- Iconic memory stores interpretations of visual experiences
- Echoic memory stores the interpretations of sounds
- Haptic memory stores the interpretations related to tactile experiences
- Olfactory memory stores information related to the sense of smell
- Gustatory memory stores information related to the sense of taste.
What is storage in psychology?
Storage is the more or less passive process of retaining information in the brain, whether in the sensory memory, the short term memory or the more permanent long-term memory.
What are the stages of stored memory?
A stored memory starts as a sensory memory, moves to short-term memory and then transfers into long-term memory. However, some experiences and information do not progress through each stage and are abandoned without being stored in short- or long-term memory.
What is the nature of memory storage?
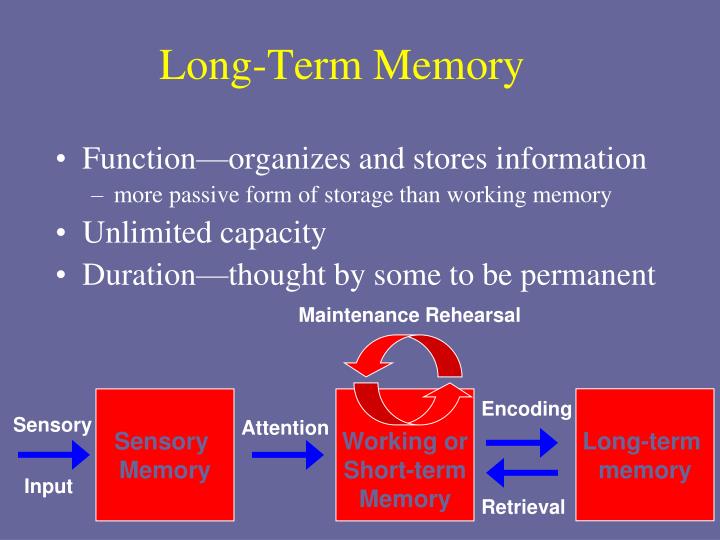
Memory Storage This concerns the nature of memory stores, i.e., where the information is stored, how long the memory lasts for (duration), how much can be stored at any time (capacity) and what kind of information is held. The way we store information affects the way we retrieve it.
What is the first stage of memory processing?
Encoding Encoding is the first stage of memory. As the term suggests, this is the stage of memory which accumulates all the information from the surrounding and encodes or stores it in our brain. The information we intake from the world around us is processed in three different forms.

What are the three stages of memory storage?
The brain has three types of memory processes: sensory register, short-term memory, and long-term memory.
What is the storage process in psychology?
Psychologists distinguish between three necessary stages in the learning and memory process: encoding, storage, and retrieval (Melton, 1963). Encoding is defined as the initial learning of information; storage refers to maintaining information over time; retrieval is the ability to access information when you need it.
What is an example of storage memory?
For example, a word which is seen (in a book) may be stored if it is changed (encoded) into a sound or a meaning (i.e. semantic processing). For example, how do you remember a telephone number you have looked up in the phone book?
What is the retrieval stage of memory?
Memory recall or retrieval is remembering the information or events that were previously encoded and stored in the brain. Retrieval is the third step in the processing of memory, with first being the encoding of memory and second, being the storage of the memory.
What does storage and memory mean?
Whereas memory refers to the location of short-term data, storage is the component of your computer that allows you to store and access data on a long-term basis. Usually, storage comes in the form of a solid-state drive or a hard drive.
Why is memory storage important?
Storage and memory are both important for your computer. If you have a disk with larger storage capacity, you can store more files and programs on your computer. And with more RAM, your computer can manipulate larger digital data and run faster.
Is storage a memory?
Storage and memory, while connected, fulfill separate roles in a computer. Memory meets temporary data access needs and storage retains data and other files over the long term. The terms memory and storage both refer to a computer's internal storage space.
How does memory storage work?
Memory is just a chip. In physical terms, an electrical signal reads the information stored in RAM. It works at the speed of electricity, which is the speed of light. When you move data from a disk to RAM storage, your computer runs anywhere from five thousand to a million times faster.
What are the 3 types of memory?
The three major classifications of memory that the scientific community deals with today are as follows: sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory.
What are the 5 stages of memory?
The 5 stages of rememberingSensing. The very beginning of the memory-making process involves the exposure to surrounding scenes and situations. ... Encoding. With the sensory information passed to the brain, the volume and complexity is too great to process. ... Consolidation. ... Storage. ... Retrieval.
Where is memory stored in the brain?
HippocampusHippocampus. The hippocampus, located in the brain's temporal lobe, is where episodic memories are formed and indexed for later access.
What is the retrieval process?
Processes of learning and memory are typically conceptualized as involving at least three stages: encoding, storage, and retrieval. Retrieval refers to accessing the stored information. Retrieval processes are inextricably bound to those of encoding and storage.
What is the process of storage?
Storing refers to the process of placing newly acquired information into memory, which is modified in the brain for easier storage. Encoding this information makes the process of retrieval easier for the brain where it can be recalled and brought into conscious thinking.
What is the first stage of information storage?
Sensory MemorySensory Memory (First Stage of Storage) In the Atkinson-Shiffrin model, stimuli from the environment are processed first in sensory memory, storage of brief sensory events, such as sights, sounds, and tastes. It is very brief storage—up to a couple of seconds. We are constantly bombarded with sensory information.
What are the 3 types of memory?
The three major classifications of memory that the scientific community deals with today are as follows: sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory.
What is the meaning of memory?
Memory refers to our ability to store and recall information, which in turn helps us later in life. In other words, our memory gives us the ability to remember something that we experienced or learned in the past, like how to tie shoelaces or the capitals of South American countries.
What is the name of the model that describes the process of memory?
In the late 1960’s, cognitive scientists Richard Atkinson and Richard Shiffrin proposed a linear model (often called “the multi-store model ”) of human memory with three sequential stages. A stored memory starts as a sensory memory, moves to short-term memory and then transfers into long-term memory.
What Are 5 Types of Sensory Memory?
The Types of Sensory Memory (Sensor y Memory Modalities) are relative to the sensory experiences they store:
How Does Short-Term (or Working) Memory Work?
Short-Term Memory, sometimes referred to as “Working Memory”, is the temporary storage and processing stage in which most of the effort for retaining memory happens.
What Are Additional Memory Techniques I Can Learn?
Brain exercises, memory aids, and training tools are great ways to improve your concentration and memory!
Why is sensory memory important?
But, as the first step in storing information for a longer term, sensory memory allows us to selectively perceive and process sensory information to initiate the memory encoding process in short-term memory.
What is sensory register?
The sensory register is another name for sensory memory, where sensory perceptions are retained in each of the five distinct sensory memory stores. Each sensory memory type holds information based on our distinct sensory experiences.
What is memory storage?
Summary. Memory storage is the process by which the brain can store facts or events so that they can be helpful in the future. It is the process by which life experiences are stored and different skill sets are learned and retained in the brain. Our brain is continuously involved in the process of memory storage.
What is episodic memory?
The episodic memories are composed of pieces of information that have a very high sentimental value, they are of the highly emotional events, and the sentimental value of the particular event associate all the other memories surrounding that specific timestamp get engraved into the long-term memory.
How does sensory information enter the brain?
As described earlier, information enters the brain through sensory organs. These organs are eyes, ears, nose, and skin. Sensory memory is created as soon as the information perceived by these organs reaches the part of the brain which processes the information. The processing of the sensory information and its conversion to memory is a complex but immediate process. Sensory memory only stays in the brain for as long as one to two seconds. During this period of a second, information of the object is processed, and the brain recalls previous memory of the objects similar to it. This process of recalling enables the brain to identify the object and name it. If the object is something unique it gets stored or passed on to the comparatively longer storage memory type.
Why does the brain keep catching information?
This is interesting to know that our brain is continuously catching information, but it never gets flooded or overwhelmed by it (in normal and non-pathological circumstances). Because our brain utilizes different levels of memory storage. The things which are at lower levels of attention and priority get forgotten. The human brain keeps discarding them and only stores the things which we need.
How does the brain store information?
Our brain is continuously involved in the process of memory storage. It receives several pieces of information even within a second, processes them, and stores valuable information in the form of memory. Memories are stored in the brain at different levels.
How do we understand the storeroom?
Storeroom as an Analogy. We can understand how the human brain stores information by using a simple analogy. Our brain is like a storeroom when we consider memory storage. Like in a store you want to keep the important things on the shelf because in that way they will become easily accessible.
What is the capability of the brain to hold onto the past or currently happening events and different pieces of information?
Memory is the capability of the brain to hold onto the past or currently happening events and different pieces of information, so they can be utilized in the future, at the time of need. Human memory storage is one of the greatest marvels of nature. The long and complex course of evolution provided human beings with a mind which is an astonishing example of adroitness and dexterity. Our brain is the main key that unlocked the attics of the food chain for us.
What is short term memory?
Short-term memory is encoded in auditory, visual, spatial, and tactile forms. Short-term memory is closely related to working memory. Baddeley suggested that information stored in short-term memory continuously deteriorates, which can eventually lead to forgetting in the absence of rehearsal.
Which part of the brain is involved in the creation of long-term memory?
Scientists speculate that the hippocampus is involved in the creation of long-term memory.
What is a dual store SAM?
The dual-store SAM model also utilizes memory storage, which itself can be classified as a type of long-term storage: the semantic matrix. The long-term store in SAM represents the episodic memory, which only deals with new associations that were formed during the study of an experimental list; pre-existing associations between items of the list, then, need to be represented on different matrix, the semantic matrix. The semantic matrix remains as another source of information that is not modified by episodic associations that are formed during the exam.
What happens when an item is introduced into the short-term store?
As an item is introduced into the short-term store, and if the short-term store has already been occupied by a maximum number of items, the item will probably drop out of the short-term storage. As items co-reside in the short-term store, their associations are constantly being updated in the long-term store matrix.
What is the difference between short term and long term memory?
In contrast to the short-term memory, long-term memory refers to the ability to hold information for a prolonged time and is possibly the most complex component of the human memory system . The Atkinson–Shiffrin model of memory (Atkinson 1968) suggests that the items stored in short-term memory moves to long-term memory through repeated practice and use. Long-term storage may be similar to learning—the process by which information that may be needed again is stored for recall on demand. The process of locating this information and bringing it back to working memory is called retrieval. This knowledge that is easily recalled is explicit knowledge, whereas most long-term memory is implicit knowledge and is not readily retrievable. Scientists speculate that the hippocampus is involved in the creation of long-term memory. It is unclear where long-term memory is stored, although there is evidence depicting long-term memory is stored in various parts of the nervous system. Long-term memory is permanent. Memory can be recalled, which, according to the dual-store memory search model, enhances the long-term memory. Forgetting may occur when the memory fails to be recalled on later occasions.
What are the two types of memory?
Modern memory psychology differentiates between the two distinct types of memory storage: short-term memory and long-term memory . Several models of memory have been proposed over the past century, some of them suggesting different relationships between short- and long-term memory to account for different ways of storing memory.
What is the process of storing and recalling information that was previously acquired?
Memory is the process of storing and recalling information that was previously acquired. Memory occurs through three fundamental stages: encoding, storage, and retrieval. Storing refers to the process of placing newly acquired information into memory , which is modified in the brain for easier storage. Encoding this information makes the process of ...
What is the phenomenon of memory?
Brian Becker, associate professor of neuropsychology at Lesley University, defines memory as “the process in which the mind interprets, stores, and retrieves information.”. When you obtain information from the world around you, Becker explains, that material is kept in the brain as a mental representation ...
What is short term memory?
Short-term memory is when the brain stores information temporarily so that it can be repeated, such as remembering a phone number you see on TV. Working memory refers to the brain storing information for the purpose of manipulating it, such as remembering a set of numbers while working on a math problem.
What is the significance of Becker's example of a computer screen?
Becker gives the examples of a computer screen and a conversation to illustrate how to recognize sensory register. When you look at a computer screen and then look away, but can still see the screen’s image, this is iconic memory at play. Similarly, when you have conversations with others and ask them to repeat themselves, only to understand what they said a moment later, it demonstrates echoic memory.
What is sensory register?
Sensory Register. In the sensory register process, the brain obtains information from the environment. This activity is short, lasting at most a few seconds. During sensory register, the brain gathers information passively through visual and auditory cues, known respectively as “iconic” and “echoic” memory.
How long does information stay in the brain?
Information stored in long-term memory can stay in the brain for a short while (a day, a week) or last as long as a lifetime. When long-term memories form, the hippocampus retrieves information from the working memory and begins to change the brain’s physical neural wiring.
What is the stage of attention?
In the memory-making process, attention is considered a stage between sensory register and short-term memory. Short-term memory formation can begin through giving your attention to the information received through sensory register.
Why are memories so difficult to access?
Transience. Memories may become increasingly difficult to access, due to either the natural aging process or damage to the hippocampus and temporal lobe.
How many stages of memory are there?
From storing the information to the final processing in order to produce a desired outcome, memory can be categorized into three stages.
What is the first stage of memory?
Encoding is the first stage of memory. As the term suggests, this is the stage of memory which accumulates all the information from the surrounding and encodes or stores it in our brain. The information we intake from the world around us is processed in three different forms.
How is LTM stored?
LTM is both stored and retrieved by association. Remembering a certain action might lead to retrieval of information about some other actions. For instance, traveling the same road you were walking the day before might lead you to retrieve information about the girl you had seen the day before.
How many items are stored in short term memory?
Short Term Memory (STM) Long Term Memory (LTM) Miller stated in 1956 that most adults are capable of storing within 5 to 9 items in their STM, short term memory, and he called it the magic number 7 (plus or minus 2).
What is memory in Sternberg's definition?
Sternberg defined memory as the means to draw past experiences in order to assess the information at the present. The complete process of structuring and processing the information involved in the storage and retrieval of such information can be defined as memory. Memory processes limitless amount of information every day, ...
What is memory in science?
Memory is the process of maintaining information over time. – Matlin, 2005. The general understanding of memory is storing certain information, which of course, isn’t a complete definition of the memory as a whole. Sternberg defined memory as the means to draw past experiences in order to assess the information at the present.
How long is short term memory?
Total capacity of Short Term memory is said to be around 0 – 30 seconds. Long Term Memory, however, is a whole different ball game when it comes to memory.
What are the stages of memory?
The three stages of memory include the process of encoding, storing, and recalling information. The encoding consists of memory creation. Storing or storage - inputs the created memory into our mind for future recall of information. .
How do the stages of memory depend on each other?
The three stages of memory depend on each other for an uninterrupted creation in memory. In other words, if each step is executed with the least odds against one who is trying to create a memory, - it will be there! In practice, it is enough to be more aware of what is going on and taking on one task at a time.
How does the brain make memories?
Get ready. The brain is making memories. The stages of memory begin with the encoding process . It is during this part of memory creation where often information is distorted. A human’s mind might not be focused, or the memory does not seem of importance to the brain at that particular time. Information coming is picked up by the human senses. We hear, see, touch, smell, and taste things. Understanding of what is going through our senses will determine how well information is encoded towards future recall. There is the utmost importance for the brain to make the best translation of what is going on in the model of memory creation. Daily, we perceive tons of information and that information is stored in both short and long-term memory. The short term memory can be forgotten in a day, while the long term memory creates significant pathways for far future recall. Due to the importance or unimportance of a particular memory, these pathways are created.
What is the second stage of memory?
The second stage in the three stages of memory is just as important as the rest. The hippocampus region in the human brain is responsible for the storage of memories. To add, when scientists examine a human brain, that is perceiving information, different areas of the brain are activated - therefore, our whole brain takes part. When brain damage occurs, this is the stage of memory that gets affected most. All previously stored memories might be tainted with altered information, a mix up can happen. Continuous memories are added to our web of ideas; this is where the pathways are formed. When approached with excellent mental acuity, less ‘corrupt’ files will be stored, and the recall process becomes user-friendly. It is the clarity of mental space, which aids in the whole process.
How does long term memory differ from short term memory?
The short term memory can be forgotten in a day , while the long term memory creates significant pathways for far future recall. Due to the importance or unimportance of a particular memory, these pathways are created. . .
Why are memories not stored at one hundred percent?
At times memories are forgotten or altered when memory formation occurs because there are multiple components at play, and all have to do their part well for promising results. The three stages of memory include the process ...
What happens when brain damage occurs?
When brain damage occurs, this is the stage of memory that gets affected most. All previously stored memories might be tainted with altered information, a mix up can happen. Continuous memories are added to our web of ideas; this is where the pathways are formed.
What is the term given to the structures and processes involved in the storage and subsequent retrieval of information?
Memory is the term given to the structures and processes involved in the storage and subsequent retrieval of information. Memory is essential to all our lives. Without a memory of the past, we cannot operate in the present or think about the future. We would not be able to remember what we did yesterday, what we have done today or ...
Why is short term memory 7?
He though that short-term memory capacity was 7 (plus or minus 2) items because it only had a certain number of “slots” in which items could be stored. However, Miller didn’t specify the amount of information that can be held in each slot.
How long can LTM be stored?
In contrast, the capacity of LTM is thought to be unlimited. Information can only be stored for a brief duration in STM (0-30 seconds), but LTM can last a lifetime. 3. Memory Retrieval.
What is the principle coding system in short-term memory?
Evidence suggests that this is the principle coding system in short-term memory (STM) is acoustic coding . When a person is presented with a list of numbers and letters, they will try to hold them in STM by rehearsing them (verbally).
Why are memory experiments criticized?
As a result, many memory experiments have been criticized for having low ecological validity.
Why are some experiments designed to investigate memory criticized?
Many experiments designed to investigate memory have been criticized for having low ecological validity. First, the laboratory is an artificial situation. People are removed from their normal social settings and asked to take part in a psychological experiment.
Can we store more information in short term memory?
However, Miller didn’t specify the amount of information that can be held in each slot. Indeed, if we can “chunk” information together we can store a lot more information in our short-term memory. In contrast, the capacity of LTM is thought to be unlimited.