What is the stage of mitosis?
The major stages of mitosis are prophase (top row), metaphase and anaphase (middle row), and telophase (bottom row).
Which phase of mitosis is shown in the diagram?
The phase of mitosis shown in the diagram is metaphase. b. This is an animal cell.
What are the 4 stages phases of mitosis in order?
These phases are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Which stage of mitosis is the cell in the center of this image in?
Metaphase. During metaphase, spindle fibers attach to the centromere of each pair of sister chromatids (Figure below). The sister chromatids line up at the equator, or center, of the cell. This is also known as the metaphase plate.
What is meiosis with diagram?
Meiosis is a type of cell division in which a single cell undergoes division twice to produce four haploid daughter cells. The cells produced are known as the sex cells or gametes (sperms and egg)....Cytokinesis II.BIOLOGY Related LinksGastrointestinal TractHeart Diagram4 more rows•Dec 6, 2021
What does the telophase look like?
0:131:42What happens in telophase? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipNext if you take a look at the shape of the cell during telophase. You will notice that the cell isMoreNext if you take a look at the shape of the cell during telophase. You will notice that the cell is beginning to elongate and that it is pinching in in the middle.
What happens in the 5 stages of mitosis?
They are also genetically identical to the parental cell. Mitosis has five different stages: interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. The process of cell division is only complete after cytokinesis, which takes place during anaphase and telophase.
What are the 4 stages of meiosis?
Meiosis I consists of four phases: prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, and telophase I.
What are the 4 stages of interphase?
By studying molecular events in cells, scientists have determined that interphase can be divided into 4 steps: Gap 0 (G0), Gap 1 (G1), S (synthesis) phase, Gap 2 (G2).
What is the stage in the mitosis that is frequently observed Why?
Expert-verified answer Knowing this, metaphase is one of the most frequently observed stages of mitosis as this is the stage that the cell organizes its chromosomes along the metaphase plate (i.e, the equator of the cell).
Is a stage of mitosis quizlet?
A process of nuclear division in eukaryotic cells conventionally divided into five stages: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Mitosis conserves chromosome number by equally allocating replicated chromosomes to each of the daughter nuclei. Area where the chromatids of a chromosome are attached.
What happens in G1 phase?
Initially in G1 phase, the cell grows physically and increases the volume of both protein and organelles. In S phase, the cell copies its DNA to produce two sister chromatids and replicates its nucleosomes. Finally, G2 phase involves further cell growth and organisation of cellular contents.
What is the second phase of mitosis?
The second phase of mitosis is metaphase, in which the chromosomes move into the equatorial plane of the spindle. As the third phase—anaphase—begins, the chromatids separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. Once the chromatids separate, they are called chromosomes.
What is metaphase?
Metaphase Metaphase is a stage during the process of cell division (mitosis or meiosis). Normally, individual chromosomes are spread out in the cell nucleus. During metaphase, the nucleus dissolves and the cell's chromosomes condense and move together, aligning in the center of the dividing cell.
What phase is cytokinesis in?
Cytokinesis begins in anaphase and ends in telophase, reaching completion as the next interphase begins. The first visible change of cytokinesis in an animal cell is the sudden appearance of a pucker, or cleavage furrow, on the cell surface.
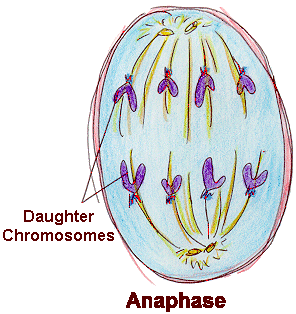
What phase of cell division comes immediately after the phase shown here?
Explanation. The correct answer is anaphase.
Define mitosis.
Mitosis is the type of cell division by which a single cell divides in such a way as to produce two genetically identical “daughter cells”.
Why is mitosis called equational division?
Mitosis is the process of cell division wherein the chromosomes replicate and get equally distributed into two daughter cells. The chromosome numbe...
List all the stages of mitosis.
The stages of Mitosis are: Prophase – The chromosomes shorten and thicken. Metaphase – Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. Anaphase – C...
What is prophase?
The process of mitosis begins with the prophase. In this stage, the chromatin condenses and the nucleolus disappears.
What happens in metaphase?
Metaphase is the second stage of the process, chromosomes get condensed at the equator, before being split apart for each of the two daughter cells.
In what cells does mitosis occur?
Mitosis occurs in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells divide by both mitosis and meiosis. For eg., skin cells divide by mitosis, whereas gametes div...
What is the primary function of mitosis?
Mitosis plays an important role in the life cycle of most living things. It helps in cell regeneration, asexual reproduction and growth.
What is mitosis?
Mitosis is a type of cell division in which one cell (the mother) divides to produce two new cells (the daughters) that are genetically identical to itself. In the context of the cell cycle, mitosis is the part of the division process in which the DNA of the cell's nucleus is split into two equal sets of chromosomes.
How many phases are there in mitosis?
Mitosis consists of four basic phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Some textbooks list five, breaking prophase into an early phase (called prophase) and a late phase (called prometaphase). These phases occur in strict sequential order, and cytokinesis - the process of dividing the cell contents to make two new cells - starts in anaphase or telophase.
Where do microtubules extend?
More microtubules extend from each centrosome towards the edge of the cell, forming a structure called the aster. Metaphase. Chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate, under tension from the mitotic spindle. The two sister chromatids of each chromosome are captured by microtubules from opposite spindle poles.
Which phase of the cell is the sister chromatids separated from each other?
Anaphase. The sister chromatids separate from one another and are pulled towards opposite poles of the cell. The microtubules that are not attached to chromosomes push the two poles of the spindle apart, while the kinetochore microtubules pull the chromosomes towards the poles.
What is the order of mitosis?
These phases occur in strict sequential order, and cytokinesis - the process of dividing the cell contents to make two new cells - starts in anaphase or telophase. Stages of mitosis: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase. Cytokinesis typically overlaps with anaphase and/or telophase. You can remember the order of the phases with ...
Why can't you see chromosomes in the nucleus?
You can’t see the chromosomes very clearly at this point, because they are still in their long, stringy, decondensed form.
Where do microtubules bind to chromosomes?
Microtubules can bind to chromosomes at the kinetochore, a patch of protein found on the centromere of each sister chromatid. ( Centromeres are the regions of DNA where the sister chromatids are most tightly connected.)
How many stages of mitosis are there?
Mitosis occurs in five stages that are in a specific order. In the following sections, there is a description of what occurs at each stage.
What is the third stage of mitosis?
The third stage of mitosis is called metaphase. During this phase, the chromosomes are aligned in the middle of the cell. Due to the fact that they are fully visible at this point, many scientists will study a map of an organisms chromosomes called a karyotype. The following occurs during this phase:
What is the difference between interphase and cytokinesis?
It is important to note that Interphase and Cytokinesis are not on this list. Interphase is the stage that occurs before mitosis and is the part of the cell cycle that includes cell growth and replication of DNA. The cell is in interphase 90% of the time, making it the most prevalent stage at any one time. Cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm that begins during anaphase and ends after telophase. Cytokinesis results in the formation of two separate daughter cells. This lesson will focus specifically on the five phases of mitosis.
What happens to the nucleolus during prophase?
During prophase, the nucleolus disappears, uncoiled DNA called chromatin condenses into chromosomes, and a mitotic spindle made out of microtubules forms. Chromosomes are the structures of protein and nucleic acid that carry genetic information.
What is the process of cell division that results in two identical daughter cells that have the same number of chromosome?
Mitosis is the process of cell division which ultimately results in two genetically identical daughter cells that have the same number of chromosomes. Mitosis occurs in all of an organism's body cells, also known as somatic cells.
Why is mitosis important?
Mitosis is essential for organism growth and replacement of damaged and worn out cells. In single-celled organisms such as yeast, mitosis is a form of asexual reproduction and will add new individuals to a population.
What happens during prometaphase?
During prometaphase, the nuclear envelope disappears, centrosomes begin to move to opposite poles, and spindle fibers connect to the kinetochores , which are protein structures near the center of the chromosomes.
What is Mitosis?
Cell division is the driving process of reproduction at the cellular level. Most eukaryotic cells divide in a manner where the ploidy or the number of chromosomes remains the same, except in the case of germ cells where the number of chromosomes is halved.
Why is mitosis important?
Mitosis is required for asexual reproduction, vegetative propagation in plants and also responsible for repair and regeneration of damaged tissues. Mitosis helps in maintaining purity of genome as no recombination or crossing over takes place.
How does mitosis help an organism?
Mitosis helps in the development of an organism. In single-celled organisms, mitosis is the process of asexual reproduction. Mitosis helps in the replacement of damaged tissues. The cells near the damaged cells begin mitosis when they do not sense the neighbouring cells.
What happens to the microtubules in prometaphase?
In the prometaphase, the nuclear envelop disintegrates. Now the microtubules are allowed to extend from the centromere to the chromosome. The microtubules attach to the kinetochores which allow the cell to move the chromosome around.
What is the process of completion of prophase?
The completion of prophase is characterised by the initiation of the assembly of the mitotic spindle, the microtubules and the proteinaceous components of cytoplasm that help in the process.
Why is mitosis also called equational cell division?
The cell is also known as equational cell division because the chromosome number in the parent cell and daughter cell is the same. In plants, mitosis leads to the growth of vegetative parts of the plant like root tip, stem tip, etc. Segregation and combination do not occur in this process. The processes occurring during mitosis have been divided ...
What stage of the cell is the chromosomes pulled?
Metaphase. At this stage, the microtubules start pulling the chromosomes with equal force and the chromosome ends up in the middle of the cell. This region is known as the metaphase plate. Thus, each cell gets an entire functioning genome. Metaphase.
What is the first stage of mitosis?
Prophase is technically the first stage of mitosis. It is also the longest phase of mitosis, where the chromatin condenses into chromosomes and the nuclear membrane breaks down (in prometaphase ). In animal cells, the centrioles located near the nucleus begin to split and move to the opposite ends of the cell.
How many stages of mitosis are there?
Stages of Mitosis. There are essentially six stages of mitosis (some textbooks tend to club prometaphase and prophase into a single stage). The stages of mitosis comprise: Interphase. Prophase. Prometaphase. Metaphase. Anaphase. Telophase.
What happens to the chromosomes in metaphase?
In metaphase, the microtubules pull on the chromosomes with equal force, and the chromosome moves to the center of the cell.
Is interphase a part of mitosis?
Technically, the interphase is not a part of mitosis, however , it is still a crucial process as it lead s up to the process of mitosis. Hence, the interphase refers to all the other stages of cell cycle other than mitosis.
What is the process of dividing chromosomes in the middle of the cell?
Metaphase. Metaphase is when chromosomes line up to split evenly. Using their spindle fibers that they formed between prophase and metaphase, the centrioles line up the chromosomes in the middle of the cell. This step is very important because each chromosome contains two sister chromatids.
How do centrioles pull apart chromosomes?
In anaphase, the chromosomes are pulled apart. The centrioles pull them apart to opposite ends of the cell by using their spindle fibers like a rope. Now genetic information is divided equally between the two halves of the parent cell.
Why do cells divide into two identical cells?
Because the cell needs to divide into two identical cells, each of the parent cell's duplicated organelles need to be separated evenly, especially the centrioles. Centrioles are barrel-shaped organelles made mostly of proteins. Prophase in mitosis.
Why is it important to split chromosomes apart?
This step is very important because each chromosome contains two sister chromatids. These sister chromatids are identical copies of one another and must be split apart to be given to each of the identical cells that will form after mitosis.
What is the last stage of mitosis?
Telophase. In telophase, the parent cell begins to form nuclear envelopes around the newly divided chromosomes. This is the last stage of mitosis, but it does not result into two new cells. After this stage comes cytokinesis, which is where the cytoplasms of each cell are completely divided.
What does it mean to enroll in a course?
Enrolling in a course lets you earn progress by passing quizzes and exams.
What is the process by which a cell divides into two cells?
The process by which a cell divides into two cells is known as mitosis. It begins with a parent cell that divides into two cells known as daughter cells. The purpose behind mitosis is for cells to reproduce identical cells that will help grow and repair the organism. Lesson. Quiz.
