What tissues are in xylem?
Xylem
- Xylem Definition. Xylem is a type of tissue in vascular plants that transports water and some nutrients from the roots to the leaves.
- Function of Xylem. ...
- Structure of Xylem. ...
- Details of Xylem Development. ...
- Types of Xylem. ...
- Differences Between Xylem and Phloem. ...
What are the types of xylem?
Xylem (XYL) is a leading global water technology company committed to solving critical water and infrastructure challenges with innovation. Our more than 16,000 diverse employees delivered revenue of $4.88 billion in 2020.
What is the structure of xylem tissue?
Xylem tissue is composed of four component parts: (4) Xylem sclerenchyma. It comprises of dead cells. Cells are long and tapering at two ends. The cell wall is hard, rigid, and lignified. Pits are present on the wall. The cells are attached. It consists of dead cells. The cells are tubular and hollow inside.
What is the difference between phloem and xylem?
Xylem and Phloem Difference
- Xylem and Phloem. Xylem and phloem are two different kinds of vascular tissues that are involved mainly in the process of transportation.
- Difference Between Xylem and Phloem Tissue. Xylem is the complex tissue of plants that helps in the transportation of water and nutrients in the plant.
- Importance of Xylem and Phloem. ...

What is the structure and function of xylem?
Abstract. Xylem is the specialised tissue of vascular plants that transports water and nutrients from the plant–soil interface to stems and leaves, and provides mechanical support and storage. The water-conducting function of xylem is one of the major distinguishing features of vascular plants.
What is the structure and function of xylem and phloem?
Differences Between Xylem and PhloemXylemPhloemFunctionsTransports soluble mineral nutrients and water molecules from the roots to the aerial parts of the plant.Transports food and other nutrients including sugar and amino acids from leaves to storage organs and growing parts of the plant.Vascular Bundles21 more rows
What is the function of the xylem cell?
The xylem transports water and minerals from the roots up the plant stem and into the leaves. In a mature flowering plant or tree, most of the cells that make up the xylem are specialised cells called vessels.
What are xylem made out of?
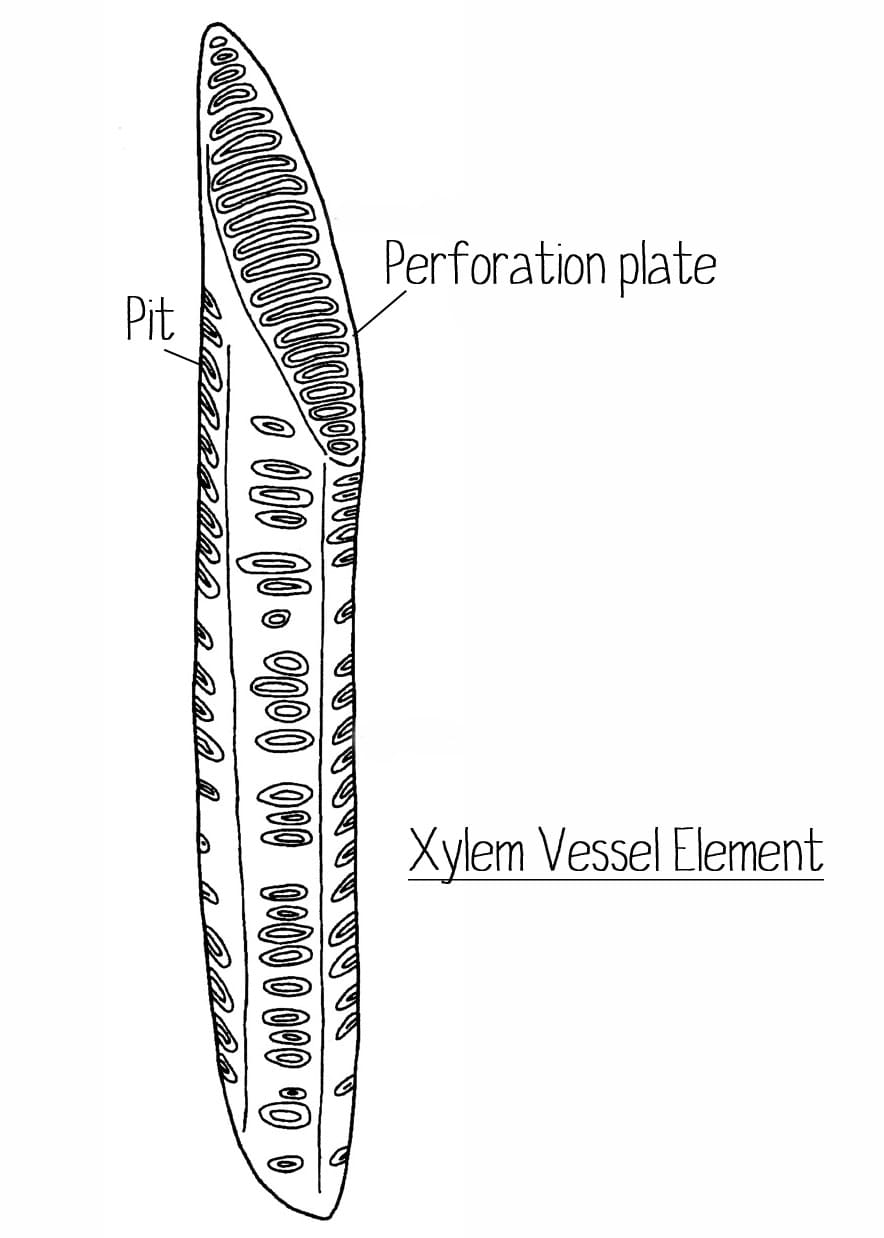
Xylem consists of tracheids, vessels, parenchyma, and fibers. Vessels consist of vessel elements joined together in files by large perforation plates, large gaps in the end walls between successive vessel elements, while tracheids have tapering ends that overlap with adjacent cells, and lack perforation plates.
What is the structure of phloem?
The phloem is a complex tissue and is formed typically by three cell types, the sieve elements, the parenchyma cells, and the sclerenchyma cells (Figure 2a–d). Sclerenchyma cells might sometimes be absent in primary and/or secondary phloem.
What is xylem short answer?
Xylem is a type of tissue in vascular plants that transports water and some nutrients from the roots to the leaves. Phloem is the other type of transport tissue; it transports sucrose and other nutrients throughout the plant.
How xylem is formed?
Xylem tissue forms from cells that are derived from meristematic cells commonly called procambium and cambium. These meristems contain pluripotent stem cells which have the ability to continuously divide and maintain the stem cell population, a so-called 'stem cell niche' (Miyashima et al., 2013).
How does xylem transport water?
The tension created by transpiration “pulls” water in the plant xylem, drawing the water upward in much the same way that you draw water upward when you suck on a straw. Cohesion (water sticking to each other) causes more water molecules to fill the gap in the xylem as the top-most water is pulled toward the stomata.
What is the function of phloem?
While the main role of the phloem tissue is to transport carbohydrates from sources to sinks through the sieve elements, phloem is also composed of parenchyma cells, which play a key role in the storage of water, non-structural carbohydrates and storage proteins (Rosell 2016).
How does the structure of the phloem help its function?
The cells that make up the phloem are adapted to their function: Sieve tubes - specialised for transport and have no nuclei. Each sieve tube has a perforated end so its cytoplasm connects one cell to the next. Companion cells - transport of substances in the phloem requires energy.
1. Where is the Xylem?
Xylem can be found in the non-woody plants and the parts of the non-woody plants. It is also found in the secondary xylem formed by the meristem ca...
2. Why are Xylem Cells Dead?
Xylem is made up of two types of cell tracheids and vessel elements. Both of the cells are dead when they are used in the xylem. Dead cells, which...
3. Brief the process of Xylem.
Tracheids and vessel members are both typically narrow, elongated and hollow; this is what xylem treachery cell consists of. The only type of water...
4. How does the process of xylem begin?
When the actively dividing shoot tips and growing cells of the root of apical meristem begin, the formation of xylem by giving rise to xylems prima...
What are the structures of xylem?
Structure of Xylem. Xylem is made up of several types of cells. Tracheids are long cells that help transport xylem sap and also provide structural support. Vessel elements are shorter than tracheids, but also help conduct water. They are found in flowering plants, but not in gymnosperms like pine trees.
Where is the xylem in a plant?
Centrarch: xylem forms one chamber in the middle of the stem, with metaxylem surrounding the protoxylem. This formation is not found in any living plants today. Exarch: xylem develops in multiple strands, and each strand develops inward towards the center of the root. Xylem in roots of vascular plants develops this way.
How do phloem and xylem work together?
Xylem and phloem both make up the vascular system of the plant, and work together to form vascular bundles that provide mechanical strength to the plant, but they have important differences. While xylem transports water, phloem transports food and nutrients. (One way to remember this is that phloem and food both begin with an “F” sound.) Xylem is unidirectional; its job is to make sure water flows upward. However, phloem is bidirectional and transports food and nutrients to all of the plant. Mature xylem is made up of dead cells that do not have cell contents, while phloem contains living cells (albeit without nuclei). The structure of xylem and phloem is also different. While xylem is made up of tracheids and vessels, phloem is made up of sieve tubes which have many holes for transporting nutrients. Xylem is star-shaped, while phloem is round and actually surrounds the xylem.
What is the difference between xylem and phloem?
Xylem is a type of tissue in vascular plants that transports water and some nutrients from the roots to the leaves. Phloem is the other type of transport tissue; it transports sucrose and other nutrients throughout the plant. Xylem and phloem give vascular plants their classification; they are the vascular tissues that transport substances throughout the plant.
How does the xylem work?
These substances are transported through passive transport, so the process doesn’t require energy. The phenomenon that allows xylem sap to flow upwards against gravity is called capillary action. This occurs when surface tension makes liquid move upward. Water is also aided in moving up through the xyle m by adhering to the xyle m cells. However, it gets harder to work against gravity to transport materials as a plant grows taller, so xylem sets an upper limit on the growth of tall trees.
How does water move through the xylem?
This occurs when surface tension makes liquid move upward. Water is also aided in moving up through the xylem by adhering to the xylem cells. However, it gets harder to work against gravity to transport materials as a plant grows taller, so xylem sets an upper limit on the growth of tall trees.
Why is the xylem called primary?
It allows the plant to grow taller and the roots to grow longer. This growth is called primary because it occurs first in the growing season, before secondary growth. Both primary and secondary xylem transport water and nutrients.
What are the components or elements of xylem?
The xylem composed of four types of cells. Among these cells, some cells are living and some are dead.
What is the function of the xylem?
The term xylem was proposed by Nageli (1858) and he derived the word from a Greek word ‘xylos’ meaning wood. The main function of xylem is to conduct water and minerals from roots to leaves.
What are the vascular bundles found in plants?
Both the xylem and phloem are complex tissues composed of more than one types of cells. Xylem and phloem are closely organized in plants. The vascular bundles found in the primary structures of plants are formed by the association of xylem and phloem.
Which part of the plant contains more tracheary elements than parenchyma?
Metaxylem usually contains more tracheary elements than parenchyma. Plants without secondary thickening, metaxylem are functional xylem part throughout the life cycle of the plant. Those plants with secondary thickening the metaxylem are replaced by the secondary xylem.
Where are primary xylem vessels formed?
The primary xylem vessels are formed from the longitudinal cells of the pro-cambia. The secondary xylem vessels are formed from cells of vascular cambium. Initials of vessels in both cambia are called primordial vessel members. Primordial vessels members have dense cytoplasm with prominent nucleus.
Where do vessels occur in angiosperms?
Vessels occur mainly in the xylem of Angiosperms. Usually, vessels are absent in Pteridophytes and Gymnosperms. The wood of Gnetum, an advanced Gymnosperm, contains plenty of vessels. The presence of vessels in the secondary wood of Gnetum is considered as one of the strongest evidence for the Gymnospermic origin of Angiosperms and thus Gnetum acts as a connecting link between Gymnosperms & Angiosperms.
What is vascular tissue?
What is vascular tissue?#N#The tissue associated with conduction of water, minerals and food materials in plants are called vascular tissue. Plants with a well-developed conductive system are thus called as ‘vascular plants’. Vascular plants are also known as ‘Tracheophyta’ (‘trachaea’ = vessels, a component of xylem, ‘phyta’= plants).
What is the Xylem made of?
The xylem is used for support in many plants and transporting water and nutrients to all areas of the plant. Xylem is made of mainly cellulose, and it is composed of three different types of plant cells.
Where is the Xylem found?
Xylem is a hard thick stem-like tissue found inside stems or roots in many land plants with these structures. It’s actually composed of several tissues
What are the two types of plant tissue?
The xylem and phloem are two of the four types of plant tissue, both central to the process of photosynthesis. The other two types are called “parenchyma” or “collenchyma.”
Why is Xylem important?
Xylem is important in the process of photosynthesis. During photosynthesis, plants use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide into glucose. Xylem plays a vital role in the transportation of this product from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
How does the xylem help plants?
The xylem also aids in a plant’s adaptation to its environment. When a plant is experiencing acute water stress (as in a drought), the wood cells shrink, pulling turgor pressure inside the xylem cell’s walls and making it easier for them to close their openings.
What causes water to flow out of the xylem?
When the water reaches the top of the plant, pressure in the xylem builds up and causes water to flow out of small openings on the xylem ends.
Why does the xylem close?
Xylem can also close in response to internal signals such as low temperatures. Acute temperature shocks such as a sudden temperature drop can cause the xylem to close to reduce water loss.
Which fiber has lignified and overlapping end walls?
These are shorter and narrower than tracheids and have much thicker cell walls but smaller pits. Xylem fibers have lignified and overlapping end walls.
Why are mosses not tall?
Mosses have no water conducting tissue and so they are not able to grow tall as they are poor at transferring water.