.PNG)
What does the smooth entoplasmic reticulum do?
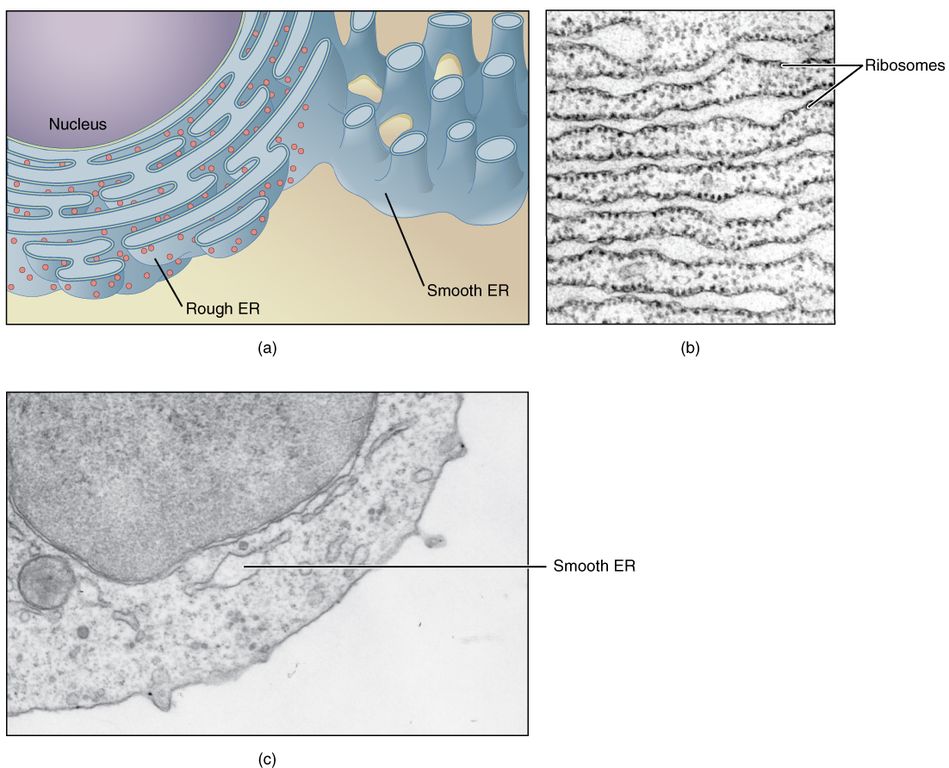
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum lacks ribosomes, so it appears more tubular and less bumpy under a microscope. Its job, much like that of the rough endoplasmic reticulum, is to manufacture and package molecules, but the smooth endoplasmic reticulum also makes lipids and some steroid hormones, and in some types of cells it metabolizes some sugars that attach to the outside of it.
What does smooth endoplasmic reticulum mean in life science?
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum (smooth ER) is a membranous organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. It is a subset of the endomembrane system of the endoplasmic reticulum. Its main functions are the synthesis of lipids, steroid hormones, the detoxification of harmful metabolic byproducts and the storage and metabolism of calcium ions within ...
What does a smooth endoplasmic reticulum look like?
What does the smooth ER look like? Rough ER looks like sheets or disks of bumpy membranes while smooth ER looks more like tubes. Rough ER is called rough because it has ribosomes attached to its surface. Smooth ER (SER) acts as a storage organelle. Click to see full answer. In this manner, what is smooth ER made of?
Are steroids synthesised in smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
Steroid-secreting cells possess abundant smooth endoplasmic reticulum whose membranes contain many enzymes involved in sterol and steroid synthesis.
What is the structure and function of a endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a large, dynamic structure that serves many roles in the cell including calcium storage, protein synthesis and lipid metabolism. The diverse functions of the ER are performed by distinct domains; consisting of tubules, sheets and the nuclear envelope.
What is the structure and function of smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum?
The rough ER, studded with millions of membrane bound ribosomes, is involved with the production, folding, quality control and despatch of some proteins. Smooth ER is largely associated with lipid (fat) manufacture and metabolism and steroid production hormone production. It also has a detoxification function.
What is the function of smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
The smooth ER is involved in the synthesis of lipids, including cholesterol and phospholipids, which are used in the production of new cellular membrane. In certain cell types, smooth ER plays an important role in the synthesis of steroid hormones from cholesterol.
What is the structure of rough endoplasmic reticulum?
The RER is morphologically distinguishable by its series of convoluted, flattened like membrane sheets (called cisternae) that arise near the nucleus and extend across the cytoplasm. Sections of the cisternae contain ribosomes, held together by microtubules of the cytoskeleton.
What are the four major functions of the endoplasmic reticulum?
This includes both plant and animal cells. The endoplasmic reticulum, sometimes referred to as the ER, is an organelle found in the cytoplasms of most eukaryotic cells and performs diverse functions such as storing calcium, lipid and steroid synthesis, carbohydrate metabolism, and protein synthesis and folding.
Which is not a function of smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
Answer and Explanation: \The correct option is a. Synthesis of carcinogens.. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is found in eukaryotic cells.
What is the structural difference between rough endoplasmic reticulum ER and smooth ER?
The most basic difference between RER and SER is the presence of ribosomes. When ribosomes attach to the surface of an ER, it gives a characteristic rough appearance; hence it is called Rough ER. On the other hand, a smooth ER does not have ribosomes on its surface. It possesses ribosomes attached to its membrane.
What is the difference between smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum function?
The main difference between these two terminologies is that the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum is known for stocking the lipids and proteins. It is not bounded by ribosomes. Whereas, the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum is bounded by the ribosomes and also stores proteins.
What is the difference between smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum function?
The main difference between these two terminologies is that the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum is known for stocking the lipids and proteins. It is not bounded by ribosomes. Whereas, the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum is bounded by the ribosomes and also stores proteins.
What is the structural difference between rough endoplasmic reticulum ER and smooth ER?
The most basic difference between RER and SER is the presence of ribosomes. When ribosomes attach to the surface of an ER, it gives a characteristic rough appearance; hence it is called Rough ER. On the other hand, a smooth ER does not have ribosomes on its surface. It possesses ribosomes attached to its membrane.
Which of the following is a function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
The major function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum is protein synthesis and their folding into proper quaternary structures.
What do the SER and RER have in common?
Both the SER and RER are large continuous sheets of membrane that fold back on themselves to form an enclosed space (lumen).
1. What is endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum is a tubular network of membranes found within the cytoplasm of the eukaryotic cell.
2. List the types of endoplasmic reticulum.
The endoplasmic reticulum is classified into two types: Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Rough endoplasmic reticulum
3. List the functions of the endoplasmic reticulum.
The endoplasmic reticulum performs the following functions: It is responsible for the production and secretion of steroid hormones. It is also resp...
What is the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER), meshwork of fine disklike tubular membrane vesicles, part of a continuous membrane organelle within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells, that is involved in the synthesis and storage of lipids , including cholesterol and phospholipids, which are used in the production of new cel lular membrane . The smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) is distinguished from the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), the other basic type of endoplasmic reticulum, by its lack of ribosomes, which are protein -synthesizing particles that can be found attached to the outer surface of the RER to give the membrane its “rough” appearance. SER occurs both in animal and in plant cells.
Which reticulum stores calcium ions?
The sarcoplasmic reticulum is a critical storage site for calcium ions, taking up the ions from the cytoplasm. It also releases calcium ions when the muscle cell is triggered by nerve stimuli, resulting in muscle contraction.
What is the function of the SER?
The functions of the SER, a meshwork of fine tubular membrane vesicles, vary considerably from cell to cell. One important role is the synthesis... In skeletal muscle cells, SER occurs as a specialized membrane structure known as the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
What are the structures that are associated with the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
In liver and heart, special structures called Glycosomes are present which are associated with the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum. Glycosomes are the protein moieties that corresponds to the enzymes involved in the synthesis of Glycogen.
What is the protein that is present in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
A protein called Reticulon is present in Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum which is responsible for the curvature and bending of the Smooth ER. The membrane of the Smooth ER does not contain Ribosome therefore it is not involved in protein synthesis and is also not a part of the endomembrane system.
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
The Endoplasmic Reticulum is composed of a double membrane enclosed by luminal space and it separates the lumen from the cytosol. Endoplasmic Reticulum is of two types, that is, smooth ER and Rough ER.
Why does the smooth endoplasmic reticulum appear rough?
Due to the absence of Ribosome on the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum, it appears smooth and while Ribosome is attached on the membrane of the rough Endoplasmic Reticulum, it appears rough.
What is the function of smooth ER?
Smooth ER is responsible for synthesis and storage of lipids like cholesterol and phospholipids which are required for building a cell’s plasma membrane. Smooth ER is extensively developed in skeletal muscles, kidney tubules and steroid producing endocrine glands.
Which reticulum releases calcium ions?
Sequestration of calcium ions: The regulated release of calcium ions from Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum of skeletal and cardiac muscles regulates the contraction of the cell. Endoplasmic Reticulum of muscle cells is known as Sarcoplasmic Reticulum. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum also releases calcium ions when a cell receives nerve impulse ...
Is the smooth endoplasmic reticulum tubular?
The membranes of Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum are highly curved and tubular, forming an interconnected system present in the cytoplasm and near to plasma membrane. According to some theories proposed by the scientists, the Smooth ER is an extension of the Rough ER which is itself an extension of the outer membrane of the nucleus. After homogenization (separation) the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum forms the fragments of rough vesicles while in case of Smooth ER smooth-surfaced vesicles are formed.
What is the difference between smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum?
Rough endoplasmic reticulum has ribosomes embedded within its structure, giving a “rough” appearance. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum does not have these ribosomes, hence appear “smooth.”
What is the Endoplasmic Reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum transpires in two forms: a type with a ribosome-studded surface and another with a smooth surface. The latter is called the smooth endoplasmic reticulum, and the former is called the rough endoplasmic reticulum. These membranes form continuous folds, eventually joining the outer layer of the nuclear membrane. Except for sperm cells and red blood cells, the endoplasmic reticulum is observed in every other type of eukaryotic cell.
Why is the rough endoplasmic reticulum called that?
The rough endoplasmic reticulum is named so because of its appearance. It is a series of connected flattened sacs having several ribosomes on its outer surface, hence the name. It synthesizes and secretes proteins in the liver, hormones and other substances in the glands.
What is the function of the smooth ER?
Smooth ER is also responsible for the production and secretion of steroid hormones. It is also responsible for the metabolism of carbohydrates. The smooth ER store and release calcium ions.
Which part of the reticulum plays a vital role in protein folding?
Rough endoplasmic reticulum also plays a vital role in protein folding.
What is the role of ER in the nervous system?
ER releases calcium ions, which are necessary for the nervous system and muscular system.
Which organelle transports the products of the rough ER to other cellular organelles?
Smooth ER transports the products of the rough ER to other cellular organelles, especially the Golgi apparatus.
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth) =. Endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes inside a cell through which proteins and other molecules move. Proteins are assembled at organelles called ribosomes. When proteins are destined to be part of the cell membrane or exported from the cell, the ribosomes assembling them attach to ...
Why do proteins stay in the endoplasmic reticulum?
They're retained and the endoplasmic reticulum becomes engorged because it seems to be constipated, in a way , and the proteins don't get out where they're suppose to go.
Which organelle is a workhorse in producing proteins and substances needed by the rest of the cell?
So the endoplasmic reticulum is an organelle that's really a workhorse in producing proteins and substances needed by the rest of the cell. William Gahl, M.D., Ph.D.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition
Eukaryotic cells have a well-defined nucleus and membrane-covered organelles. One such organelle is the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) found in both eukaryotic animal and plant cells. It often appears as two interconnected sub-compartments: rough ER and smooth ER.
Smooth ER Function
What does the smooth ER do? The smooth ER is like a factory that manufactures many products that a cell needs to function. Exactly what it makes depends on the type of cell. Imagine two factories in two different locations. One is in the middle of Florida, while the other is in California.
What is the function of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
Functions of the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (smooth ER) Inside the cells of the adipose tissue, it synthesizes the fats. It is involved in the synthesis and lysis of glycogen. The hydrolysis of the glycogen is known as glycogenolysis. Enzymes like glycosomes are present in it.
Where is the smooth endoplasmic reticulum found?
The Smooth endoplasmic reticulum is more abundant near the plasma membrane and may be connected to the plasma membrane. In the metabolically active cells such as pancreatic cells and liver, it is present quite extensive. In the storage cells, it is present simply. In the adipose cell, it is found as tubules. In the spermatocytes, it is reduced.
How much does the endoplasmic reticulum increase the surface?
So compared to the external surface it increases the internal surface about 30 to 40 times. The Endoplasmic reticulum is of two types: Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) and Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
What are the enzymes in the endoplasmic reticulum?
The Endoplasmic reticulum contains different enzymes like ATPase, reductase, dehydrogenase, phosphatase, etc which perform various synthetic activities. It also performs metabolic activities as well.
What is the intracellular space?
At the other end, it connects the cell membrane. The intracellular space is divided into two parts. i.e inside the endoplasmic reticulum and another one is the rest of the cytoplasm. Depending upon the cell, its extend may vary from one to another.
Which endoplasmic reticulum can pass to the Golgi complex?
Through the smooth endoplasmic reticulum, the synthetic products of the rough endoplasmic reticulum can pass to the Golgi complex.
Which part of the reticulum is responsible for the exchange of molecules?
The endoplasmic reticulum consists of the membrane, through which the exchange of molecules occurs.
What is the function of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum serves as a transitional area for transport vesicles. It also functions in carbohydrate and lipid synthesis. Cholesterol and phospholipids are examples.
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of tubules and flattened sacs that serve a variety of functions in plant and animal cells . The two regions of the ER differ in both structure and function. Rough ER has ribosomes attached to the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. Smooth ER lacks attached ribosomes.
What is the role of the endoplasmic reticulum in eukaryotic cells?
It plays a major role in the production, processing, and transport of proteins and lipids. The ER produces transmembrane proteins and lipids for its membrane and many other cell components including lysosomes, secretory vesicles, ...
What is the purpose of smooth ER?
Smooth ER also serves as a transitional area for vesicles that transport ER products to various destinations. In liver cells the smooth ER produces enzymes that help to detoxify certain compounds.
How are proteins sent to the Golgi apparatus?
Some proteins are sent to the Golgi apparatus by special transport vesicles. After the proteins have been modified in the Golgi, they are transported to their proper destinations within the cell or exported from the cell by exocytosis .
What is the smooth ER?
Typically, the smooth ER is a tubule network and the rough ER is a series of flattened sacs. The space inside of the ER is called the lumen. The ER is very extensive extending from the cell membrane through the cytoplasm and forming a continuous connection with the nuclear envelope. Since the ER is connected with the nuclear envelope, ...
Which structure helps support the cell and aids in organelle movement?
Cytoskeleton: a network of fibers throughout the cytoplasm that helps support the cell and aids in organelle movement.
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a continuous membrane system that forms a series of flattened sacs within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. All eukaryotic cells contain an ER. In animal cells, the ER usually constitutes more than half of the membranous content of the cell. The ER can be classified in two functionally distinct forms: ...
Who introduced the term "endoplasmic reticulum"?
In the late 1940s and early 1950s, Porter and colleagues Helen P. Thompson and Frances Kallman introduced the term endoplasmic reticulum to describe the organelle. Porter later worked with Romanian-born American cell biologist George E. Palade to elucidate key characteristics of the ER. Kara Rogers.
What is the color of the mitochondria in a pancreatic acinar cell?
A scanning electron micrograph of a pancreatic acinar cell, showing mitochondria (blue), rough endoplasmic reticulum (yellow; ribosomes appear as small dots), and Golgi apparatus (gray, at centre and lower left).
What is the ER in eukaryotic cells?
All eukaryotic cells contain an endoplasmic reticulum (ER). In animal cells, the ER usually constitutes more than half of the membranous content of the cell. Differences in certain physical and functional characteristics distinguish the two types of ER, known as rough ER and smooth ER. Rough ER is named for its rough appearance, ...
What is the role of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in the liver?
In cells of the liver, it contributes to the detoxification of drugs and harmful chemicals. The sarcoplasmic reticulum is a specialized type of smooth ER that regulates the calcium ion concentration in the cytoplasm of striated muscle cells. Get a Britannica Premium subscription and gain access to exclusive content.
What percentage of the membrane content of an animal cell is ER?
In animal cells, the ER usually constitutes more than half of the membranous content of the cell.
Where are proteins transported to the Golgi apparatus?
Proteins targeted for transport to the Golgi apparatus are transferred from ribosomes on rough ER into the rough ER lumen , which serves as the site of protein folding, modification, and assembly. endoplasmic reticulum; organelle.