The Structure of a Root
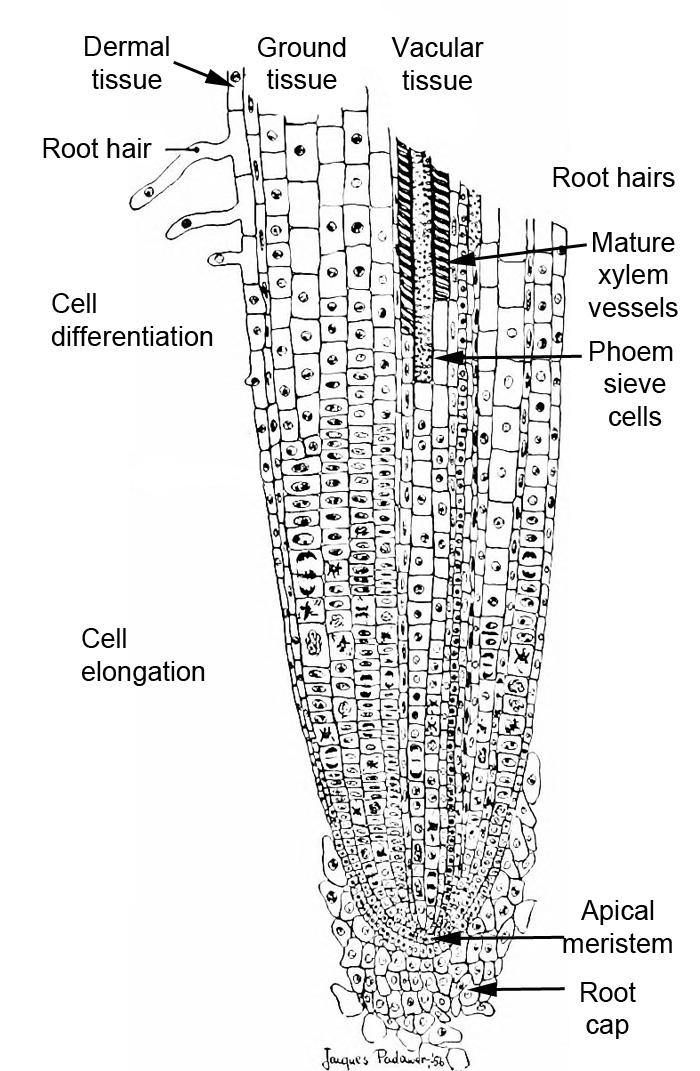
- Cell Division (the Root's Tip) The tip of the root is made up of cells that divide often. This is called the region of cell division. ...
- Cell Elongation Just above the region of cell division is the region of cell elongation. This is where the cells grow to the normal size of root cells. ...
- Cell Maturation (Root Hair Zone)
How to create a root?
Use the new SharePoint admin center
- In the upper right, make sure the All sites view is selected.
- In the URL column, select to sort A to Z so the current root site appears at the top of the list.
- Select the root site (https ://contoso. ...
- Select Replace site.
- In the URL of the site you want to use box, enter the full or relative URL of the site that you want to become the new root site.
What are the parts of a root?
There are different parts of roots as mentioned below:
- Root Cap: The root is covered at the apex of the root system by the root cap.
- Region of Meristematic Activity: Above the rootcap is the region of meristematic activity which possess cells that are small in size and have dense protoplasm.
- Region of Elongation: This region undergoes rapid elongation and is responsible for the growth of the root.
What are the three types of roots?
Types of Root Systems. Plants have three types of root systems: 1.) taproot, with a main taproot that is larger and grows faster than the branch roots; 2.) fibrous, with all roots about the same size; 3.) adventitious, roots that form on any plant part other than the roots. Fibrous systems are characteristic of grasses and are shallower than ...
What is the main purpose of a root?
Roots are important because they have four vital functions to the health and vigor of a tree, or any plant for that matter. Absorption. The root tips, and the root tips only, absorb water and minerals from the surrounding soil. Conduit. Those roots also conduct water and minerals up into the leaves and up into the trunk of the tree to feed the ...

What is the structure and function of roots?
root, in botany, that part of a vascular plant normally underground. Its primary functions are anchorage of the plant, absorption of water and dissolved minerals and conduction of these to the stem, and storage of reserve foods.
What is the meaning of root structure?
A developed system of roots. The network of underground roots and other plant structures found below ground level.
What is the structure of the root tip?
The root tip can be divided into three zones: a zone of cell division, a zone of elongation, and a zone of maturation and differentiation (Figure 10.3. 1). The zone of cell division is a continuation of the root cap; it is made up of the actively dividing cells of the root meristem.
What are the two types of root structures?
Taproots and fibrous roots are the two main types of root systems. In a taproot system, a main root grows vertically downward with a few lateral roots. Fibrous root systems arise at the base of the stem, where a cluster of roots forms a dense network that is shallower than a taproot.
What are the 4 types of roots?
Types of RootsFibrous Roots. Fibrous roots are found in monocot plants. ... Taproots. Taproots are found in the majority of dicot plants. ... Adventitious Roots. Adventitious roots are similar to the fibrous roots. ... Creeping Roots. ... Tuberous Roots. ... Water Roots. ... Parasite Roots.
What is root and its type?
Plants have three types of root systems: 1.) taproot, with a main taproot that is larger and grows faster than the branch roots; 2.) fibrous, with all roots about the same size; 3.) adventitious, roots that form on any plant part other than the roots.
What is internal structure of root?
The inner part of the root includes the vascular tissue (xylem and phloem). Stele is the name of this area which is surrounded by a layer of cells known as the endodermis, thought to be the cortex's innermost layer.
What is the function of root?
Roots absorb water and nutrients from the soil. They anchor the plant firmly. They help in storing food and nutrients. Roots transport water and minerals to the plant.
What are types of root?
There are two types of root systems: taproots and fibrous roots (also known as adventitious roots; Figure 2.1. 2). Tap roots have a prominent primary root that develops when the seed germinates and the radicle emerges. From there, secondary or lateral roots grow.
What is called root?
root. In biology, the part of a plant that grows downward and holds the plant in place, absorbs water and minerals from the soil, and often stores food. The main root of a plant is called the primary root; others are called secondary roots. The hard tip is called the root cap, which protects the growing cells behind it ...
What are roots made of?
A root system consists of primary and secondary roots. Each root is made of dermal, ground, and vascular tissues. Roots grow in length and width from primary and secondary meristem.
What are types of root?
There are two types of root systems: taproots and fibrous roots (also known as adventitious roots; Figure 2.1. 2). Tap roots have a prominent primary root that develops when the seed germinates and the radicle emerges. From there, secondary or lateral roots grow.
What are types of root system?
There are two main types of root systems. Dicots have a tap root system, while monocots have a fibrous root system, which is also known as an adventitious root system. A tap root system has a main root that grows down vertically, from which many smaller lateral roots arise.
What is root system in plants?
What are Roots? Roots are the important underground part of all vascular plants. This part of the plant is mainly responsible for anchoring it down into the ground and absorbing the essential mineral elements, nutrients, and water from the soil. It is also used to store food.
What is root in plants?
Roots absorb water and minerals and transport them to stems. They also anchor and support a plant, and store food. A root system consists of primary and secondary roots. Each root is made of dermal, ground, and vascular tissues. Roots grow in length and width from primary and secondary meristem.
Why do plants need roots?
Roots with a higher surface area will be better adapted to absorbing water because they have more area to interact with the soil environment. Increased interaction with the soil environment can also contribute to increased anchorage, but there are always trade-offs. If roots become too fine, they will be easily broken and lose the anchorage function. Additionally, finer roots can also lose more water if the soil environment becomes dry.
Which layer of the cell is responsible for producing lateral roots?
Encircling the conducting tissues is a meristematic layer called the pericycle. This single cell layer is responsible for producing lateral roots. Unlike root hairs which emerge on the outside of the root ( exogenous, exo- meaning outside), lateral roots emerge from the internal tissues ( endogenous, endo- meaning inside).
What is the waxy layer of suberin that covers the endodermis called?
Because these areas are no longer taking up water, the vascular cylinder is sealed off by a waxy layer of suberin that covers the endodermis called the casparian strip.
What are the primary meristems?
Primary meristems produce the primary tissues in the root: 1 Protoderm → Epidermis 2 Ground meristem → Cortex (and pith in monocots) 3 Procambium → Primary xylem and primary phloem
What is the innermost layer of the cortex?
Just outside the pericycle is the innermost layer of the cortex called the endodermis. The endodermis regulates what enters and exits the vascular cylinder. When the root is young, the epidermis contains many root hairs whose function is to absorb water. This water is transported through the cortex and into the xylem.
Which meristem divides in two directions?
This meristem divides in two directions, producing a root cap to the outside of the root to protect the growing tip and the primary meristems to the inside: the protoderm, ground meristem, and procambium. Primary meristems produce the primary tissues in the root: Protoderm → Epidermis. Ground meristem → Cortex (and pith in monocots)
What happens when you move up in the root?
As you move up in the root, the cells begin to get larger, developing into primary tissues. This region is called the zone of elongation. Further up the root, the larger cells begin to differentiate into specialized cells. In the xylem and phloem, you can find sclerenchyma with secondary walls.
What are the layers of the root system?
The root is subdivided and extended through the soil particles, it is composed of a number of the layers which are the epidermis layer, the cortex layer, the xylem (wood) layer and the pith layer.
What is the structure of a plant?
The plant structure. The plant consists of the root system and the shoot system, The root system consists of the roots, The shoot system consists of the leaves and the stems, The plant takes the raw materials from the environment to make its food by the photosynthesis process.
Why is the root system important?
The root system is very important for the plant as it is branched and extended through the soil particles to fix the plant in the soil. The root system covers a large area of the soil to search for the water and the mineral salts that the plant needs, then absorbs them from the soil by the root hairs, and raises them to the other parts ...
How does the root system absorb water?
The root system absorbs the water and the minerals from the environment, It anchors the plant in the ground, and it stores the food that has been made in the leaves by the photosynthesis process, So, the food can be used later by the plant to grow and survive. Excretion in plants, Importance & types of transpiration for the plant. ...
What is the structure of root hairs?
Structure of the root hairs. Hydrogen is combined with the carbon dioxide to produce the food (glucose) for the plant, whereas the oxygen, which is a by-product of the entire process, is let out through the stomata.
What is the purpose of the root network?
The root network spreads out to absorb water (and mineral salts) from a large amount of soil. It is also adapted to hold the plant firmly and provide support (anchor) to the plant in the soil.
What does the anatomy of the root system reveal?
For instance, the anatomy of the root system reveals its various roles in storage, anchorage, and the acquisition and transport of nutrients and water. Because of this, the study of anatomy has much to tell us about the physiology of plants.
What determines when and where roots encounter nutrients?
Patterns of root growth determine when and where roots encounter nutrients. The amount of biomass underground, compared to the aboveground biomass, gives us an idea of how much the plant is "spending" on its root system.
How do plants acquire nutrients?
Plant anatomy and morphology are critical components of nutrient acquisition and transport. Radial, or concentric, arrangement of tissues within the root determines patterns and rates of nutrient transport from the soil to the vascular tissue. The presence of certain features, such as the casparian band in the endodermis, allow passage of needed compounds and prevent uptake of toxic substances. Patterns of root growth determine when and where roots encounter nutrients. The amount of biomass underground, compared to the aboveground biomass, gives us an idea of how much the plant is "spending" on its root system. If it is spending a lot, this might mean that it is growing a lot or is having a hard time getting what it needs to grow.
What is the study of an organism's structure and the development of that form?
Microtomy and Microscopy. Anatomy is the study of the structure of living organisms, while morphology is the study of an organism's form and the development of that form. In biological organisms, there is usually a relationship between form and function, reflective of designs that serve a particular purpose.
What is the material that covers the root of a tooth called?
Also called cement, this bone-like material covers the tooth’s root. It’s connected to the periodontal ligament. Periodontal ligament. The periodontal ligament is made of connective tissue and collagen fiber.
What is the part of the tooth that extends into the bone and holds the tooth in place?
The root is the part of the tooth that extends into the bone and holds the tooth in place. It makes up approximately two-thirds of the tooth. It’s made up of several parts: Root canal. The root canal is a passageway that contains pulp. Cementum. Also called cement, this bone-like material covers the tooth’s root .
What bone holds teeth in place?
Blood vessels supply the periodontal ligament with nutrients, while nerves help control the amount of force used when you chew. Jaw bone. The jaw bone , also called the alveolar bone, is the bone that contains the tooth sockets and surrounds the teeth’s roots; it holds the teeth in place.
How to keep your teeth strong?
Follow these tips to keep your teeth strong and healthy: brush twice daily using a fluoride toothpaste. floss between your teeth once a day. replace your toothbrush every three months. go in for professional dental cleanings every six months. limit your intake of sugary foods and drinks.
What are the two points on the top of your teeth that help you crush and grind food?
Premolars. The two points on each premolar help you crush and tear food. Molars. Multiple points on the top surface of these teeth help you chew and grind food. Read on to learn more about the anatomy and structure of your teeth and conditions that can affect your teeth. We’ll also provide some dental health tips.
What is the pulp of a tooth?
Pulp is the innermost portion of the tooth. It’s made of tiny blood vessels and nerve tissue. Pulp cavity. The pulp cavity, sometimes called the pulp chamber, is the space inside the crown that contains the pulp.
What are the different types of teeth?
There are four types of teeth, and each plays an important role in how you eat, drink, and speak. The different types include: Incisors. These are the chisel-shaped teeth that help you cut up food. Canines. These pointy teeth allow you to tear and grasp food. Premolars.
Where is the hair root located?
The hair root is in the skin and extends down to the deeper layers of the skin. It is surrounded by the hair follicle (a sheath of skin and connective tissue), which is also connected to a sebaceous gland. Each hair follicle is attached to a tiny muscle (arrector pili) that can make the hair stand up. Many nerves end at the hair follicle too.
How much of the body is terminal hair?
Children’s bodies mostly have vellus hair, for instance. About 30 percent of the body’s surface is covered with terminal hair in women, compared to about 90 percent in men. Go to: