- The values of mean, median, and mode in a normal curve are located on the same point.
- It is a symmetric curve cantered around the mean, whereas 50% of the observation lies on the right side of the mean and 50% of the observaions lies on the left side of the mean.
- It is a bell shaped and unimodal curve.
What are the properties of a normal curve?
- Its shorthand notation is X ∼ N (μ,σ2) X ∼ N ( μ, σ 2). ...
- It has a symmetric shape: it can be cut into two halves that are mirror images of each other; as such, skewness = 0.
- Kurtosis = 3. ...
- The mean, mode, and median are all equal and lie directly in the middle of the distribution.
What is the percentage of normal curve?
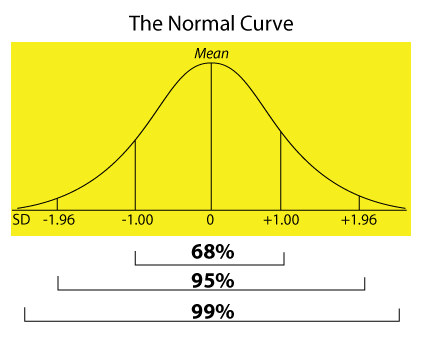
The empirical rule says that for any normal (bell-shaped) curve, approximately: 68% of the values (data) fall within 1 standard deviation of the mean in either direction 95% of the values (data) fall within 2 standard deviations of the mean in either direction
How to find equation of normal to the curve?
- Take a general point, ( x, y ), on the parabola and substitute for y.
- Take the derivative of the parabola.
- Using the slope formula, set the slope of each normal line from (3, 15) to equal to the opposite reciprocal of the derivative at and solve for x. ...
- Plug each of the x- coordinates (–8, –4, and 12) into to obtain the y- coordinates.
What are the characteristics of a normal distribution curve?
- The values of mean, median, and mode in a normal curve are located on the same point.
- It is a symmetric curve cantered around the mean, whereas 50% of the observation lies on the right side of the mean and 50% of the observaions lies on the ...
- It is a bell shaped and unimodal curve.
What are the characteristics of a standard normal curve?
Characteristics of a Normal Curve All normal curves are bell-shaped with points of inflection at μ ± σ . All normal curves are symmetric about the mean . Therefore, by the definition of symmetry, the normal curve is symmetric about the mean . The area under an entire normal curve is 1.
How do you find the standard normal curve to the right?
To find the area to the right of a positive z-score, begin by reading off the area in the standard normal distribution table. Since the total area under the bell curve is 1 (as a decimal value which is equivalent to 100%), we subtract the area from the table from 1.
What does a normal curve means?
normal curve. noun. statistics a symmetrical bell-shaped curve representing the probability density function of a normal distribution. The area of a vertical section of the curve represents the probability that the random variable lies between the values which delimit the section.
What is the difference between normal distribution and standard normal distribution?
The difference between a normal distribution and standard normal distribution is that a normal distribution can take on any value as its mean and standard deviation. On the other hand, a standard normal distribution has always the fixed mean and standard deviation.
How do you find the area of the standard normal curve?
To find a specific area under a normal curve, find the z-score of the data value and use a Z-Score Table to find the area. A Z-Score Table, is a table that shows the percentage of values (or area percentage) to the left of a given z-score on a standard normal distribution.
Why is normal curve important?
It is the most important probability distribution in statistics because it accurately describes the distribution of values for many natural phenomena. Characteristics that are the sum of many independent processes frequently follow normal distributions.
Why is the normal curve is important to study?
The normal distribution is the most important probability distribution in statistics because many continuous data in nature and psychology displays this bell-shaped curve when compiled and graphed.
What is another name for the normal curve?
A bell curve is a common type of distribution for a variable, also known as the normal distribution. The term "bell curve" originates from the fact that the graph used to depict a normal distribution consists of a symmetrical bell-shaped curve.
How do you find the area under the standard normal curve to the left of Z?
How to find area left of a z score: StepsStep 1: Split your given decimal into two after the tenths decimal place. For example, if you're given 0.46, split that into 0.4 + 0.06.Step 2: Look up your decimals from Step 1 in the z-table. ... Step 3: Add 0.500 to the z-value you just found in step 2.
How do you find the area of az score right?
Area to the Right of a Positive z Score Since the total area under the bell curve is 1, we subtract the area from the table from 1. For example, the area to the left of z = 1.02 is given in the table as . 846. Thus the area to the right of z = 1.02 is 1 - .
How does R calculate normal distribution?
In R, there are 4 built-in functions to generate normal distribution:dnorm() dnorm(x, mean, sd)pnorm() pnorm(x, mean, sd)qnorm() qnorm(p, mean, sd)rnorm() rnorm(n, mean, sd)
How do you calculate the z-score?
How do you calculate the z-score? The formula for calculating a z-score is is z = (x-μ)/σ, where x is the raw score, μ is the population mean, and σ is the population standard deviation. As the formula shows, the z-score is simply the raw score minus the population mean, divided by the population standard deviation.
What is the empirical rule for a curve?
The empirical rule also helps one to understand what the standard deviation represents. The empirical rule says that for any normal (bell-shaped) curve, approximately: 68% of the values (data) fall within 1 standard deviation of the mean in either direction. 95% of the values (data) fall within 2 standard deviations of the mean in either direction.
How many values fall within 1 standard deviation of the mean?
68% of the values (data) fall within 1 standard deviation of the mean in either direction
Why does the distribution of the weights of large eggs at a grocery store look like a normal curve?
Thus, the distribution of the weights of cartons of large eggs at a grocery store will look like a normal curve because the weight of a carton arises from the sum of the weights of the dozen eggs inside.
What is a predictable pattern of interest?
The predictable pattern of interest is a type of symmetry where much of the distribution of the data is clumped around the center and few observations are found on the extremes. Data that has this pattern are said to be bell-shaped or have a normal distribution. It can be shown that variables that arise as a result of the sum or average of a fixed number of individual smaller components of a similar nature will have this shape. Thus, the distribution of the weights of cartons of large eggs at a grocery store will look like a normal curve because the weight of a carton arises from the sum of the weights of the dozen eggs inside. Many measures used by psychologists to gauge levels of characteristics like stress or anxiety or happiness are based on questionnaires that score your answers to lots of individual questions and then sum them up to get a final measure. The distributions of such measures within a homogeneous group of people will then approximately follow a normal curve
How to convert a normal distribution to a standard normal distribution?
Any normal distribution can be converted into the standard normal distribution by turning the individual values into z -scores. In a z -distribution, z -scores tell you how many standard deviations away from the mean each value lies.
When you standardize a normal distribution, the mean becomes 0?
When you standardize a normal distribution, the mean becomes 0 and the standard deviation becomes 1. This allows you to easily calculate the probability of certain values occurring in your distribution, or to compare data sets with different means and standard deviations.
How does the mean affect the curve?
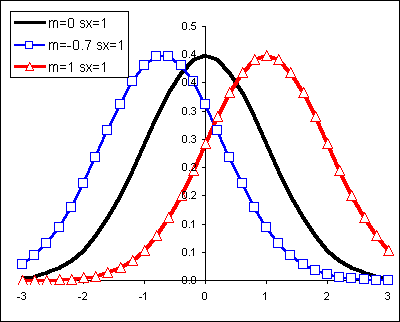
The mean determines where the curve is centered. Increasing the mean moves the curve right, while decreasing it moves the curve left. The standard deviation stretches or squeezes the curve. A small standard deviation results in a narrow curve, while a large standard deviation leads to a wide curve.
How to compare sleep duration during and before lockdown?
To compare sleep duration during and before the lockdown, you convert your lockdown sample mean into a z -score using the pre-lockdown population mean and standard deviation.
What is the standard deviation of SAT scores?
The data follows a normal distribution with a mean score ( M) of 1150 and a standard deviation ( SD) of 150 . You want to find the probability that SAT scores in your sample exceed 1380.
What is the area under the curve?
The standard normal distribution is a probability distribution, so the area under the curve between two points tells you the probability of variables taking on a range of values. The total area under the curve is 1 or 100%.
How to find the probability of a mean z score of 2.24?
To find the probability of your sample mean z -score of 2.24 or less occurring, you use the z -table to find the value at the intersection of row 2.2 and column +0 .04.
How to find the normal curve?
A typical four-decimal-place number in the body of the Standard Normal Cumulative Probability Table gives the area under the standard normal curve that lies to the left of a specified z-value. The probability to the left of z = 0.87 is 0.8078 and it can be found by reading the table: 1 Since z = 0.87 is positive, use the table for POSITIVE z-values. 2 Go down the left-hand column, label z to "0.8." 3 Then, go across that row until under the "0.07" in the top row.
What is the 10th percentile of the standard normal distribution?
Therefore, the 10th percentile of the standard normal distribution is -1.28 .
What is the closest value to 0.1000?
We search the body of the tables and find that the closest value to 0.1000 is 0.1003. We look to the leftmost of the row and up to the top of the column to find the corresponding z-value.
How to transform a random variable to a standard random variable?
For any normal random variable, we can transform it to a standard normal random variable by finding the Z-score. Then we can find the probabilities using the standard normal tables.
How to find the probability between two values?
To find the probability between these two values, subtract the probability of less than 2 from the probability of less than 3. In other words,
What is the probability to the left of z = 0.87?
The probability to the left of z = 0.87 is 0.8078 and it can be found by reading the table:
What is the mean of a special case of normal distribution?
A special case of the normal distribution has mean μ = 0 and a variance of σ 2 = 1. The 'standard normal' is an important distribution.
What is the area under a standard normal curve?
You know Φ (a), and you realize that the total area under the standard normal curve is 1 so by numerical conclusion: P (Z > a) is 1 Φ (a).
What is standard normal distribution?
The standard normal distribution is one of the forms of the normal distribution. It occurs when a normal random variable has a mean equal to zero and a standard deviation equal to one.
What is the normal distribution table?
A standard normal distribution table is utilized to determine the region under the bend (f (z)) to discover the probability of a specified range of distribution. The normal distribution density function f (z) is called the Bell Curve since its shape looks like a bell.
How to find cumulative probability of a z score?
For example, a part of the standard normal table is given below. To find the cumulative probability of a z-score equal to -1.21, cross-reference the row containing -1.2 of the table with the column holding 0.01. The table explains that the probability that a standard normal random variable will be less than -1.21 is 0.1131; that is, P (Z < -1.21) = 0.1131. This table is also called a z-score table.
What is the empirical rule of standard normal distribution?
The empirical rule, or the 68-95-99.7 rule of standard normal distribution, tells us where most values lie in the given normal distribution. Thus, for the standard normal distribution, 68% of the observations lie within 1 standard deviation of the mean; 95% lie within two standard deviations of the mean; 99.7% lie within 3 standard deviations of the mean.
How to convert raw data into z score?
Converting raw data into the form of z-score, using the conversion equation given as z = (X – μ) / σ.
What is a z score?
A z-score of a standard normal distribution is a standard score that indicates how many standard deviations are away from the mean an individual value (x) lies:
How to fit a normal curve to data?
Formula of the normal curve. Once you have the mean and standard deviation of a normal distribution, you can fit a normal curve to your data using a probability density function. In a probability density function, the area under the curve tells you probability.
What is the standard normal distribution?
The standard normal distribution, also called the z-distribution, is a special normal distribution where the mean is 0 and the standard deviation is 1.
What is the difference between mean and standard deviation?
The mean is the location parameter while the standard deviation is the scale parameter.
What is the standard deviation of SAT scores?
The data follows a normal distribution with a mean score ( M) of 1150 and a standard deviation ( SD) of 150.
How to get a population mean?
In research, to get a good idea of a population mean, ideally you’d collect data from multiple random samples within the population. A sampling distribution of the mean is the distribution of the means of these different samples.
How many values are within 1 standard deviation from the mean?
Around 68% of values are within 1 standard deviation from the mean.
Why are normal distributions also called bell curves?
Normal distributions are also called Gaussian distributions or bell curves because of their shape.
What does the area under the normal distribution curve represent?
The area under the normal distribution curve represents probability and the total area under the curve sums to one.
Why is the normal distribution called the bell curve?
The normal distribution is often called the bell curve because the graph of its probability density looks like a bell. It is also known as called Gaussian distribution, after the German mathematician Carl Gauss who first described it.
Why is the normal distribution important in statistics?
The normal distribution is the most important probability distribution in statistics because many continuous data in nature and psychology displays this bell-shaped curve when compiled and graphed.
What are the properties of normal distribution?
What are the properties of the normal distribution? The normal distribution is a continuous probability distribution that is symmetrical on both sides of the mean, so the right side of the center is a mirror image of the left side. The area under the normal distribution curve represents probability and the total area under the curve sums to one.
What is the probability of randomly selecting a score between -1 and +1?
68% of data falls within the first standard deviation from the mean. This means there is a 68% probability of randomly selecting a score between -1 and +1 standard deviations from the mean.
How to add distribution curve in SPSS?
It is also advisable to a frequency graph too, so you can check the visual shape of your data (If your chart is a histogram, you can add a distribution curve using SPSS: From the menus choose: Elements > Show Distribution Curve).
What is the probability of a random selection of a score between -3 and +3 standard deviations?
99.7% of data will fall within three standard deviations from the mean. This means there is a 99.7% probability of randomly selecting a score between -3 and +3 standard deviations from the mean.
What is the standard deviation of 81.85% of the population?
So 81.85% of the population are between −1 and +2 Standard Deviations from the Mean.
What is the standard deviation of 17.36%?
So 17.36% of the population are between 0 and 0.45 Standard Deviations from the Mean.
What is the area of the normal curve?
We know that the total area of the Normal Curve extends from -3σ to + 3σ that is over a range of 6σ.
Why is the normal curve important?
Normal Curve has great significance in mental measurement and educational evaluation. It gives important information about the trait being measured.
What is the area under the normal probability curve?
The table of areas of normal probability curve is then referred to find out the proportion of area between the mean and the Z value. Though the total area under N P C. is 1, but for convenience, the total area under the curve is taken to be 10,000 because of greater ease with which fractional parts of the total area, may be then calculated.
What is the area of the curve between M and 2?
According to the table of area under N.P.C. (Table-A) the area of the curve that lie between M and + 2σ is 47.72%. The total percentage of cases below the score 60 is 50 + 47.72 = 97.72% or 98%.
What percentage of cases are high in the measured trait?
2. Most of the cases are average in the measured trait and their percentage in the total population is about 68.26%. 3. Approximately 15.87% of (50-34.13%) cases are high in the trait measured. 4.
What is Amit's percentile rank in mathematics?
In a class Amit’s percentile rank in the mathematics class is 75. The mean of the class in mathematics is 60 with standard deviation 10. Find out Amit’s marks in mathematics achievement test.
What point does the normal probability curve end at?
For practical purposes we take the curve to end at points -3σ and +3σ distant from the mean as the normal curve does not actually meet the base line. Table of area under normal probability curve shows that 4986.5 cases lie between mean and ordinate at +3σ.
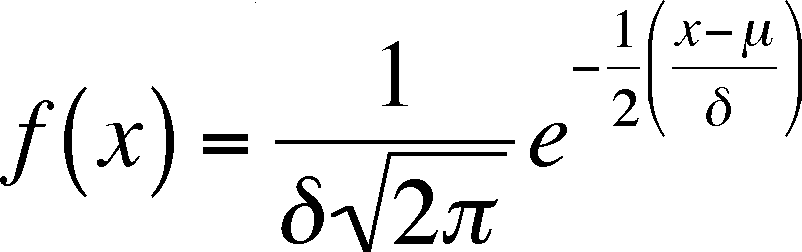
Normal Distribution vs The Standard Normal Distribution
Standardizing A Normal Distribution
- When you standardize a normal distribution, the mean becomes 0 and the standard deviation becomes 1. This allows you to easily calculate the probability of certain values occurring in your distribution, or to compare data sets with different means and standard deviations. While data points are referred to as x in a normal distribution, they are called z or z-scores in the z-distributi…
Use The Standard Normal Distribution to Find Probability
- The standard normal distribution is a probability distribution, so the area under the curve between two points tells you the probability of variables taking on a range of values. The total area under the curve is 1 or 100%. Every z-score has an associated p-value that tells you the probability of all values below or above that z-score occuring. Thi...
Step-By-Step Example of Using The z-distribution
- Let’s walk through an invented research example to better understand how the standard normal distribution works. As a sleep researcher, you’re curious about how sleep habits changed during COVID-19 lockdowns. You collect sleep duration data from a sample during a full lockdown. Before the lockdown, the population mean was 6.5 hours of sleep. The lockdown sample mean i…