
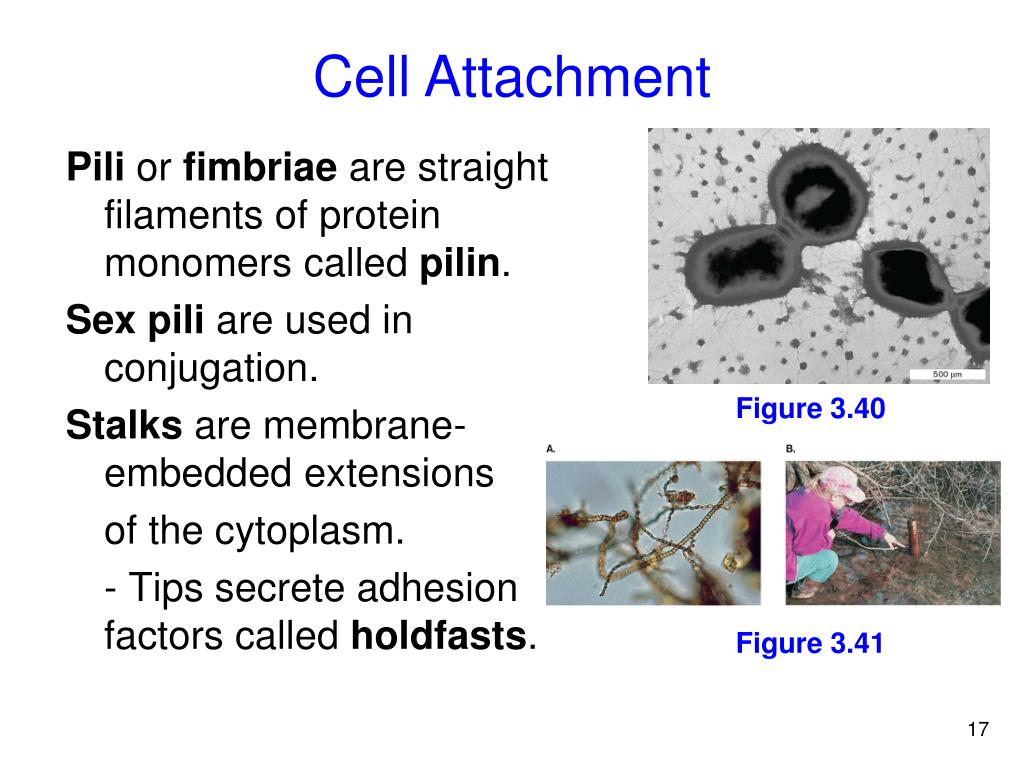
What is the structure and function of pili
Pilus
A pilus is a hairlike appendage found on the surface of many bacteria. The terms pilus and fimbria can be used interchangeably, although some researchers reserve the term pilus for the appendage required for bacterial conjugation. All pili are primarily composed of oligomeric pilin pr…
What is a pili and what is it used for?
Feb 27, 2020 · What is the structure and function of pili? Pili. The first external structure is the pilus (plural: pili). A pilus is a thin, rigid fiber made of protein that protrudes from the cell surface. The primary function of pili are to attach a bacterial cell to specific surfaces or to other cells. Click to see full answer.
What does pili do for the cell?
Mar 25, 2020 · Pili are hair-like structures in bacterial walls that allow bacterial cells to adhere to other surfaces throughout their environment. Pili are also known as fimbriae. Medically, pili are virulence factors for pathogenic bacteria. A virulence factor is any property of a bacterial cell that allows the bacterium to infect another organism.
What is the difference between Pili and fimbriae?
Structure of Pili and Fimbriae: Both fimbriae and pili are like flagella as both are the appendages on bacterial cell wall. They originate from cytoplasm that protrudes outside after penetrating the peptidoglycan layer of cell wall. Fimbriae are made up of 100% protein called fimbrilin or pilin which consists of about 163 amino acids (Fig.4.4).
What does pili do in a prokaryotic cell?
Jan 31, 2021 · Pili are short, hair-like structures on the cell surface of prokaryotic cells. They can have a role in movement, but are more often involved in adherence to surfaces, which facilitates infection, and is a key virulence characteristic. Structure of a bacterial cell. Image Credit: Logika600 / Shutterstock Gram-Negative and Gram-Positive
What is the major function of pili?
What is the structure and function of pili and fimbriae?
What is the function of pili in prokaryotic cell?
What is the role of a pili?
They can have a role in movement, but are more often involved in adherence to surfaces, which facilitates infection, and is a key virulence characteristic.
What is a pili?
Pili are short, hair-like structures on the cell surface of prokaryotic cells. They can have a role in movement, but are more often involved in adherence to surfaces, which facilitates infection, and is a key virulence characteristic. Structure of a bacterial cell. Image Credit: Logika600 / Shutterstock.
Which is shorter, pili or flagella?
Pili are shorter and thinner than flagella. While flagella are rigid, with torque generated by the motor, pili are less rigid and straighter. Pili can be found evenly around the surface of the cell, or localized to one or both of the poles.
Where are pili found?
Pili can be found evenly around the surface of the cell, or localized to one or both of the poles. They are typical of Gram-negative bacteria, but can be found in Gram-positive bacteria and archaea as well. In Gram-negative bacteria, pili can be categorized into four groups depending on their assembly pathways.
What are the different types of pili?
These groups are chaperone-usher pathway pili, type IV pili, curli pili and the CS1 pilus family. The pili of Gram-positive bacteria are, as far as we know, less varied.
What is the role of pili in adherence?
Pili can also help the bacterial cells avoid attacks by white blood cells. Streptococcus pyogenes has M-protein and pili which can resist engulfment by phagocytes, as well as their role in adherence. There are also pili involved in the exchange of genetic material, called the F pili. The pili are involved in conjugation.
What is the role of pili in phagocytes?
Pili can also help the bacterial cells avoid attacks by white blood cells. Streptococcus pyogenes has M-protein and pili which can resist engulfment by phagocytes, as well as their role in adherence. There are also pili involved in the exchange of genetic material, called the F pili.
What is the function of a pili?
What Is the Function of Pili? Pili are hair-like structures in bacterial walls that allow bacterial cells to adhere to other surfaces throughout their environment.
What are pili in biology?
Pili are hair-like structures in bacterial walls that allow bacterial cells to adhere to other surfaces throughout their environment. Pili are also known as fimbriae. Medically, pili are virulence factors for pathogenic bacteria.
What is a pili?
Pili are also known as fimbriae. Medically, pili are virulence factors for pathogenic bacteria. A virulence factor is any property of a bacterial cell that allows the bacterium to infect another organism. Pili are considered virulence factors because they allow bacterial cells to adhere to tissues and can help the bacterial cells resist attack ...
What is a virulence factor?
A virulence factor is any property of a bacterial cell that allows the bacterium to infect another organism. Pili are considered virulence factors because they allow bacterial cells to adhere to tissues and can help the bacterial cells resist attack from immune cells in the human body. In turn, the bacterial cells can colonize ...
What are pili in biology?
Pili are generally referred to as the appendages, which are involved in the conjugation. They are also known as long conjugative pili. They are longer than fimbriae and involved in the cell to cell attachment during conjugation for DNA transfer. They are also termed as “sex pili” as they facilitate gene transfer and recombination in ...
What is the function of pili in bacteria?
The disease-causing strains of bacteria possess fimbriae or pili. Pili increases the bacterial ability to adhere to tissues and colonise by multiplying rapidly. Bacteria without fimbriae or pili are generally non-pathogenic.
What are the characteristics of a bacterial cell?
They are hair-like, filamentous, surface appendages present on the bacterial cell. The main characteristics are: 1 A bacterial cell may have 1000 fimbriae present on the surface. They can be seen only under the electron microscope. 2 They are shorter than flagella. The length is ~0.5 𝝁m and thickness is ~10 nm. 3 They originate from the cytoplasmic membrane. They are present on motile as well as non-motile cells. 4 They are composed of helically arranged subunits of a protein called pilin, which aggregates to form slender tubes. 5 Fimbriae are antigenic and bacteria of different genera may have the same antigen. 6 Fimbriae and pili can be classified based on their structure and functions. 7 Fimbriae help bacteria in adherence to the host tissue and favourable microenvironments to draw nutrition. E.g. bacteria get attached to the surface by fimbriae of liquid culture media forming a pellicle. 8 Sex pili are a special type of fimbriae, present on the ‘male bacterium’ and are longer and fewer (up to 10 in each cell) in number than fimbriae. They are involved in the attachment with the ‘female bacterium’ by forming a conjugation tube for the DNA transfer from the male donor to the female recipient. 9 Type IV pili are responsible for twitching motility.
What are pili and fimbriae?
Fimbriae and pili are hair-like appendages present on the bacterial cell wall similar to flagella. They are shorter than flagella and more in number. They are involved in the bacterial conjugation, attachment to the surface and motility. They are present in both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria but more prevalent in Gram-negative bacteria.
What are the functions of fimbriae?
Fimbriae and pili can be classified based on their structure and functions. Fimbriae help bacteria in adherence to the host tissue and favourable microenvironments to draw nutrition. E.g. bacteria get attached to the surface by fimbriae of liquid culture media ...
What are fimbriae in a bacterial cell?
Fimbriae help bacteria in adherence to the host tissue and favourable microenvironments to draw nutrition. E.g. bacteria get attached to the surface by fimbriae of liquid culture media forming a pellicle. Sex pili are a special type of fimbriae, present on the ‘male bacterium’ and are longer and fewer (up to 10 in each cell) in number than fimbriae.
What is the name of the pili that attach to the host surface?
Fimbriae are also called “short attachment pili”. They attach to the host surface and help bacteria colonise and cause infection. They are present on the overall surface or concentrated towards the poles.
How big are pili?
The pili are 0.2-20 µm long with a diameter of about 250 Å. Pili are genetically governed by plasmids, the number of which varies from 3 to 5.
What are the appendages of the bacterial cell wall?
Both fimbriae and pili are like flagella as both are the appendages on bacterial cell wall. They originate from cytoplasm that protrudes outside after penetrating the peptidoglycan layer of cell wall. Fimbriae are made up of 100% protein called fimbrilin or pilin which consists of about 163 amino acids (Fig.4.4).
What are the functions of fimbriae?
Fimbriae have the adhesive properties which attach the organism to the natural substrate or to the other organism. Fimbriae agglutinate the blood cells such as erythrocytes, leucocytes, eplithelial cells, etc.
What is a pili?
Pili (singular: Pilus) are longer in length and thicker when compared to fimbriae. They can be found in some Gram-positive species of bacteria and all Gram-negative bacteria as well as archaea. Generally, there are two main types of pili. These include:
What are the functions of type IV pili?
Some of the other functions associated with type IV pili include: 1 Electrical conductivity 2 Adhesion of bacterial cells to eukaryotic cells (of a host) 3 Protein production
What is the F pilus?
Compared to the other pili, the F pilus (of F sex pilus) has been given more attention and is, therefore, better understood. Encoded by the F plasmid, the F pilus is found in "male" Gram-negative bacteria (F+).
What is the name of the bacteria that are thicker than fimbriae?
Pili (singular: Pilus) are longer in length and thicker when compared to fimbriae. They can be found in some Gram-positive species of bacteria and all Gram-negative bacteria as well as archaea.
What is a type IV pili?
Type IV pili are a type of Pili found in some Gram-positive bacteria (e.g., clostridia) and the majority of Gram-negative bacteria. They have several important functions ranging from their role in locomotion to DNA exchange.
What is type I fimbriae?
Type I fimbriae are some of the most common structures in the family Enterobacteriaceae. Here, they are involved in the adherence of the bacteria to the cells of the host. However, this binding has been shown to be specific to glycoproteins that consist of one or N-linked high mannose structures.
What is the size of a type III fimbria?
Type III fimbriae are thin fimbriae ranging about 5nm in diameter and between 0.5 and 2um in length. Like type II fimbriae, type III fimbriae are especially common among members of the family Enterobacteriaceae and Klebsiella spp.
What is the function of a type IV pili?
Type IV Pili Functions. There are different functions of Type IV Pili such as; Adhesion: The primary functions of Type IV pili is Adhesion. It helps in Adhesion of bacterial cell to different types of surfaces, the filament also allows the cell to adhere to other bacteria.
What are the two types of pili?
There are two types of Pili such as short attachment pili and long conjugation pili. The short one is known as fimbriae and the long one is known as “F” or sex pili.
What is a fimbria?
The fimbriae or fimbria (Singular) are bristle-like short fibers occurring on the surface of several gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. It helps in attachment of bacterial cells on the surface of host cell and on some inanimate objects. For example, E. coli utilizes them to get attached to the mannose receptors.
What is the function of fimbriae?
The main function of fimbriae is to help in the attachment of bacterial cells on a solid surface or host cell surface.
What is type 1 fimbria?
Type I fimbriae are commonly found in the family Enterobacteriaceae. They helps in the adherence of the bacteria to the cells of the host. However, this binding has been shown to be specific to glycoproteins that consist of one or N-linked high mannose structures.
What is the role of type III fibroid?
The Type III Fimbriae helps in adhesion of bacteria to abiotic surfaces and also helps in formation of biofilm. bacteria get benefits from this, that it helps in pathogenesis by promoting antibiotic resistance among some species of bacteria.
What is the difference between a pili and a fimbria?
Fimbriae are tiny bristle-like fibers arising from the surface of bacterial cells. Pili are hair like microfibers that are thick tubular structure made up of pilin. Diameter. These are comparatively thinner in diameter.

Table of Content
Structure and Function of Fimbriae and Pili
Fimbriae
- Pili can also help the bacterial cells avoid attacks by white blood cells. Streptococcus pyogenes has M-protein and pili which can resist engulfment by phagocytes, as well as their role in adherence. There are also pili involved in the exchange of genetic material, called the F pili. The pili are involved in conjugation. This is the transfer of gen...
Pili Or Conjugative Pili
Type IV Pili