Explore
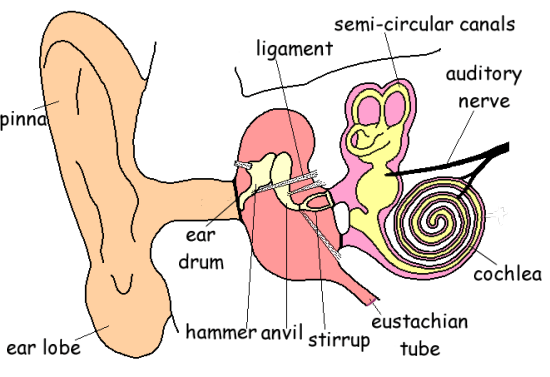
Structure composing the external ear. Pinna (auricle), external auditory canal, tympanic membrane. structure composing the internal ear. semicircular canals, cochlea, vestibule. collectively calles the ossicles. incus (anvil), malleus (hammer), stapes (stirrup)
What are 3 structures compose the outer ear?
inner ear, also called labyrinth of the ear, part of the ear that contains organs of the senses of hearing and equilibrium.The bony labyrinth, a cavity in the temporal bone, is divided into three sections: the vestibule, the semicircular canals, and the cochlea.Within the bony labyrinth is a membranous labyrinth, which is also divided into three parts: the semicircular ducts; two saclike ...
What are the structures composing the inner ear?
The outer ear includes:
- auricle (cartilage covered by skin placed on opposite sides of the head)
- auditory canal (also called the ear canal)
- eardrum outer layer (also called the tympanic membrane)
What are the different parts of the outer ear?
The Normal Ear
- Outer ear
- Middle ear
- Inner ear
What are the various parts of the outer ear called?
What is the outer ear made of?
What are the parts of the ear?
How does the ear work?
What causes earwax buildup?
What part of the ear is the most important for hearing?
Which part of the ear is not supported by cartilage?
What nerves run through the ear?
See more
What is the structure of the ear?
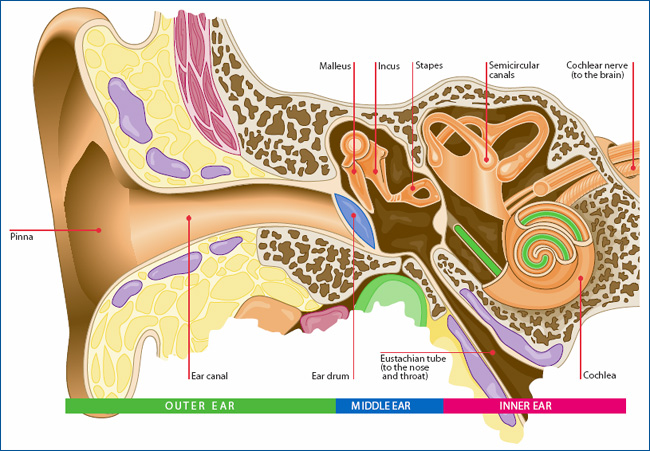
The ear is divided into three interconnecting sections: external, middle and inner ears (Fig 1). While the external and middle ears are mainly concerned with the transmission of sound, the inner ear contains the cochlea – often called the organ of hearing – and also houses the body's organ of balance.
What are the structures in the outer ear and state their functions?
The outer ear consists of the visible portion on the side of the head, known as the pinna [1], and the external auditory canal (ear canal) [2]. The purpose of the pinna is to catch sound waves, amplify them slightly, and funnel them down the ear canal to the tympanic membrane (eardrum) [3].
What is the structure between the outer and inner ear?
External auditory canal or tube. This is the tube that connects the outer ear to the inside or middle ear.
What is the function of outer ear?
The Outer Ear It collects sound waves and channels them into the ear canal (external auditory meatus), where the sound is amplified. The sound waves then travel toward a flexible, oval membrane at the end of the ear canal called the eardrum, or tympanic membrane. Sound waves cause the eardrum to vibrate.
What is external ear?
The external ear is composed of the pinna and the external auditory meatus. Its principal functions are to collect and funnel sound to the tympanic membrane (eardrum) and to provide cues about the location of wideband sound sources in the vertical plane.
Which structure is part of the middle ear?
The middle ear consists of three bones: the hammer (malleus), the anvil (incus) and the stirrup (stapes), the oval window, the round window and the Eustachian tube.
What are the 3 parts of the ear?
Parts of the EarOuter Ear. The outer ear is made up of three parts; ... Middle Ear. The middle ear is made up of the eardrum and three small bones (ossicles) that send the movement of the eardrum to the inner ear.Inner Ear. The inner ear is made up of: ... The ear (auditory) Nerve.
What is the outer ear?
This structure helps to give each of us our unique appearance. The medical term for the outer ear is the auricle or pinna.
What are the three bones in the middle ear?
Three of the smallest bones of the body are found in the middle ear; they are called the malleus, the incus and the stapes . These bones are also known as the hammer, anvil and the stirrup. The medical term for all three bones together is the middle ear ossicles.
Where does the ear canal start?
The ear canal starts at the outer ear and ends at the ear drum. The canal is approximately an inch in length. The skin of the ear canal is very sensitive to pain and pressure. Under the skin the outer one third of the canal is cartilage and inner two thirds is bone. EAR DRUM.
What is the ear drum?
The medical term for the ear drum is the tympanic membrane. The ear drum is a transparent gray membrane. Attached to the center part of the drum is the middle ear bone (the malleus). The space inside the ear drum is called the middle ear.
What is the outer ear?
The outer ear is the external part of the ear. The function of the outer ear is to collect sound waves and to direct them into the ear. Important parts of the outer ear are the pinna, the ear canal and the ear drum. Read more about the anatomy, the outer ear parts and the function of the outer ear.
What is the function of the auditory canal?
The external auditory canal’s function is to transmit sound from the pinna to the eardrum.
How does the pinna help the ear?
This is where the pinna helps by overcoming the difference in pressure inside and outside the ear.
What is the purpose of ear wax?
At the same time, earwax (cerumen) in the external auditory canal functions as a barrier to help keeping unwanted materials like dirt, dust, and insects out of the human ear.
Why is the eardrum so sensitive?
The eardrum is an extremely sensitive part of the outer ear anatomy. Pressure from sound waves makes the eardrum vibrate. In order to protect the eardrum, the auditory canal is slightly curved making it more difficult for insects, for example, to reach the eardrum.
What is the outer ear?
Outer ear. The external ear comprises of two components . There is a cartilaginous portion, known as the pinna or auricle and a bony, tubular segment called the external acoustic meatus. The former portion of the auditory system is the first point at which sound wave modification begins.
Where is the outer ear located?
The outer ear is situated superficially next to several bony landmarks. It is posterior to the zygomatic process of the temporal bone as well as the proximal part of the mandibular process and the auricular surface of the mandibular notch.
What is the lobule in the 6 o'clock position?
Finally, in the 6 o’clock position is the soft, fibrofatty structure called the lobule. There are two groups of muscles associated with the external ear. The intrinsic group of muscles consists of the tragicus and antitragicus, obliquus auriculae, transversus auriculae and the helicis major and minor.
What is superior to the tragus in the 5 o'clock position?
Superior to the tragus in the 10 o’clock position is the crus of the helix.
What is the tragus in the ear?
On that note, the tragus is the first of several cartilaginous flaps in the ear. As previously mentioned, it projects posteriorly from the 9 o’clock position to provide a lateral border to the distal end of the external acoustic meatus. Posteroinferior to the tragus in the 5 o’clock position is the antitragus.
Where does the auricularis anterior begin?
Auricularis anterior begins in the epicranial aponeurosis and inserts in the spine of the helix. It is the smallest of the three extrinsic muscles. Thirdly, auricularis superior is the largest of the extrinsic muscles. It also begins at the epicranial aponeurosis and inserts in the cranial part of the auricle.
Which muscle group is the anterior, posterior, and superior auricular?
The extrinsic muscle group includes the anterior, posterior and superior auricular muscles. Auricularis posterior originates as three aponeurotic muscular fasciculi from the mastoid process to insert in the ponticulus (oblique ridge on the eminentia conchae) on the cranial aspect of the external ear.
What are the two parts of the external ear?
The external ear can be divided functionally and structurally into two parts; the auricle (or pinna), and the external acoustic meatus – which ends at the tympanic membrane.
What is the name of the blood in the ear?
An auricular haematoma refers to a collection of blood between the cartilage of the ear and the overlying perichondrium. It is usually occurs as a result of trauma, commonly seen in contact sports (e.g. rugby).
What is the external acoustic meatus?
External Acoustic Meatus. The external acoustic meatus is a sigmoid shaped tube that extends from the deep part of the concha to the tympanic membrane. The walls of the external 1/3 are formed by cartilage, whereas the inner 2/3 are formed by the temporal bone.
What is the second innermost curvature of the auricle?
A second innermost curvature runs in parallel with the helix – the antihelix. The antihelix divides into two cura; the inferoanterior crus, and the superoposterior crus. In the middle of the auricle is a hollow depression, called the concha. It continues into the skull as the external acoustic meatus.
What is the concha in the skull?
It continues into the skull as the external acoustic meatus. The concha acts to direct sound into the external acoustic meatus. Immediately anterior to the beginning of the external acoustic meatus is an elevation of cartilaginous tissue – the tragus. Opposite the tragus is the antitragus.
What is the clinical relevance of the tympanic membrane?
Clinical Relevance: Perforation of the Tympanic Membrane. The tympanic membrane is a relatively thin connective tissue structure, and is susceptible to perforation (usually by trauma or infection). An infection of the middle ear ( otitis media) causes pus and fluid to build up behind the tympanic membrane.
Where is the handle of the malleus located?
On the inner surface of the membrane, the handle of malleus attaches to the tympanic membrane, at a point called the umbo of tympanic membrane. The handle of malleus continues superiorly, and at its highest point, a small projection called the lateral process of the malleus can be seen.
What is the outer ear called?
It is also sometimes referred to as the auricle or the pinna. Although the outer ear is the least important part of the ear’s hearing function, it provides the necessary structure and protection. Its dish-like shape is also essential for collecting sound waves. This sound collection is the primary purpose of all of the parts ...
What is the human ear?
Ear Anatomy. The human ear is the highly advanced result of millions of years of evolutionary progress. Everyone knows that the ear is the organ used for hearing, but not many people are aware that it’s also necessary for balance. Most people also consider the ear just one part of the human body, but it’s a complex organ composed of many smaller, ...
What is the external auditory meatus?
The external auditory meatus, or ear canal, is a narrow canal that leads from the concha to the tympanic membrane, or eardrum. Sound waves are delivered through this canal. This canal is prone to ear infections.
How to treat middle ear pressure imbalance?
This middle ear pressure imbalance can usually be alleviated by yawning or working the jaw, which exercises the mastoid bone and opens the eustachian tube. COVID 19 can occasionally enter the middle ear through the Eustachian tube. If you have been exposed to COVID 19, seek appropriate treatment or services.
What is the name of the two forks on the top of the ear called?
It is more rigid and provides more strength to the outer ear. It looks somewhat Y-shaped, and the two forks at the top of the ‘Y’ are called the superior crus and the inferior crus.
What is the concha in the ear?
The concha is the smaller cavity that funnels sound waves into the ear canal. It is bordered by the antihelix, the tragus, and the antitragus. Hearing amplification devices, such as MD HearingAids or other services, are typically nestled within this cavity.
Which part of the ear transmits sound signals to the inner ear?
It also divides the outer ear from the middle ear. It then transmits a clarified, amplified sound signal to the inner ear components. The Ossicles (malleus incus stapes) are the small, connected bones inside the middle ear that transmit sound signals from the tympanic membrane to the next area.
What is the inner ear?
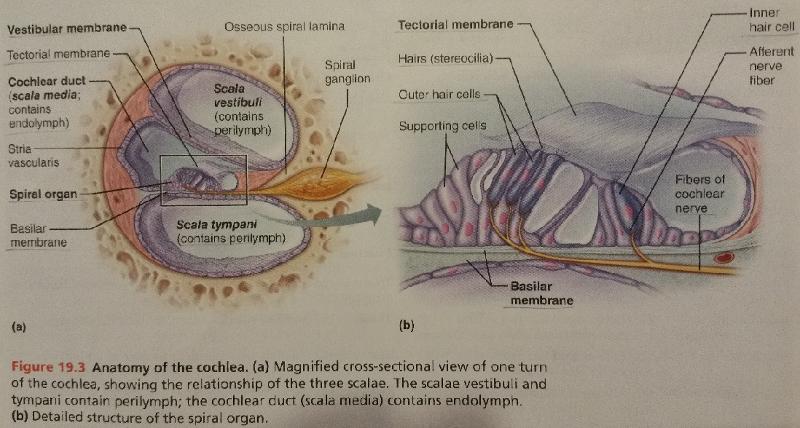
Inner Ear. The inner ear is called the labyrinth. It is composed of a group of interconnected canals and sacs. The membranous labyrinth is present inside the bony labyrinth and surrounded by a fluid known as perilymph. The endolymph is filled within the membranous labyrinth.
What are the three main sections of the ear?
Structure of ear comprises three main sections: the outer ear, middle ear and inner ear. Let’s learn in detail about the structure and functions of each of these sections.
What is the role of otoliths in the ear?
Otoliths are calcium ear stones, which press stereocilia against gravity and play an important role in spatial orientation. Each semicircular canal is filled with endolymph and present at the right angle to each other and connects to the utricle. The base of canals is swollen and known as the ampulla.
What are the three canals of the cochlea?
The cochlea is made up of three canals, upper vestibular canal or scala vestibuli, middle cochlear duct or scala media and the lower tympanic canal or scala tympani, which are separated by thin membranes. The scala vestibuli is filled with the perilymph and terminates at the oval window.
What are the three bones in the human body?
It contains a chain of three tiny bones malleus, incus and stapes, present in the same order. Malleus is a hammer-shaped bone, attached to the tympanic membrane. Incus is an anvil-shaped bone, present between the malleus and stapes. Stapes is the smallest bone of the body.
What is the eardrum made of?
They also have wax glands. Tympanic membrane or eardrum is made up of connective tissue. Skin covers the outer portion and from inside, it is covered by mucous membrane. Pinna receives the sound in the form of vibration. The sound waves reach and vibrate the eardrum through the external auditory canal.
What is the connection between the middle ear and the pharynx?
It is stirrup-shaped and attached to the oval window of the cochlea. The eustachian tube is the connection between the middle ear and the pharynx. It equalises pressure between the middle ear and the outer atmosphere. The middle ear amplifies the sound waves and transmits to the inner ear.
What is the outer ear?
Outer ear. The part of the ear that is visible along the side of the head. The outer ear consists of the pinna, or auricle (the visible projecting portion of the ear), the external acoustic meatus (the outside opening to the ear canal), and the external ear canal, which leads to the eardrum. Middle ear.
What are the parts of the ear?
Ear. The hearing organ. It is composed of three sections; The outer, middle and inner ear. However in terms of function, the ear has four components, the three stated above and the brain. Tympanic Membrane (eardrum) It is a thin, circular, tough and flexible layer of tissue which separates the middle and external ear.
What is the middle ear?
Middle ear. A part of the ear that consists of the tympanic membrane, a cavity connected to the pharynx through the eustachian tube. The middle ear also contains the ossicular chain (malleus, incus, and stapes), which connect the eardrum to the internal ear.
What is the first section of the middle ear?
When sound waves enter the pinna and ear canal, they strike the tympanic membrane - vibrating it and transmitting these vibrations further into the ear, reaching the bones in the middle ear. Maleus (hammer) The 'maleus' is the first section of the middle ear ossicular chain.
Which part of the ear is responsible for hearing?
The middle ear communicates with the pharynx, equilibrates with external pressure, and transmits the eardrum vibrations to the inner ear. Inner ear. The inner, liquid-filled, membranous portion of the ear, involved in hearing and balance. Oval window.
Which part of the ossicular chain transmits vibrations to the inner ear?
It is a small bone which receives vibrations from the tympanic membrane and transmits the vibrations to the inner ear - through the other two parts of the ossicular chain (incus & stapes). Incus (anvil) The 'incus', is the second section of the middle ear ossicular chain. It is also (like the maleus) a small bone.
Which organ of the ear produces nerve impulses in response to sound vibrations?
Organ of corti . A structure in the cochlea of the inner ear which produces nerve impulses in response to sound vibrations. Basilar membrane. A supporting membrane, especially the membrane that supports the organ of Corti in the ear and aids in translating sound vibrations into electrical signals. Upgrade to remove ads.
What is the outer ear made of?
Structure. The outer ear—sometimes called the auricle or pinna—is mostly made of skin and cartilage. 1 It is made up of several components: 2 . Helix: The outermost curvature of the ear, extending from where the ear joins the head at the top to where it meets the lobule.
What are the parts of the ear?
There are three parts to the ear—the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. These sections work together to collect sound from the world around you and send it to the brain where speech and auditory centers translate the information. The outer ear is the part of the ear that you can see and where sound waves enter ...
How does the ear work?
The outer ear is divided into several sections, but they all work together toward one purpose: The helix, antihelix, superior and inferior crus, the tragus and antitragus, the concha, and the external acoustic meatus all work together to funnel and direct sound waves from the world around you to the inner parts of your ears. Sound waves are carried from the outer ear and ear canal to the tympanic membrane, where vibrations are sent through the middle and inner ears and become electrical impulses (sound signals). These signals then give your brain information about both sound and the direction and balance of your body.
What causes earwax buildup?
Cerumen impaction: Various skin cells and glands in the ear canal secrete waxy substances that protect the canal, but can also cause a buildup of earwax, or cerumen. Normally, cerumen can be removed as it builds, but in some cases it builds to the point that it obstructs the ear canal or eardrum.
What part of the ear is the most important for hearing?
The outer ear is the part of the ear that you can see and where sound waves enter the ear before traveling to the inner ear and brain. While the outer ear may not be as complex as its counterparts, it serves a vital function in your sense of hearing. AndreiDavid / Getty Images.
Which part of the ear is not supported by cartilage?
Tragus and antitragus: These two cartilage prominences border the concha at the top and bottom. Lobule: The lobule is the bottom-most part of the ear, often called the earlobe. It is the only part of the outer ear that is not supported by cartilage.
What nerves run through the ear?
The skin of the ear canal is thin and very sensitive, and branches of the facial and vagus nerves run under portions of the ear canal and other parts of the outer ear. 2 Other cranial nerves run through the ear as well, but have little to no known function. 3 . Hearing Loss and Deafness.