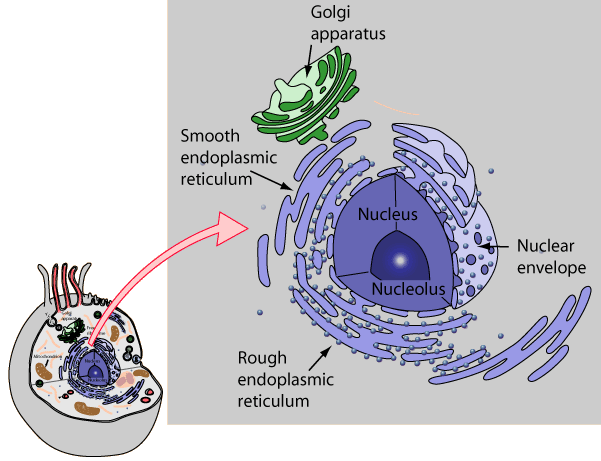
What is the structure and function of the Golgi?
The Golgi apparatus is a central intracellular membrane-bound organelle with key functions in trafficking, processing, and sorting of newly synthesized membrane and secretory proteins and lipids. To best perform these functions, Golgi membranes form a unique stacked structure.
Is Golgi a membrane structure?
The golgi apparatus is a membrane bound organelle found in most cells. It is responsible for packaging proteins into vesicles prior to secretion and therefore plays a key role in the secretory pathway.
What is the function of a Golgi?
The Golgi complex prepares proteins and lipid (fat) molecules for use in other places inside and outside the cell. The Golgi complex is a cell organelle. Also called Golgi apparatus and Golgi body.
What shape is Golgi?
The full shape of the Golgi apparatus in epididymal cells formed a basket-like structure with oval-shaped cisterns, while the Golgi apparatus in an acinar cell from the pancreas was composed of elongated ribbon-like structures that were connected to each other, making a coarse network.
What is true about the structure of the Golgi apparatus?
What is true about the structure of the Golgi apparatus? It is widely distributed throughout the cytosol. It is continuous with the outer nuclear membrane. It contains an inner membrane that is folded into cristae.
Is Golgi body double membrane structure?
Golgi bodies on the other hand, are single membrane organelles. They help in packaging and distribution of proteins.
What is Golgi made of?
Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound cell organelle found in the cytoplasm adjacent to the endoplasmic reticulum. It has 5 to 8 series of compartments known as cisternae. Cisternae are a flat, disk-like, stacked pouches which make up the Golgi bodies.
What is the size of Golgi body?
0.5 to 2.0 μmThe size and morphology of individual plant Golgi stacks vary tremendously between different cell types and species. The cisternal membranes and associated vesicles can be from 0.5 to 2.0 μm in diameter.
How Golgi is formed?
Each Golgi stack is formed by five to eight tightly aligned flattened cisternae, which can be classified as three separate modules: the cis-Golgi network, which is close to the ER and receives the ER output, the stacked cis-, medial-, and trans-Golgi cisternae that contain glycosylation enzymes and process cargo ...
Is Golgi a non membrane?
The membranous organelles include: Nucleus. Endoplasmic reticulum. Golgi apparatus.
What are membrane structures examples?
The common membranes used in membrane structures include:PVC coated polyester fabric.Translucent Polyethylene fabric.PVC coated glass fiber fabric.PTFE coated glass fiber fabric; foils like.ETFE foil.PVC foil.
What are the 4 structures of the cell membrane?
The principal components of the plasma membrane are lipids (phospholipids and cholesterol), proteins, and carbohydrate groups that are attached to some of the lipids and proteins. A phospholipid is a lipid made of glycerol, two fatty acid tails, and a phosphate-linked head group.
What are the 7 structural components of cell membrane?
The tails are made of long fatty acid chains which are non-polar, thus making the tails hydrophobic. The amphipathic nature of the phospholipids results in a bilayer structure of the membrane....PhospholipidsPhosphatidylcholine.Phosphatidylethanolamine.Phosphatidylserine.Sphingomyelin.
What is the Golgi apparatus?
Golgi apparatus, also called Golgi complex or Golgi body, membrane-bound organelle of eukaryotic cells (cells with clearly defined nuclei) that is made up of a series of flattened, stacked pouches called cisternae. The Golgi apparatus is responsible for transporting, modifying, and packaging proteins and lipids into vesicles for delivery ...
What are the three compartments of the Golgi apparatus?
The apparatus has three primary compartments, known generally as “cis,” “medial,” and “trans.”. The cis Golgi network and the trans Golgi network, which are made up of the outermost cisternae at the cis and trans faces, ...
What happens to secretory proteins as they move through the Golgi apparatus?
As the secretory proteins move through the Golgi apparatus, a number of chemical modifications may transpire . Important among these is the modification of carbohydrate groups. Also within the Golgi or secretory vesicles are proteases that cut many secretory proteins at specific amino acid positions. Organelle.
How many cisternae are there in the Golgi apparatus?
In general, the Golgi apparatus is made up of approximately four to eight cisternae, although in some single-celled organisms it may consist of as many as 60 cisternae. The cisternae are held together by matrix proteins, and the whole of the Golgi apparatus is supported by cytoplasmic microtubules.
Which apparatus undergoes exocytosis?
The exocytosis of secretory proteins may be regulated, whereby a ligand must bind to a receptor to trigger vesicle fusion and protein secretion. Golgi apparatus: exocytosis. Soluble and secretory proteins leaving the Golgi apparatus undergo exocytosis. The secretion of soluble proteins occurs constitutively.
Where do proteins and lipids arrive in the cis face?
The proteins and lipids received at the cis face arrive in clusters of fused vesicles. These fused vesicles migrate along microtubules through a special trafficking compartment, called the vesicular-tubular cluster, that lies between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus.
Which two networks are responsible for sorting proteins and lipids that are received (at the cis face)?
Two networks, the cis Golgi network and the trans Golgi network, which are made up of the outermost cisternae at the cis and trans faces, are responsible for the essential task of sorting proteins and lipids that are received (at the cis face) or released (at the trans face) by the organelle. The proteins and lipids received at ...
What is the function of the Golgi?
In fact, one of the functions of the Golgi is to make new vesicles out of the existing membrane of the Golgi and put into those vesicles the glycoproteins and other substances that are made in the Golgi network.
What is the Golgi body?
=. A Golgi body, also known as a Golgi apparatus, is a cell organelle that helps process and package proteins and lipid molecules, especially proteins destined to be exported from the cell. Named after its discoverer, Camillo Golgi, the Golgi body appears as a series of stacked membranes.
Where is the Golgi body located?
Some of them are tubules, and some of them are vesicles. The Golgi is located right near the nucleus.
Do carbohydrates move out of the Golgi?
For example, carbohydrates are put on some of the proteins, and then afterwards these glycoproteins--meaning they have carbohydrate as well as protein on them, these glycoproteins move out of the Golgi to the rest of the cell. And they do so inside other vesicles. Those vesicles are actually made from the Golgi network.
Can you add videos to your watch history?
Videos you watch may be added to the TV's watch history and influence TV recommendations. To avoid this, cancel and sign in to YouTube on your computer.
Structure of Golgi Apparatus
Between the "cis" face and the "trans" face, the Golgi apparatus is structurally polarised, with three major compartments. These faces are biochemically separate, with each section having a distinct enzymatic composition. The membranes on the cis face are usually thinner than the others.
Function of Golgi Apparatus
Secretion: All glandular cells rely on the Golgi complex to concentrate and package their products in a soluble protein coat observable under an electron microscope as dark staining. Exocytosis or reverse pinocytosis is how they get out of the cells.
Things to Remember
The Golgi complex (also known as the Dalton Complex, Apparato Reticulare, or Golgi Apparatus) is a cytoplasmic structure composed of smooth membrane saccules or cisternae, a network of tubules with vesicles and vacuoles.
Sample Questions
Ques. What is the role of Golgi Apparatus in formation of new cell walls? (2 marks)
What are the functions of the dictyosomes?
The dictyosomes release substances in the form of tiny vesicles budded from the saccules on the inner face.
What is the outer surface of a dictyosome?
On its outer surface the dictyosome is often bounded by canaliculae or cisternae of endoplasmic reticulum. Numerous spherical vesicles found in the vicinity of dictyosome are budded off by the cisternae at their ends. Palade (1956-58) has shown that the golgi bodies originate from smooth surfaced endoplasmic reticulum (Fig. 6.3).
What are the differences between cisternae and osmic acid?
The cisternae on the outer face react only with silver salt and osmic acid while those on the inner face do not react with silver salt and osmic acid.
What are the two types of vesicles in a golgi body?
The vesicles of golgi bodies are chiefly of two types: 1. Small and spherical vesicles. 2. Broad flattened vesicles in parallel or often in semi-circular array, the cisternae (Singular— cisterna) (Fig. 6.3). The cisternae are characterized by their dilated edges. They are compactly arranged in parallel fashion.
How thick is the dictyosome?
The number of vesicles per dictyosome varies presumably because of different functional stages of golgi complex. The unit membrane of these cisternae is about 35 å thick, smooth surfaced, and not associated with ribosome granules.
What is the name of the stack of flattened saccules?
They are compactly arranged in parallel fashion. The stack of flattened cisternae or saccules is known as ‘dictyosome’ . The dictyosome has a polarity; its convex side forming the outer faces and concave side forming the inner face. The cisternae on the outer face are very flat and thin whereas those on the inner face or concave side are comparatively much dilated and thick.
What did biologists believe about golgi bodies?
Most of the early biologists believed that it was an artifact of fixation or staining procedures. Studies with phase contrast microscopes in the early 1940s also indicated the existence of golgi bodies. The study of electron micrographs of thin sections of cells in 1950s finally proved beyond doubt the existence of golgi bodies in all the cells ...
Where is the Golgi apparatus located?
The Golgi apparatus is a series of stacked membranes that are located within the cytoplasm (i.e., gel-like fluid held in the cell membrane) in all eukaryotic cells (i.e., complex cells). It can typically be found adjacent to the nucleus and rough endoplasmic reticulum (an organelle involved in protein synthesis).
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
The function of the Golgi apparatus is processing and packaging proteins that have exited the rough endoplasmic reticulum to be further transported inside and/or outside the cell. In plant cells, the Golgi body also serves as the site for the synthesis of complex polysaccharides.
What are the most important facts to know about the Golgi apparatus?
The Golgi apparatus, also known as the Golgi body or Golgi complex, is an organelle that processes and packages proteins and lipid molecules (i.e., fat molecules) that are later exported to other cell compartments or secreted from the cell. The Golgi body has Golgi stacks, which are involved in modifying proteins and other complex polysaccharides. Transport vesicles pick up the molecules from the rough endoplasmic reticulum and transport them to the cis face of the Golgi stacks, where they fuse with the Golgi membrane and are sorted. They are then moved through the Golgi cisternae and undergo remodeling and other modifications. The modified protein or lipid molecules then depart from the trans face of the Golgi stacks where they are either secreted from the cell, or transported to another cell compartment.
Where do transport vesicles pick up proteins?
Transport vesicles usually pick up the molecules from the rough endoplasmic reticulum and transport them to the cis face (i .e., area of the Golgi apparatus located nearby to the endoplasmic reticulum) of the Golgi stacks, where they fuse with the Golgi membrane and are sorted based on their next destination. They are then moved through the Golgi cisternae as they undergo remodeling and other modifications. The modified protein or lipid molecules then depart from the trans face (i.e., area of the Golgi apparatus pointing towards the plasma membrane) of the Golgi stacks where they are either secreted from the cell, or transported to another cell compartment.
How many cisternae are in a dictyosome?
Each stack of cisternae forms a dictyosome which may contain 5 to 6 Golgi cisternae in animal cells or 20 or more cisternae in plant cells. Each cisterna is bounded by a smooth unit membrane (7.5 nm thick), having a lumen varying in width from about 500 to 1000 nm.
Why are the margins of each cisterna curved?
The margins of each cisterna are gently curved so that the entire dictyosome of the Golgi apparatus takes on a bow-like appearance.
What are the functions of the Golgi apparatus?
Golgi vesicles are often, referred to as the “traffic police” of the cell. They play a key role in sorting many of the cell’s proteins and membrane constituents, and in directing them to their proper destinations. To perform this function, the Golgi vesicles contain different sets of enzymes in different types ...
What is the Golgi apparatus?
The Golgi apparatus or the Golgi body or Golgi complex or simply Golgi is a cellular organelle present in most of the cells of the eukaryotic organisms. It is referred to as the manufacturing and the shipping center of the cell. Golgi is involved in the packaging of the protein molecules before they are sent ...
What is the role of clathrin coated vesicles in the ER?
The clathrin-coated vesicles are known to play a role in intracellular traffic of membranes and of secretory products, i.e., between ER and Golgi, as well as, between the GELR region and the endosomal and lysosomal compartments.
What is the role of Golgi complex in animal cells?
They are also involved in the transport of lipid molecules around the cell. 5. The Golgi complex also plays an important role in the production of proteoglycans. The proteoglycans are molecules that are present in the extracellular matrix of the animal cells. 6.
Which vesicles contain different sets of enzymes in different types of vesicles?
To perform this function, the Golgi vesicles contain different sets of enzymes in different types of vesicles— cis, middle and trans cisternae—that react with and modify secretory proteins passing through the Golgi lumen or membrane proteins and glycoproteins that are transiently in the Golgi membranes as they are en route to their final destinations.
What is the ATP7B gene?
The ATP7B gene codes for copper-transporting ATPase 2 (also known as Wilson disease protein or WDP ), an enzyme located in the Golgi apparatus of many cells such as hepato cytes and neurones. WDP normally allows copper to bind to caeruloplasmin, a protein which transports copper to various parts of the body.
What is the function of the golgi apparatus?
The golgi apparatus modifies proteins and lipids that it receives from the endoplasmic reticulum. These biochemicals leave the golgi by exocytosis before being delivered to different intracellular or extracellular targets.
Why are biochemicals chemically labelled in the golgi?
Biochemicals are chemically labelled in the golgi to ensure appropriate delivery to the correct destination. Once they bud off the trans-Golgi they will enter a specific pathway according to this signalling sequence.
What is the structure of the Golgi?
Structure. The golgi is made of 5-8 folds called cisternae. The cisternae contain specific enzymes creating five functional regions which modify proteins passing through them in a stereotypical way, as follows: Cis-Golgi network: faces the nucleus, forms a connection with the endoplasmic reticulum and is the entry point into the Golgi apparatus.
What are lysosomal proteins?
Lysosomal proteins– such as enzymes are packaged into specific vesicles. These proteins are typically tagged with mannose-6-phosphatein the Golgi
What is Wilson's disease?
Wilson’s disease is an autosomal recessive disorder characterised by an abnormal accumulation of copper in the body. The liver is particularly susceptible to this accumulation. Mutation of the ATP7B gene is implicated in the development of Wilson disease.
What happens if you have too much copper in your blood?
If copper levels are too high, WDP leaves the Golgi, allowing copper to be excreted in bile instead of transported around the body. Patients experience symptoms and signs of liver failure, such as itching, abdominal swelling, fatigue, jaundice, ascites and Kayser-Fleischer rings (deposition of copper in the cornea).