
Basically, spinal cord functions can be broadly categorized into two parts — first, information transmission, and second, reflex coordination. The spinal cord has a crucial role to play in various functions of our body — including the movement of our limbs and the transmission of sensory and motor nerve impulses to and from the brain.
What are the parts and functions of the spinal cord?
Spinal Cord: Parts and Functions (with Images) The spinal cord Is a tubular bundle containing a long, thin structure of nerve tissue and supporting cells. This region of the body comprises a large part of the organism. Specifically, it slides from the Medulla bulb of the Trunk of the brain (Brain) to the lumbar region.
What are the 5 sections of the spinal cord?
The spinal cord nerves can be grouped as:
- Cervical
- Thoracic
- Sacral
- Lumbar
- Coccygeal
What are facts about the spinal cord?
What is the spinal cord?
- The spinal cord is like a thick electrical cable that carries messages back and forth between your brain and your body
- Just like the skull protects your brain, the spine protects your spinal cord, which is very delicate
- The spinal cord carries signals from the brain that tell your body what to do, such as moving your arms or legs
Is the spinal cord the same as the vertebrae?
Thus, the main difference between spinal cord and vertebrae is that spinal cord is one of the two components of the central nervous system while a series of vertebrae form the vertebral column. Additionally, the spinal cord is made up of nervous tissue while vertebrae are mainly made up of bones.

What are the 3 main functions of the spinal cord?
Sensory, motor, and reflex functions are affected or impeded when the brain can't transmit impulses past the injury site in the spinal cord. The higher up the damage on the spinal cord, the more significant the damage and loss of function.
What is the function of spinal cord cells?
They provide structure for the body, take in nutrients from food, convert those nutrients into energy, and carry out specialized functions. Cells also contain the body's hereditary material and can make copies of themselves. Cells have many parts, each with a different function.
What is the main function of the spinal cord quizlet?
One main function of the spinal cord is to receive sensory information from the body(via the peripheral nervous system) and send these messages to the brain for processing.
What neural function is processed directly by the spinal cord?
The primary role of the spinal cord is to relay sensory, motor, and autonomic messages between the brain and the rest of the body. 1 Myelinated nerves along the pathways of the spinal cord send electrical signals to each other to facilitate these actions.
What is spinal cord in human body?
A column of nerve tissue that runs from the base of the skull down the center of the back. It is covered by three thin layers of protective tissue called membranes. The spinal cord and membranes are surrounded by the vertebrae (back bones). The spinal cord and the brain make up the central nervous system (CNS).
What is the structure of the spinal cord?
Structure Of Spinal Cord. The Spinal cord runs through a hollow case from the skull enclosed within the vertebral column. Spinal nerves arise from different regions of the vertebral column and are named accordingly, the regions are – Neck, chest, pelvic and abdominal. Cross-section of spinal cord displays grey matter shaped like a butterfly ...
What is the spinal cord?
Spinal Cord. The spinal cord is a part of the central nervous system. It is a long pipe-like structure arising from the medulla oblongata, part of the brain consisting of a collection of nerve fibres, running through the vertebral column of the backbone. It is segmented with a pair of roots ...
How many spinal nerves are there?
Several spinal nerves emerge out of each segment of the spinal cord. There are 8 pairs of cervical, 5 lumbar, 12 thoracics, 5 sacral and 1 co ccygeal pair of spinal nerves
How long is the spinal cord?
In adults, the spinal cord is usually 40cm long and 2cm wide. It forms a vital link between the brain and the body.
Why is it important to understand the physiology of the spinal cord?
Understanding the physiology of the spinal cord helps in detecting and determining the various methods to deal with diseases and damage related to the spinal cord. Also Read: Peripheral Nervous System.
What are the three layers of meninges?
Three layers of meninges surround the spinal cord and spinal nerve roots. Dura mater. Arachnoid mater. Pia mater. Dura mater consists of two layers- periosteal and meningeal. Epidural space is present between the two layers. Subarachnoid space lies between the arachnoid mater and pia mater.
What is the subarachnoid space?
Subarachnoid space lies between the arachnoid mater and pia mater. It is filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
Which branch of the spinal cord supplies the spinal cord?
The spinal cord is supplied by branches of the vertebral and segmental arteries.
Where is the spinal cord located?
It is situated inside the vertebral canal of the vertebral column. During development, there’s a disproportion between spinal cord growth and vertebral column growth. The spinal cord finishes growing at the age of 4, while the vertebral column finishes growing at age 14-18.
How many segments are there in the spinal cord?
Like the vertebral column, the spinal cord is divided into segments: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal. Each segment of the spinal cord provides several pairs of spinal nerves, which exit from vertebral canal through the intervertebral foramina. There are 8 pairs of cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, ...
What veins drain into the vertebral plexus?
Anterior and posterior spinal veins drain into radicular veins, which then empty into the (internal and external) vertebral venous plexus. This network eventually empties into the vertebral (neck) and segmental (trunk) veins. Blood supply is always an inevitable part of any anatomy study unit.
How many spinal nerves are there?
Spinal nerves. 31 pair of nerves that emerge from the segments of the spinal cord to innervate the body structures; 8 pairs of cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 1 coccygeal pair of spinal nerves.
What does "scull" mean in medical terms?
You can easy remember the extent of the spinal cord with a mnemonic ' SCULL ', which stands for ' S pinal C ord U ntil L2 (LL)'.
How many neurons are involved in monosynaptic reflexes?
Monosynaptic reflexes play out with only two neurons participating in the reflex arc, one sensory and one motor. The first-order neuron (sensory) is in the spinal ganglion, while the second-order neuron (motor) is in the anterior horn of the spinal cord). The sensory neuron gathers impulses from the muscle and sends this information to the motor neuron which innervates the same muscle. The motor neuron then causes contraction of the innervated muscle. An example of a monosynaptic reflex is the stretch reflex.
What are the functions of the spinal cord?
The spinal cord’s major functions include: 1 Electrochemical communication. Electrical currents travel up and down the spinal cord and across nerves, sending signals which allow different segments of the body to communicate with the brain. 2 Walking. While a person walks, a collection of muscle groups in the legs are constantly contracting and relaxing. The action of taking step after step may seem incredibly simple to us since we have been doing it all of our lives, but there are actually a lot of factors that have to be coordinated properly to allow this to happen. This central pattern generators in the spinal cord are made up of neurons which send signals to the muscles in the legs, making them relax or contract, and produce the alternating movements which occur when a person walks. 3 Reflexes. Reflexes are involuntary responses resulting from stimuli involving the brain, spinal cord, and nerves of the peripheral nervous system.
What is the spinal cord?
The spinal cord is a complex cylinder of nerves that starts at the base of your brain and runs down the vertebral canal to the backbone. It is part of the body’s collection of nerves, called the central nervous system, along with the brain. In each of the spinal cord’s many segments lives a pair of roots that are made up of nerve fibers. These roots are referred to as the dorsal (which is towards the back) and the ventral (which is away from the back) roots. We depend on the spinal column to be the main support of our body. It allows us to stand upright, bend, and twist while protecting the spinal cord from injury. If the spinal cord is injured, it often causes issues like:
What is the white matter of the spinal cord?
White Matter & Grey Matter. The spinal cord is split into grey matter (which is in the shape of a butterfly) and white matter (which is the material surrounding the grey). The white matter is made up of nerve fibers, called axons, which run up and down the length of the cord. Each group of axons carries a specific type of information it needs ...
How many pairs of spinal nerves are there?
A nerve is an organ shaped like a small cord that is made up of several axons that are bound together. There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves
How long will it take technology to reverse spinal cord damage?
Research is progressing quickly, and in just 5 years we could have the means to reverse the most severe of spinal cord injuries.
What are involuntary responses resulting from stimuli involving the brain, spinal cord, and nerves of?
Reflexes . Reflexes are involuntary responses resulting from stimuli involving the brain, spinal cord, and nerves of the peripheral nervous system.
Why do we depend on the spinal column?
We depend on the spinal column to be the main support of our body. It allows us to stand upright, bend, and twist while protecting the spinal cord from injury. If the spinal cord is injured, it often causes issues like: Permanent changes in the body’s strength; Loss of sensation; and.
What is the spinal cord?
The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system. This long structure runs down the center of your back, and it mediates messages between the brain and the peripheral nerves. The spinal cord is primarily composed of nerves, which are organized in systematic pathways, also described as tracts.
What is the function of the spine?
The spine (backbone) encloses and protects the spinal cord. Damage to the spinal cord can occur as a result of problems such as traumatic injuries, infections, and disease. Treatment for conditions that affect the spinal cord often includes rehabilitation and may also involve medication and/or surgery.
What is the area of the spinal cord called?
The deep, central area of the spinal cord is referred to as gray matter, and the portion that is located nearer to the outer edge of the spinal cord is referred to as white matter. A coating called myelin (a type of fat) insulates all nerves.
What are the three regions of the spinal cord?
From top to bottom, the regions of the spinal cord include the cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral levels. Each of these levels corresponds to spinal nerves that emerge from the spinal cord toward structures of the body, such as the arms, legs, and trunk.
Where are sensory nerves located?
The sensory nerve pathways are located toward the posterior (back) of the spinal cord , while the motor nerve pathways run along the lateral (sides) and anterior (front) regions of the spinal cord. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), with nutrients and immune cells, flows around the spinal cord.
Where does motor control occur in the spinal cord?
Motor control of the voluntary (on purpose) muscles of the body travels through the spinal cord in the corticospinal tract. Motor signals are initiated in the motor strip, a region of the cerebral cortex of the brain.
Which part of the spinal cord is composed of nerves that send motor signals to the spinal nerves?
This region is the frontal portion of the gray matter of the spinal cord, and it is composed of nerves that send motor signals to the spinal nerves.
What is the spinal cord?
The spinal cord is a long bundle of nerves and cells that extends from the lower portion of the brain to the lower back. It carries signals between the brain and the rest of the body. This article covers the key anatomy of the spinal cord and its functions.
Where is the spinal cord located?
The spinal cord is a long bundle of nerves and cells that extends from the lower portion of the brain to the lower back. It carries signals between the brain and the rest of the body.
What is the middle layer of the spinal cord?
Arachnoid mater: The arachnoid mater is the middle layer of spinal cord covering.
What are the three layers of tissue that protect the spinal cord?
Three layers of tissue protect the spinal cord: the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater. Doctors call these layers “meninges.”. The layers are as follows: Dura mater: This is the outermost layer of the spinal cord’s meninges. It is a tough, protective coating.
How long is the spinal cord?
According to some estimates, females have a spinal cord of about 43 centimeters (cm), while males have a spinal cord of about 45 cm. The spinal cord comprises three parts: the cervical (neck), thoracic (chest), and lumbar (lower back) regions.
Why is it important to know the location of spinal cord coverings?
Having knowledge of the location and structure of the protective spinal cord coverings can help healthcare professionals provide pain relief for certain procedures.
Which layer of the spinal cord directly covers the spinal cord?
Pia mater: The pia mater is the layer that directly covers the spinal cord.
What is the spinal cord?
The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system (CNS) that extends from the brain stem to the lumbar region and is contained within the vertebral column. Humans have a total of 31 segments that each give rise to a pair of sensory nerve roots (one on each side) and a pair of motor nerve roots (one on each side). It receives sensory (afferent) information and induces various autonomic (involuntary) and somatic (voluntary) responses (efferent responses). It acts to transmit signals from the motor cortex to the body, and it relays afferent signals from sensory neurons in the sensory ganglia (dorsal root ganglia, outside the spinal cord) to the sensory cortex.
Which part of the spinal cord transmits information to the peripheral nerves?
The ventral horn of the spinal cord transmits the information to the peripheral nerves or muscles via ventral nerve roots.
What is the middle region of the spinal cord?
This diagram shows a cross-section of the spinal cord and typical H or butterfly appearance due to the two dorsal horns and two ventral horns, The middle region consists of the central canal that contains CSF. This picture also shows motor neurons located in the ventral horn and the dorsal and ventral nerve roots. The neurons outside the spinal cord that give to the dorsal nerve roots comprise the sensory ganglia. The dorsal and ventral nerve roots combine to form spinal nerves.
How does sensory information get to the brain?
Afferent (sensory) information is detected by various mechanoreceptors and relayed to the sensory ganglia outside the spinal cord . Sensory information that is instead relayed directly to the brain includes sight, sound, taste, and smell. This information passes through the ganglia and transmitted to the spinal cord via the dorsal nerve roots. Through various tracts, the spinal cord transmits this information to the brain, in particular, the thalamus or cerebellum. The second-order neurons in the spinal cord decussate (crossover) sensory information to the contralateral side, which then ascends to the brain. In contrast, efferent information is transmitted from neurons in the brain to motor neurons in the ventral horn. This can occur via various tracts. The motor neurons in the ventral horn transmit information to peripheral nerves or muscle via ventral nerve roots. The dorsal and ventral nerve roots combine outside of the spinal cord to form spinal nerves.
What is the white matter of the spinal cord?
In the spinal cord, the white matter consists of myelinated tracts. It is deep to the meninges and on the outside of the grey matter. The grey matter contains nerve cell bodies and their associated myelinated axons.
What is the mnemonic for the three layers of the spinal cord?
A mnemonic to remember these three layers is 'DAP'. Denticulate ligaments attach to the middle region of the spinal cord and suspend it in the vertebral column.
Which part of the spinal cord is responsible for the transmission of sensory information to the brain?
In the dorsal horn of the spinal cord, the fibers of second-order neurons decussate (crossover) to the contralateral side and ascend to the brain. Several tracts relay sensory information to the brain. These include:
What is the function of the spinal cord?
Spinal cord performs two main functions: ADVERTISEMENTS: (i) The stimuli are passed from and to the brain through the spinal cord. (ii) It is the centre of spinal reflex action. Biology, Human Physiology, Human Spinal Cord.
What is the internal structure of the spinal cord?
Internal Structure: The internal anatomy of the spinal cord is best seen in cross section. Two indentations, the posterior median sulcus and the anterior median fissure, separate the spinal cord into left and right symmetrical halves. The inner butterfly-shaped area is the grey matter of the spinal cord. Grey matter is so named because it lacks ...
Why does the spinal cord not extend to the coccygeal region?
The spinal cord does not extend to the coccygeal region because during development the vertebral column elongates more rapidly than the spinal cord. The filum terminate anchors the spinal cord within the vertebral column. In-fact, the filum terminale is a long slender filament at the end of the spinal cord.
How long is the spinal cord?
It is continuous, to the level of the second lumbar vertebra. In an adult the spinal cord is from 42 to 45 centimeters long. Its diameter varies at different levels, being enlarged in the cervical and lumbar regions.
Where does the spinal cord end?
The spinal cord ends as the conus medullaris. The conus medullaris ends at the level of the intervertebral disc between the first and second lumbar vertebral in adults. Actually the conus medullaris is a conical portion of lower spinal cord. ADVERTISEMENTS:
What are the three membranes that surround the spinal cord?
The spinal cord is surrounded by the same three protective membranes (meninges) as found in the brain, viz., a thin innermost piamater, the middle webby arachnoid membrane (arachnoid mater) and the outer tough duramater . ADVERTISEMENTS:
Which vertebra contains spinal nerves that branch from the spinal cord at higher levels?
By adulthood the area within the vertebral column below the second lumbar vertebra contains spinal nerves that branch from the spinal cord at higher levels.
What are the parts of the spine?
A healthy spine has three natural curves that make an S-shape. These curves absorb shocks to your body and protect your spine from injury. Many different parts make up your spine:
What is the spine?
Your spine, or backbone, is your body's central support structure. It connects different parts of your musculoskeletal system. Your spine helps you sit, stand, walk, twist and bend. Back injuries, spinal cord conditions and other problems can damage the spine and cause back pain.
What are the spine segments?
The 33 vertebrae make up five distinct spine segments. Starting at the neck and going down toward your buttocks (rear end), these segments include:
How can I keep my spine healthy?
Strong back muscles can protect your spine and prevent back problems. Try to do back-strengthening and stretching exercises at least twice a week. Exercises like planks strengthen the core (abdominal, side and back muscles) to give your spine more support. Other protective measures include:
How does the spine help you walk?
The spine supports your body and helps you walk, twist and move. The disks that cushion vertebrae may compress with age or injury, leading to a herniated disk. Exercises can strengthen the core muscles that support the spine and prevent back injuries and back pain. Appointments & Access.
What is the lower part of the spine called?
Lumbar (lower back): Five vertebrae (L1 to L5) make up the lower part of the spine. Your lumbar spine supports the upper parts of the spine. It connects to the pelvis and bears most of your body’s weight, as well as the stress of lifting and carrying items. Many back problems occur in the lumbar spine.
What causes spine pain?
Other conditions that affect spine health include: Arthritic conditions, such as ankylosing spondylitis (AS). Back strains and sprains. Birth defects such as spina bifida. Bone spurs (jagged edges on vertebrae that put pressure on the spinal cord and nerves).
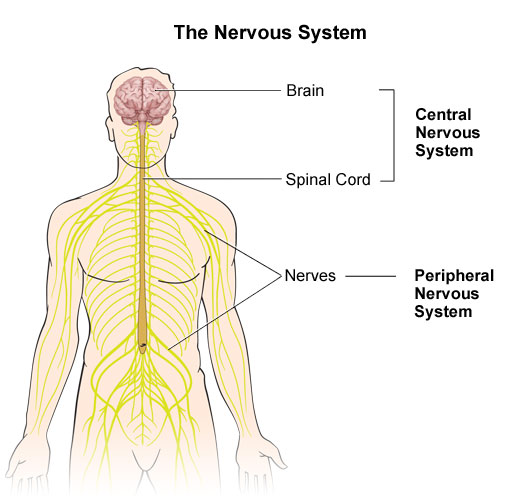
The Major Functions of The Spinal Cord
The Structure of The Spinal Cord
- Theoverall structureof the spinal cord is enclosed by the protection of the vertebral column. The spinal nerves are located in the spaces between the arches of the vertebrae. Spinal nerves are divided into these separate regions: 1. Cervical (neck) 2. Thoracic (chest) 3. Lumbar (abdominal) 4. Sacral (pelvic) 5. Coccygeal (tailbone)
Spinal Cord Injury
- A spinal cord injury (SCI) is when a part of the cord or the nerves located at the base of the spine are damaged. This can have a major effect on the body’s sensory, motor, and reflex capabilities if the brain is unable to send information past the location of the injury." The closer the injury is to the brain, the more expansive the damage. As you can probably imagine, an SCI can alter a pers…