vibrational cycle. As the period is time, hence is measured in units of time such as seconds or minutes. Frequency – Frequency of a wave is the number of waves passing a point in a certain time. The unit of frequency is hertz (Hz) which is equal ...
What is the difference between amplitude and displacement?
Amplitude is the maximum displacement from the neutral position . This represents the energy of the wave. Greater amplitude carries greater energy. Displacement is the position of a particular point in the medium as it moves as the wave passes. Maximum displacement is the amplitude of the wave.
What is mechanical wave?
Mechanical waves: A wave which needs a medium in order to propagate itself. Sound waves, waves in a Slinky, and water waves are all examples of this.
What are the properties of waves?
Properties of Waves. The prime properties of waves are as follows: Amplitude – Wave is an energy transport phenomenon. Amplitude is the height of the wave, usually measured in meters. It is directly related to the amount of energy carried by a wave.
What is the introduction of waves?
Introduction of Waves. Transfers energy. Usually involves a periodic, repetitive Movement. Does not result in a net movement of the medium or particles in the medium (mechanical wave). There are some basic descriptors of a wave. Wavelength is the distance between an identical part of the wave.
What is a wave?
Wave. A wave is a disturbance in a medium that carries energy without a net movement of particles. It may take the form of elastic deformation, a variation of pressure, electric or magnetic intensity, electric potential, or temperature.
What is the term for a disturbance that does not need any object medium for propagation and can easily travel through the?
Electromagnetic Waves: These waves are the disturbance that does not need any object medium for propagation and can easily travel through the vacuum. They are produced due to various magnetic and electric fields. The periodic changes that take place in magnetic electric fields and therefore known as Electromagnetic Wave.
What type of sound wave is found only in solids?
Sound waves in solids are composed of compression waves (just as in gases and liquids), and a different type of sound wave called a shear wave, which occurs only in solids. Shear waves in solids usually travel at different speeds, as exhibited in seismology.
How fast is sound?
The speed of sound is the distance travelled per unit of time by a sound wave as it propagates through an elastic medium. At 20 °C (68 °F), the speed of sound in air is about 343 metres per second (1,235 km/h; 1,125 ft/s; 767 mph; 667 kn), or a kilometre in 2.9 s or a mile in 4.7 s. It depends strongly on temperature as well as the medium through which a sound wave is propagating. At 0 °C (32 °F), the speed of sound is about 331 metres per second (1,192 km/h, 741 mph).
How does temperature affect sound?
Since temperature (and thus the speed of sound) decreases with increasing altitude up to 11 km, sound is refracted upward, away from listeners on the ground, creating an acoustic shadow at some distance from the source. The decrease of the speed of sound with height is referred to as a negative sound speed gradient .
What is the main factor that affects the speed of sound?
In the Earth's atmosphere, the chief factor affecting the speed of sound is the temperature . For a given ideal gas with constant heat capacity and composition, the speed of sound is dependent solely upon temperature; see Details below. In such an ideal case, the effects of decreased density and decreased pressure of altitude cancel each other out, save for the residual effect of temperature .
How can sound transmission be illustrated?
The transmission of sound can be illustrated by using a model consisting of an array of spherical objects interconnected by springs.
What does C mean in math?
The speed of sound in mathematical notation is conventionally represented by c, from the Latin celeritas meaning "velocity".
How fast does sound travel?
However, the speed of sound varies from substance to substance: typically, sound travels most slowly in gases, faster in liquids, and fastest in solids. For example, while sound travels at 343 m/s in air, it travels at 1,481 m/s in water (almost 4.3 times as fast) and at 5,120 m/s in iron (almost 15 times as fast).
Answer
The material or substance that a wave moves through is called a MEDIUM. The medium affects the speed of the wave that passes through it. One factor that affects the speed of a wave is the TYPE of medium. Some waves move faster in solids and some waves move faster in liquids and gases.
New questions in Physics
What is the force of friction in a scenario when friction does 375 J of work in bringing a car to a stop after it slides along the road for 25 m?
