
What was the Square Deal
Square Deal
The Square Deal was President Theodore Roosevelt's domestic program. Roosevelt reflected three basic goals: conservation of natural resources, control of corporations, and consumer protection. These three demands are often referred to as the "three Cs" of Roosevelt's Square Deal. Thus, it aimed at helping middle class citizens and involved attacking plutocracy and bad trusts while at th…
What is the Square Deal in history?
She also recently served on the Test Development Committee for the SAT U.S. History Subject Test. The Square Deal refers to Theodore Roosevelt’s domestic policies that focused on the “Three C’s”: Conservation of natural resources. These reforms fundamentally redefined the relationship between the federal government and the economy.
What did Roosevelt say about the Square Deal in 1910?
In 1910, Roosevelt summarized his domestic policies by saying: I stand for the square deal.
What does “I am for the Square Deal” mean?
But when I say that I am for the square deal, I mean not merely that I stand for fair play under the present rules of the game, but that I stand for having those rules changed so as to work for a more substantial equality of opportunity and of reward for equally good service.
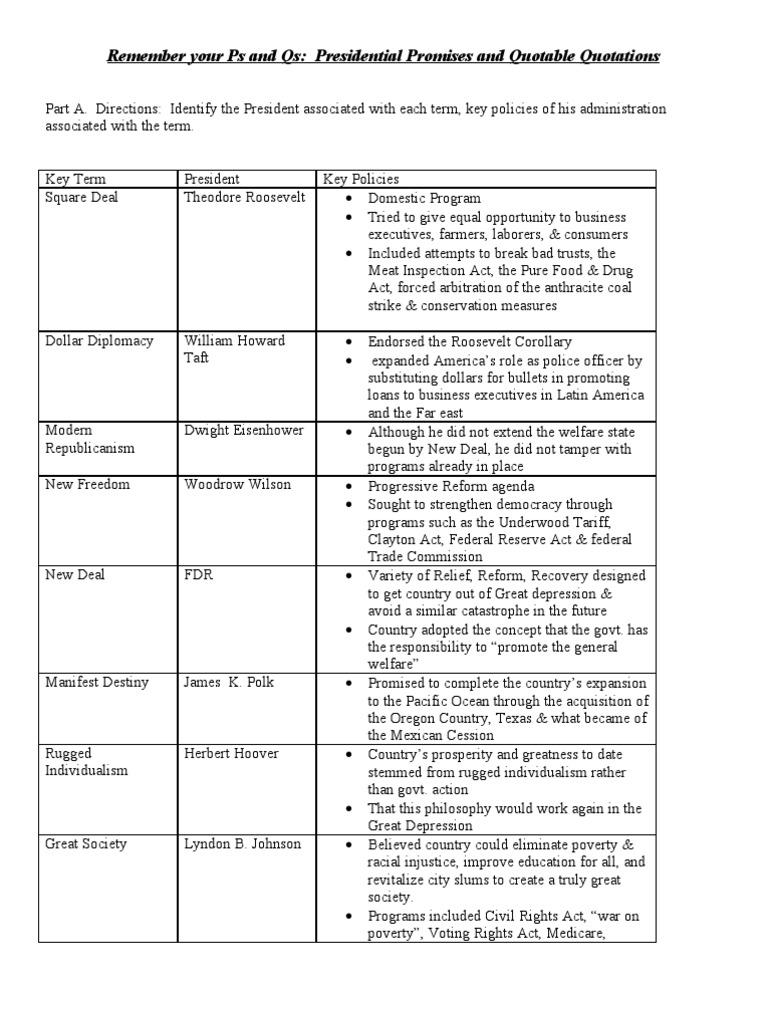
What did the Square Deal Do Apush?
The Square Deal refers to Theodore Roosevelt's domestic policies that focused on the “Three C's”: Control of corporations, Consumer protection. Conservation of natural resources.
What is the Square Deal and why is it important?
Enacted through Theodore Roosevelt's presidency in the early 20th century, the Square Deal was a set of policies that attempted to prevent further labor abuses and improve workplace safety, protect the natural landscape, and improve the overall health and well-being of Americans.
What does Square Deal mean in US history?
Square Deal. noun U.S. History. the stated policy of President Theodore Roosevelt, originally promising fairness in all dealings with labor and management and later extended to include other groups.
What did Roosevelt's Square Deal accomplish?
Parker by 336 to 140 electoral votes—Roosevelt put teeth into his Square Deal programs. He pushed Congress to grant powers to the Interstate Commerce Commission to regulate interstate railroad rates. The Hepburn Act of 1906 conveyed those powers and created the federal government's first true regulatory agency.
What was the Square Deal quizlet?
It called for control of corporations, consumer protection, and conservation of natural resources. It denounced special treatment for the large capitalists and is the essential element to his trust-busting attitude. This deal embodied the belief that all corporations must serve the general public good.
What did the Square Deal support?
More recently, historians have distilled the Square Deal to the “three C's” of consumer protection, corporate regulation, and conservationism, as shorthand for the most important domestic goals of Theodore Roosevelt's presidency.
Was the Square Deal successful?
Square Deal was one of the most successful policy programs that had been initiated by the government. It was popular among both the liberals and conservatives alike. As a result, several acts were passed including the Sherman Antitrust Act which stopped firms that were bad monopolies and encouraged the good ones.
Was the Square Deal successful?
Square Deal was one of the most successful policy programs that had been initiated by the government. It was popular among both the liberals and conservatives alike. As a result, several acts were passed including the Sherman Antitrust Act which stopped firms that were bad monopolies and encouraged the good ones.
How do you use Square Deal in a sentence?
All we want is a fair and square deal. It is in the national interest to see that the miners get a fair and square deal. I do not care what anybody says, farming has not had a square deal. We will give the industry a square deal.
What did Woodrow Wilson's New Freedom do?
The New Freedom sought to achieve this vision by attacking what Wilson called the Triple Wall of Privilege — the tariff, the banks, and the trusts. Tariffs protected the large industrialists at the expense of small farmers. Wilson signed the Underwood-Simmons Act into law in 1913, which reduced tariff rates.
What did the Hepburn Act accomplish?
The Hepburn Act is a 1906 United States federal law that expanded the jurisdiction of the Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) and gave it the power to set maximum railroad rates. This led to the discontinuation of free passes to loyal shippers.
Summary
Was a domestic program propagated by Theodore Roosevelt. It was based on aimed at the middle class citizen.
Exact Definition
Was a domestic program propagated by Theodore Roosevelt. It was based on 3 basic ideas; conservation of natural resources, control of corporations, and consumer protection. This was entirely aimed at the middle class citizen.
Importance
It aimed at helping middle class citizens and involved attacking plutocracy and bad trusts while at the same time protecting business from the extreme demands of organized labor. This led to the creation of several commissions who were tasked with regulating big business.
What is the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People?
National Association for the Advancement of Colored People; an organization formed in 1909 which aimed for equality among all races.
What is the central figure of a political system?
A political system in which the president is the central figure and participates actively in both foreign and domestic policy.
