
Procedures
Blalock-Taussig shunt is the operation of choice, at any age, for palliation of severe tetralogy of Fallot. Recent advances in techniques for the correction of tetralogy of Fallot in infancy [la] have not yet eliminated the need for creation of a systemic- pulmonary artery shunt as an emergency lifesav-
Self-care
Tetralogy of Fallot is 4 congenital heart defects. Children are born with this condition. This condition gets in the way of the heart's ability to pump oxygen-rich blood to the body. All children with tetralogy of Fallot need to have surgery to fix it. After surgery, most children will live healthy lives.
Is there a choice of palliation for Tetralogy of Fallot?
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is the leading cyanotic congenital heart disease ... To review the incidence, pattern, management and treatment outcomes of TOF at the OAUTHC. A retrospective audit was undertaken of hospital records, including echocardiograms ...
What is tetralogy of Fallot and how is it repaired?
Surgery for tetralogy of Fallot involves open-heart surgery to correct the defects (intracardiac repair) or a temporary procedure that uses a shunt. Most babies and older children have intracardiac repair. Intracardiac repair This open-heart surgery is usually done during the first year after birth and involves several repairs.
What is tetralogy of Fallot and how is it treated?
What is the goal of tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) therapy?
See more

When is surgery done for tetralogy of Fallot?
Tetralogy of Fallot surgery is typically done in the first year of a child's life to correct a congenital (something that's there from birth) heart defect.
Is TOF surgery is risky?
Adults with repaired ToF develop late complications, such as progressive exercise intolerance, arrhythmias, and heart failure [4, 6]. These complications are mainly due to pulmonary regurgitation, which leads to right ventricle dysfunction [7].
How is VSD surgery done?
During this surgery, a surgeon makes a cut down the front of the chest and divides the breastbone to reach the heart. A heart-lung machine is used to pump blood and act as the lungs during the surgery. Then the surgeon patches up the hole between the ventricles.
What is ICR surgery?
For those with congenital heart disease (CHD) associated with pulmonary hypertension (PH), a 2-stage procedure of pulmonary artery banding (PAB) and then intracardiac repair (ICR) in early infancy is performed to prevent such pulmonary vascular diseases in early infancy.
How long do tetralogy of Fallot patients live?
Tetralogy of Fallot is a rather common complex cardiac malformation with an incidence of 0.1/1000 live births. Without surgical intervention, patients had a 1 year survival rate of 66%, 49% after 2 years and only 10–15% after more than 20 years [1,2].
Is tetralogy of Fallot lifelong?
Historically, children born with TOF didn't live long enough to need care as adults. However, new treatment technologies are making it possible for these children to live full, active lives.
How long does a VSD surgery take?
The repair will take about 2 hours. The healthcare provider puts a small, flexible tube (catheter) into several blood vessels in the groin. One of the catheters will have a small device inside it. The provider threads the catheter through the blood vessel all the way to the ventricular septum.
What is the success rate of VSD surgery?
Overall, 96% of people with an unrepaired small defect live more than 25 years after diagnosis. Moderate: Survival rates for people with unrepaired moderate VSDs are a little bit lower, with about 86% of them surviving at least 25 years after diagnosis.
How long does it take for baby to recover from VSD surgery?
Your child will need at least 3 or 4 more weeks at home to recover. For larger surgeries, recovery may take 6 to 8 weeks. Talk with your child's health care provider about when your child can return to school, daycare, or take part in sports. Pain after surgery is normal.
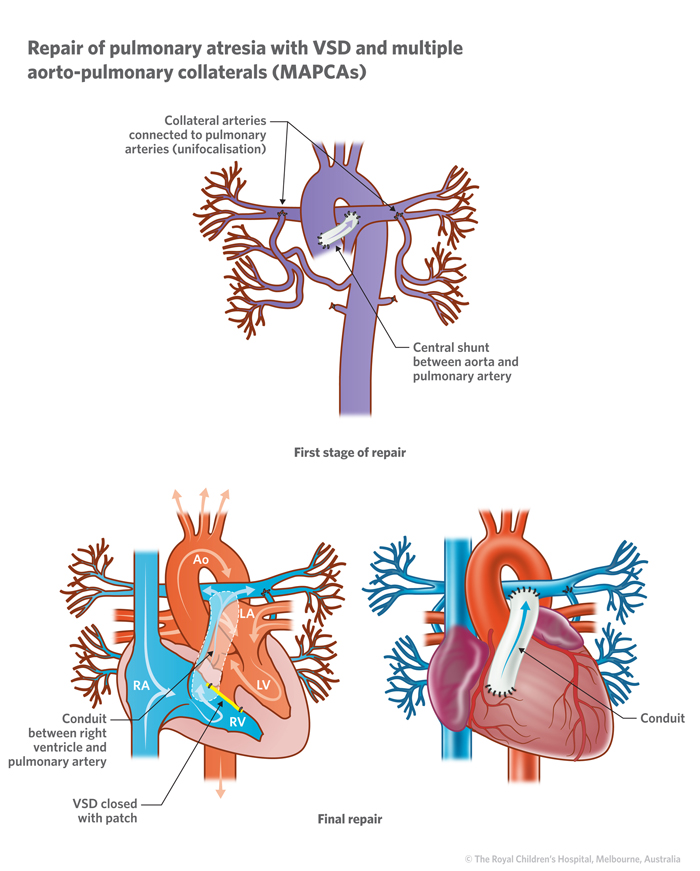
What is a central shunt for TOF?
A central shunt is an anastomosis between the ascending aorta and the main pulmonary artery made of PTFE. A central shunt uses a short PTFE connection between the ascending aorta and the main pulmonary artery.
What is the tetralogy of Fallot?
Tetralogy (teh-TRAL-o-je) of Fallot (fah-LO) is a congenital heart defect. A congenital heart defect is a problem with the heart's structure that's present at birth. This type of heart defect changes the normal flow of blood through the heart. Tetralogy of Fallot is a rare, complex heart defect that occurs in about 5 out of every 10,000 babies.
What is the goal of Fallot surgery?
The goal of surgery is to repair the four defects of tetralogy of Fallot so the heart can work as normally as possible. Surgery involves widening or replacing the pulmonary valve and enlarging the passage from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery. This improves blood flow to the lungs.
Why does my baby have a tet spell?
Low levels of oxygen in the blood cause cyanosis. Babies who have unrepaired tetralogy of Fallot sometimes have "tet spells" in response to an activity like crying or having a bowel movement. A tet spell occurs when the oxygen level in the blood suddenly drops. This causes the baby to become very blue.
Why does cytonosis occur?
Cyanosis occurs because the oxygen level in the blood is below normal. Tetralogy of Fallot must be repaired with open-heart surgery, either soon after birth or later in infancy. The timing of the surgery depends on how severely the pulmonary valve is narrowed.
Why do babies with fallot not gain weight?
Babies who have tetralogy of Fallot may not gain weight or grow as quickly as children who have healthy hearts because they tire easily while feeding. Children who have tetralogy of Fallot also may have clubbing. Clubbing is the widening or rounding of the skin or bone around the tips of the fingers.
What are the symptoms of Fallot?
Cyanosis is a bluish tint to the skin, lips, and fingernails. Other signs and symptoms include a heart murmur, delayed growth and development, and clubbing. Clubbing is the widening or rounding of the skin or bone around the tips of the fingers.
What are the long term problems with Fallot?
Teenagers and adults who had surgery to repair tetralogy of Fallot may have long-term heart problems, such as heart function problems, arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats), or problems resulting from the original repair. These problems are treated with medicines, procedures, and surgery.
When is Fallot surgery done?
This open-heart surgery is usually done during the first year after birth and involves several repairs. Adults with tetralogy of Fallot rarely may undergo this procedure if they didn't have surgical repair as children.
How to treat fallot?
Treatment. Surgery is the only effective treatment for tetralogy of Fallot. Surgical options include intracardiac repair or a temporary procedure that uses a shunt. However, most babies and older children have intracardiac repair.
What is aortic root dilation?
Aortic root dilation, in which the ascending aorta enlarges. Sudden cardiac death. Complications can continue throughout childhood, adolescence and adulthood for people with tetralogy of Fallot. Most adults with repaired tetralogy of Fallot may require another procedure or intervention during their lifetimes.
What is the best test for Fallot?
Echocardiography. Echocardiograms use high-pitched sound waves to produce an image of the heart. Sound waves bounce off the heart and produce moving images that can be viewed on a video screen. This test is generally used to diagnose tetralogy of Fallot. It allows your or your baby's doctor to determine if there is a ventricular septal defect ...
What is the purpose of a ventricular septal defect patch?
The surgeon places a patch over the ventricular septal defect to close the hole between the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles). He or she also repairs or replaces the narrowed pulmonary valve and widens the pulmonary arteries to increase blood flow to the lungs.
What is the procedure to check a baby's heart?
This test can also help your or your baby's doctor to plan treatment for the condition. Electrocardiogram. An electrocardiogram records the electrical activity in the heart each time it contracts. During this procedure, patches with wires (electrodes) are placed on your or your baby's chest, wrists and ankles.
What happens if you have a tetralogy of Fallot?
People with repaired tetralogy of Fallot have a higher risk of heart rhythm disturbances called arrhythmias. These can originate from the atria or the ventricles. Sometimes they may cause dizziness or fainting. You may need medicine to control them. Sometimes patients also need *blood thinners to reduce the risk of stroke related to the arrhythmias. In rare cases, you may need a procedure in the cardiac catheterization laboratory or the operating room to eliminate these arrhythmias and control symptoms. See the Arrhythmias section for more information. Some patients need pacemakers or implantable defibrillators to treat their arrhythmias.
What causes tetralogy of fallot in children?
In most children, the cause of tetralogy of Fallot isn't known. It's a common type of heart defect. It may be seen more commonly in children with Down syndrome or DiGeorge syndrome. Some children can have other heart defects along with tetralogy of Fallot.
What to do after Fallot repair?
You may need to take medicine before or after your operation to help your heart muscle contract or to control heart rhythm abnormalities.
Where does blood travel in a fallot child?
In a child with tetralogy of Fallot, blood can travel across the hole (VSD) from the right pumping chamber (right ventricle) to the left pumping chamber (left ventricle) and out into the body artery (aorta). Obstruction in the pulmonary valve leading from the right ventricle to the lung artery prevents the normal amount ...
Can tetralogy of Fallot be repaired?
Most adults with tetralogy of Fallot have had it repaired in childhood. Many people are symptom free but may have residual or recurrent problems. These include valve leakage of blood into the heart's right side, blockage of blood leaving the heart's right side and heart rhythm problems. Some patients with these problems may have limited exercise ...
Can a repaired fallot cause dizziness?
Patients with repaired tetralogy of Fallot have a higher risk of heart rhythm disturbances called arrhythmias. Sometimes these may cause dizziness or fainting. Generally, the long-term outlook is good, but some patients may need medicines, heart catheterization or even more surgery.
Is Fallot a heart defect?
It's a common type of heart defect. It may be seen more commonly in patients with Down syndrome (in association with AV canal defects) or DiGeorge syndrome. Some patients can have other heart defects along with tetralogy of Fallot.
How to treat fallot tetralogy?
Tetralogy of Fallot can be treated by surgery soon after the baby is born . During surgery, doctors widen or replace the pulmonary valve and enlarge the passage to the pulmonary artery. They also will place a patch over the ventricular septal defect to close the hole between the two lower chambers of the heart.
What is the tetralogy of fallot?
Facts about Tetralogy of Fallot. Tetralogy of Fallot (pronounced te-tral-uh-jee of Fal-oh) is a birth defect that affects normal blood flow through the heart. It happens when a baby’s heart does not form correctly as the baby grows and develops in the mother’s womb during pregnancy.
What is fallot test?
During pregnancy, there are screening tests (also called prenatal tests) to check for birth defects and other conditions. Tetralogy of Fallot might be seen during an ultrasound (which creates pictures of the body).
What are the four defects of the heart called?
Tetralogy of Fallot is made up of the following four defects of the heart and its blood vessels: A hole in the wall between the two lower chambers―or ventricles―of the heart. This condition also is called a ventricular septal defect. A narrowing of the pulmonary valve and main pulmonary artery. This condition also is called pulmonary stenosis.
Why is Fallot a critical heart defect?
Because a baby with tetralogy of Fallot may need surgery or other procedures soon after birth, this birth defect is considered a critical congenital heart defect. Congenital means present at birth. This heart defect can cause oxygen in the blood that flows to the rest of the body to be reduced.
Why does Fallot have blue skin?
Infants with tetralogy of Fallot can have a bluish-looking skin color―called cyanosis―because their blood doesn’t carry enough oxygen. At birth, infants might not have blue-looking skin, but later might develop sudden episodes of bluish skin during crying or feeding. These episodes are called tet spells. Infants with tetralogy of Fallot ...
When is tetralogy of fallot diagnosed?
After a Baby Is Born. Tetralogy of Fallot usually is diagnosed after a baby is born, often after the infant has an episode of turning blue during crying or feeding (a tet spell). Some findings on a physical exam may make the health care provider think a baby may have tetralogy of Fallot, including bluish-looking skin or a heart murmur ...
How old do you have to be to fix tetralogy of fallot?
All children with tetralogy of Fallot need to have surgery to fix it. Most children have it before they turn 1 year old. It's often done around 6 months of age. A team of heart surgeons will do your child's surgery. To fix TOF your doctor may use a patch to close ventricle septal defect (VSD).
How does tetralogy of Fallot affect the heart?
This condition gets in the way of the heart's ability to pump oxygen-rich blood to the body. All children with tetralogy of Fallot need to have surgery to fix it. After surgery, most children will live healthy lives.
What is the TOF in a child?
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is a group of 4 congenital heart defects. This means that your child is born with them. These 4 problems occur together (tetralogy refers to 4). They are:
What does a fallot test show?
This test records the electrical activity of the heart. It also shows abnormal rhythms (arrhythmias or dysrhythmias) and spots heart muscle stress. These issues may be caused by caused by tetralogy of Fallot.
Can a child be tired after tof surgery?
After surgery, your child may become tired easily and sleep more. Eventually, most children are able to be active. Children's activity levels, appetite, and growth become normal soon after surgery. But, some children who had surgery for TOF can have problems learning or growing normally.
Does TOF cause cyanosis?
Some children with TOF may only have slightly lower than normal oxygen levels in their blood. These children don't usually have bluish skin (cyanosis). Other children with TOF will have low oxygen levels in their blood.
Why is tetralogy of fallot unknown?
Tetralogy of Fallot occurs during fetal growth, when the baby's heart is developing . While factors such as poor maternal nutrition, viral illness or genetic disorders might increase the risk of this condition , in most cases the cause of tetralogy of Fallot is unknown.
What are the four abnormalities that make up the tetralogy of Fallot?
The four abnormalities that make up the tetralogy of Fallot include: Pulmonary valve stenosis. Pulmonary valve stenosis is a narrowing of the pulmonary valve — the valve that separates the lower right chamber of the heart (right ventricle) from the main blood vessel leading to the lungs (pulmonary artery).
What are the four congenital defects in Fallot?
The four defects include a ventricular septal defect (VSD), pulmonary valve stenosis, a misplaced aorta and a thickened right ventricular wall (right ventricular hypertrophy). They usually result in an insufficient amount of oxygenated blood reaching the body.
Why does Fallot have blue skin?
Infants and children with tetralogy of Fallot usually have blue-tinged skin because their blood doesn't carry enough oxygen. Tetralogy of Fallot is often diagnosed during infancy or soon after. However, tetralogy of Fallot might not be detected until later in life in some adults, depending on the severity of the defects and symptoms.
What causes fallot in babies?
These risk factors include: A viral illness during pregnancy, such as rubella (German measles) Alcoholism during pregnancy. Poor nutrition during pregnancy.
Why does fallot occur?
Causes. Tetralogy of Fallot occurs during fetal growth, when the baby's heart is developing. While factors such as poor maternal nutrition, viral illness or genetic disorders might increase the risk of this condition, in most cases the cause of tetralogy of Fallot is unknown.
Which artery is shifted slightly to the right in Fallot?
Normally the aorta — the main artery leading out to the body — branches off the left ventricle. In tetralogy of Fallot, the aorta is shifted slightly to the right and lies directly above the ventricular septal defect.
Overview
Tetralogy of Fallot is a heart condition in which a baby is born with four changes in how their heart developed. These issues make it hard for the baby’s heart to send enough oxygen to the entire body.
Symptoms and Causes
Tetralogy of Fallot symptoms can be mild, moderate or severe. They usually get worse over time without treatment.
Diagnosis and Tests
Your healthcare provider can diagnose tetralogy of Fallot before or after your baby is born. They usually find it in the first few weeks or months of life.
Management and Treatment
Without tetralogy of Fallot surgery, symptoms usually get worse. Your baby can have surgery soon after birth that will make blood move through the heart the way it should. They can make the pulmonary valve and the path to the pulmonary artery bigger.
Prevention
Although healthcare providers don’t know the cause of tetralogy of Fallot, you may be able to reduce your unborn baby’s risk of tetralogy of Fallot in these ways:
Living With
After tetralogy of Fallot surgery, your child will need regular follow-up appointments with a provider who specializes in children’s hearts. This care will continue into adulthood.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Specialist to consult
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment
- All babies who have tetralogy of Fallot need corrective surgery performed by a heart (cardiovascular) surgeon. Without treatment, your baby might not grow and develop properly. Your doctor will determine the most appropriate surgery and the timing of the surgery based on your or your child's condition. Some children may need medicine while waiting ...
What Is Tetralogy of Fallot?
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Occurrence
- After tetralogy of Fallot treatment, your doctor might recommend lifestyle changes and tips to help you manage your or your child's condition, including: 1. Preventing infection.A child, adolescent or adult who has severe heart defects might need to take preventive antibiotics before certain dental procedures and surgeries. Your or your child's doctor can tell you if this is necess…
Causes and Risk Factors
- It's natural to feel worried if you or your child are diagnosed with a congenital heart defect. Here are a few ways to help you ease stress and anxiety and best manage your or your child's condition. 1. Join a support group.A support group allows you to share personal experiences and feelings with others who are going through similar challenges. Some people find that a support …
Diagnosis
- You're likely to start by seeing your primary care doctor. You or your child will be referred to a doctor trained in treating heart conditions (cardiologist). Here's some information to help you get ready for your appointment, and what to expect from your or your child's doctor.
Treatments
References
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that each year about 1,660 babies in the United States are born with tetralogy of Fallot.1In other words, about 1 in every 2518 babies born in the United States each year are born with tetratology of Fallot.