| Enzyme | Origin | Substrates |
|---|---|---|
| Bromelain | A. comosus extract (stem or fruit) | Action on both myofibrillar proteins and collagen (Sullivan and Calkins,2010) |
| Ficin | F. glabrata latex | |
| Zingibain | Ginger (Z. officinale) extract | |
| Protease formulation | B. subtillis |
See more
Is gelatin a substrate for bromelain?
The proteolytic activity of bromelain is conducted by a group of substrates, including gelatin, chromogenic tripeptides, and casein [26,27], and results in several amino acids—tyrosine, alanine, and lysine [28]—from the digestion of proteins.
What is the substrate in the pineapple enzyme lab?
In this biology lab, students will use pineapple juice as an enzyme and Jell-O as a substrate to illustrate an enzyme/substrate complex. The initial guided procedure will allow students to discover that the processing of food, specifically canned pineapple, will denature the enzymes and render them useless.
What does the enzyme bromelain break down?
Bromelain is a mixture of enzymes found in pineapples (Ananas comosus) that digest protein (proteolytic). Pineapple has been used for centuries in Central and South America to treat indigestion and reduce inflammation.
What is the product of bromelain?
Bromelain is a type of enzyme called a proteolytic enzyme. It is found in pineapple juice and in the pineapple stem. Bromelain causes the body to make substances that fight pain and swelling. Bromelain also contains chemicals that seem to interfere with tumor cells and slow blood clotting.
Is bromelain a protease?
Bromelain is a complex mixture of protease extracted from the fruit or stem of the pineapple plant.
Why does bromelain break down gelatin?
Pineapples, unlike most other fruit, contain an enzyme called bromelain, that breaks up the gelatin into it's amino acid building blocks. [Enzymes are biomolecules that catalyze chemical reactions; most of them are proteins themselves.] Due to the bromelain, your jello doesn't become (or stay) solid.
What protein does bromelain break down?
Even more specifically, bromelain is a cysteine protease, meaning that it breaks apart proteins wherever they have a cysteine amino acid. The bromelain in pineapple breaks down the proteins of the protective mucous lining and surface tissue of our mouths and tongues.
What is the substrate that the enzyme digests?
ProteinEnzymeProduced BySubstrate Acting OnPepsinStomach chief cellsProteinsTrypsin Elastase ChymotrypsinPancreasProteinsCarboxypeptidasePancreasPeptidesAminopeptidase DipeptidaseLining of intestinePeptides
What is mode of action of bromelain?
Bromelain influences blood coagulation by increasing the serum fibrinolytic ability and by inhibiting the synthesis of fibrin, a protein involved in blood clotting [47].
What is the structure of bromelain?
Bromelain is a glycoprotein with an oligosaccharide in its molecular structure consisting of xylose, fucose, mannose and N-aceltylglucosamine.
What type of biological molecule is bromelain?
Bromelain is a complex mixture of proteinases derived from pineapple stems and fruit.
How is bromelain extraction from pineapple?
The marketable bromelain is mostly extracted from the stem of pineapple through centrifugation, ultrafiltration, lyophilization (Corzo et al. 2011. Pineapple fruit bromelain affinity to different protein substrates.
What biomolecule does the enzyme we tested in pineapple digest?
Pineapple contains the enzyme bromelain, which can digest collagen protein.
What are the enzymes doing to the pineapple?
There are many types of enzymes as well. Bromelain in pineapple is a type of enzyme known as a protease, which breaks other proteins apart by cutting the chains of amino acids. Even more specifically, bromelain is a cysteine protease, meaning that it breaks apart proteins wherever they have a cysteine amino acid.
What enzyme in papaya will utilize gelatin as substrate?
papainpapain | enzyme | Britannica.
What kind of enzymes is in the pineapple that works on the gelatin?
Pineapple, kiwi and papaya all contain proteolytic enzymes, in other words enzymes capable of breaking down protein molecules. And gelatin, the substance that makes Jell-O gel, is a protein. Pineapple, kiwi and papaya all contain proteolytic enzymes, in other words enzymes capable of breaking down protein molecules.
What is bromelain used for?
People sometimes use it as a medicine.#N#Bromelain is used for pain, muscle soreness, burns, and many other conditions , but there is no good scientific evidence to support these uses.
Is bromelain safe for breast feeding?
When applied to the skin: Bromelain is POSSIBLY SAFE for most people when applied to the skin in appropriate amounts. Pregnancy and breast-feeding: There isn't enough reliable information to know if bromelain is safe to use when pregnant or breast-feeding. Stay on the safe side and avoid use.
Is bromelain safe for pregnant women?
Pregnancy and breast-feeding: There isn't enough reliable information to know if bromelain is safe to use when pregnant or breast-feeding. Stay on the safe side and avoid use. Allergies: You might have an allergic reactionto bromelain if you are allergic to pineapple, latex, ragweed, Echinacea, chrysanthemums, marigolds, daisies, wheat, celery, papain, carrot, fennel, cypress pollen, grass pollen, or other plants. Surgery: Bromelain might increase the risk of bleeding during and after surgery. Stop using bromelain at least 2 weeks before a scheduled surgery.
Does bromelain slow blood clotting?
Medications that slow blood clotting (Anticoagulant / Antiplatelet drugs) interacts with BROMELAIN. Bromelain might slow blood clotting. Taking bromelain along with medications that also slow clotting might increase the chances of bruising and bleeding.
Is bromelain safe to take?
When taken by mouth: Bromelain is POSSIBLY SAFE for most people when taken by mouth in appropriate amounts. Bromelain may cause some side effects, such as diarrhea and stomach and intestinal discomfort. Bromelain may also cause allergic reactions, especially in people who have other allergies.
Does bromelain help with PLC?
Early research shows that bromelain might help treat episodes of PLC. Pain after surgery. Some research shows that bromelain slightly reduces pain after removal of wisdom teeth. But it doesn't seem to reduce lockjaw or swelling. Swelling ( inflammation) of the nasal cavity and sinuses (rhinosinusitis).
Does bromelain help with muscle soreness?
Muscle soreness caused by exercise. Taking bromelain by mouth after intense exercise does not seem to prevent muscle soreness. It also doesn't reduce pain or weakness or improve flexibility. Insufficient Evidence for.
What is bromelain made of?
Bromelain is a mixture of proteolytic enzymes from the main stump of Ananas comosus. Bromelain is produced from the main pineapple stumps harvested after 4 years. The main stumps are pressed and put through an extraction process with water. The juice is then precipitated with acetone to produce raw bromelain.
What is the name of the enzymes found in pineapple fruit?
Bromelain is a mixture of proteolytic enzymes from the main stump of Ananas comosus. Enzymes from protein-digesting and milk-clotting enzymes found in pineapple fruit juice and stem tissue are called fruit bromelain and stem bromelain , respectively. O'Neil, M.J. (ed.).
Is stem bromelain an OTC?
Drug products containing certain active ingredients offered over-the-counter (OTC) for certain uses. A number of active ingredients have been present in OTC drug products for various uses, as described below. However, based on evidence currently available, there are inadequate data to establish general recognition of the safety and effectiveness of these ingredients for the specified uses: stem bromelain is included in digestive aid products.
Is bromelain a carbohydrate?
It has a role as a carbohydrate allergen. Protein-digesting and milk-clotting enzymes found in PINEAPPLE fruit juice and stem tissue. Enzymes from the two sources are distinguished as fruit bromelain and stem bromelain. This enzyme was formerly listed as EC 3.4.22.4.
Is bromelain an allergen?
/HUMAN EXPOSURE STUDIES/ ...Papain and Bromelain are used as tenderizers of meat and to clarify beer. Therefore, these enzymes are also potential ingestive allergens and may represent an unrecognized cause of an allergic reaction following a meal. As contact allergens the enzymes play a minor role; biodetergents in particular present no increased risk of skin damage for the user.
Where does bromelain come from?
Bromelain is a protein-digesting enzyme mixture derived from the stem, fruit, and juice of the pineapple plant. It has a centuries-long history of being used to treat medical ailments, primarily throughout Central and South America.
What are the side effects of bromelain?
As with all supplements, it’s important to discuss bromelain with your doctor prior to using it. Bromelain may cause mild side effects in some people, particularly when taken in high doses. These include: 1 diarrhea 2 nausea 3 vomiting 4 heavier-than-normal menstrual bleeding
How long does bromelain help with sinusitis?
Study participants were given bromelain daily for a 3-month period.
Why do people take bromelain?
People use bromelain topically, to remove dead skin from burns, and orally, to reduce inflammation and swelling — particularly of the nasal passages. Bromelain is also used as a digestive aid, for osteoarthritis, and to reduce soreness in aching muscles.
Does bromelain help cancer?
A 2010 study. Trusted Source. indicated that bromelain shows promise in combating cancer. Bromelain may have the ability to positively impact cancer cell growth, and it may help to control the key pathways supporting malignancy.
Is bromelain good for blood pressure?
Cardiovascular disease. reported that bromelain was effective at treating cardiovascular diseases, such as peripheral artery disease, stroke, heart attack, and high blood pressure. Bromelain inhibits the ability of blood platelets to stick or clump together (aggregation).
Is bromelain a natural substance?
Bromelain is a natural substance derived from pineapples. It has been studied extensively and may have significant, positive effects on multiple health conditions, including burns, osteoarthritis, and cancer.
What is the difference between papain and bromelain?
While these enzymes are processed and sold as supplement s, papain is naturally found in unripe papaya fruit, whereas bromelain comes from the juice and stems of pineapple. Speak with your doctor before taking any supplements.
What is a substrate in chemistry?
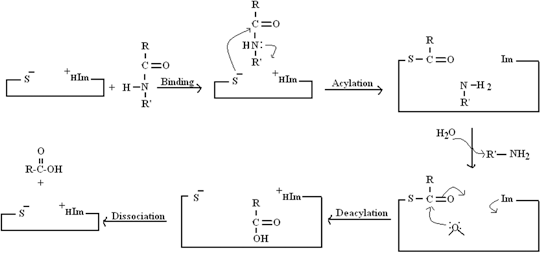
A substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrate (s). In the case of a single substrate, the substrate binds with the enzyme active site, and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. The substrate is transformed into one or more products, which are then released from the active site. The active site is now free to accept another substrate molecule. In enzymes with more than one substrate, these may bind in a particular order to the active site, before reacting together to produce products.
What breaks down proteins into amino acids?
As proteases, papain and bromelain help break proteins down into smaller segments called peptides and eventually into amino acids. Since your pancreas already produces proteases like pepsin, trypsin and chymotrypsin on its own
What enzymes make milk curdle?
Taking an eg from daily life , curd formation Chymosin, for example, is an enzyme that alters the casein structure to make milk curdle. Proteases are other enzymes that disrupt the casein structure by chopping up proteins, causing milk to curdle.
What is the lock and key model of enzymes?
The lock-and-key model of enzymes says that enzymes bind specific molecules and carry out reactions on those molecules. The enzyme recognizes the shape of its substrate and it is able to hold it in position in what is called the active site. The active site is the part of the enzyme that binds the substrate and carries out the reaction.
What does it mean when an enzyme is specific?
Enzyme specificity means that the enzyme only binds certain molecules that have the right shape. It will leave other molecules alone.
What happens when an enzyme is bound?
Once the molecule is bound, the enzyme carries out some change in the molecule. It might add new pieces on to the molecule or els
