What are the possible causes of angina?
What causes it?
- Coronary artery disease. When a substance called plaque builds up on the walls of the heart’s arteries, causing them to narrow.
- Coronary microvascular disease. When the small arteries of the heart become damaged, reducing the flow of blood.
- Spasms. A sudden spasm of the arteries around the heart can cause them to narrow, limiting blood flow.
- Blood clots. ...
What does prinzmental angina mean?
Prinzmetal’s angina is a form of chest pain, pressure, or tightness (angina) caused by spasms in the arteries that supply blood to the heart. It is a form of unstable angina, meaning that it occurs at rest, often without a predictable pattern. This is in contrast to stable angina, in which chest pain occurs in a predictable pattern during exertion or exercise.
How is Prinzmetal's diagnosed?
So, the things healthcare providers look for to diagnose Prinzmetal angina are:
- typical "anginal" chest pain,
- accompanied by dramatic changes on the ECG,
- which are relieved by nitrate administration,
- with "normal' coronary arteries demonstrated on cardiac catheterization.
Is princemetal angina hereditary?
Studies on Prinzmetal angina haven’t shown it to be hereditary. However, some studies indicate that there may be a genetic factor in the condition. For instance, there is a higher occurrence of Prinzmetal angina in Japanese people than white people.

Who gets Prinzmetal angina?
Prinzmetal's angina is rare, representing about two out of 100 cases of angina, and usually occurs in younger patients than those who have other kinds of angina.
What is prinzmetal's variant angina?
Prinzmetal angina (vasospastic angina or variant angina) is a known clinical condition characterized by chest discomfort or pain at rest with transient electrocardiographic changes in the ST segment, and with a prompt response to nitrates. These symptoms occur due to abnormal coronary artery spasm.
What causes vasospastic angina?
Vasospastic angina is also known as prinzmetal angina, variant angina or coronary artery spasm. It develops when a coronary artery supplying blood and oxygen to your heart goes into spasm and suddenly narrows.
How is prinzmetal's angina diagnosed?
It is diagnosed by history, electrocardiogram, or coronary-artery angiography. Provocative tests, such as the cold-pressor test or intravenous ergonovine maleate, are sometimes used to aid diagnosis of PVA.
What is the drug of choice for Prinzmetal angina?
(Prinzmetal Angina) Symptoms include angina at rest and rarely with exertion. Diagnosis is by electrocardiography (ECG) and provocative testing with ergonovine or acetylcholine. Treatment is with calcium channel blockers and sublingual nitroglycerin.
What drugs cause coronary artery spasm?
Coronary spasm is also associated with smoking, cocaine, amphetamine, marijuana and alcohol consumption, which can often explain myocardial infarction in young patients with few traditional cardiovascular risk factors.
What does prinzmetal mean?
Prinzmetal angina, or variant angina, is caused by such a spasm in a coronary artery. These spasms can produce ischemia (oxygen starvation) in the part of the heart muscle supplied by the affected artery, and the symptoms of angina follow.
Is Prinzmetal angina stable or unstable?
Unstable angina is dangerous and requires emergency treatment. Variant angina (Prinzmetal angina). Variant angina, also called Prinzmetal angina, isn't due to coronary artery disease. It's caused by a spasm in the heart's arteries that temporarily reduces blood flow.
Can caffeine cause coronary artery spasm?
In vitro, caffeine has physiological effects on the concentration of intracellular calcium in the vascular smooth muscle and could induce coronary vasospasm; in vivo, caffeine reduces myocardial blood flow during exercise [97] .
How long do coronary artery spasms last?
Coronary artery spasms usually happen during sleep at the same time each day. They can last for up to 30 minutes and sometimes result in a loss of consciousness.
Is coronary artery spasm hereditary?
Coronary artery spasms do not seem to be hereditary. The primary causes of coronary artery spasms include: Smoking. Exposure to extreme cold.
Can anxiety cause angina?
Panic disorder is associated with elevated rates of microvascular angina. Microvascular angina is a condition in which a patient with chest pain has coronary blood flow abnormalities in small cardiac vessels despite normal coronary angiography.
Can Prinzmetal angina be cured?
Prinzmetal angina is a rare condition that produces angina due to spasm in a coronary artery. While Prinzmetal angina can sometimes lead to severe consequences (especially in smokers or people who abuse cocaine or amphetamines), it can usually be treated very successfully once the correct diagnosis is made.
How long can you live with variant angina?
Two hundred forty-five patients with variant angina were followed for an average of 80.5 months (range, 36-184 months). Survival rate at 1, 3, 5, and 10 years was 98%, 97%, 97%, and 93%, respectively. Survival rate without myocardial infarction at 1, 3, 5, and 10 years was 86%, 85%, 83%, and 81%, respectively.
What does prinzmetal mean?
Prinzmetal's variant angina (PVA) is characterized by recurrent episodes of chest pain (angina) that usually occur when a person is at rest, between midnight and early morning. Typical angina, by contrast, is often triggered by physical exertion or emotional stress.
How is variant angina treated?
Variant angina is often treated with medications called calcium channel blockers. These medications can decrease variant angina attacks and are often used in combination with nitrates during attacks. If another condition is contributing to your angina, such as CAD, then it will need to be treated as well..
Who Gets Prinzmetal Angina?
Prinzmetal angina is more common in women than in men. People with this condition are often relatively young, quite healthy, and commonly have very few risk factors for typical heart disease—with the exception of smoking. Smoking is commonly a major factor in provoking angina in people with this condition because tobacco products can cause arterial spasm. The autonomic nervous system may play a role as well.
What is the first line agent for vasospastic angina?
Calcium channel blockers are often the first line agent used for vasospastic angina. If additional medication is required, a nitrate may be added to a calcium channel blocker.
What is acetylcholine ergonovine?
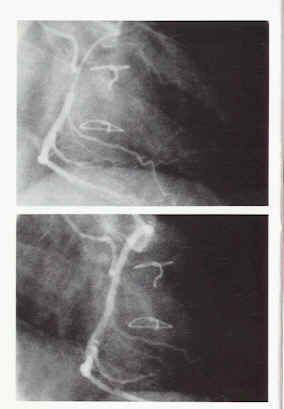
Testing with acetylcholine or ergonovine is performed during a cardiac catheterization. This kind of testing yields the correct diagnosis more reliably than the hyperventilation test. In this test, one of these drugs is injected intravenously (ergonovine) or directly into a coronary artery ( acetylcholine). In people with Prinzmental angina, this often provokes the same localized coronary artery spasm that causes their symptoms. This localized spasm can be visualized during the catheterization procedure. Currently, testing with acetylcholine is considered safer than testing with ergonovine and is the preferred invasive provocative test. 1
Can Prinzmental angina cause heart block?
While in general the outlook of patients with Prinzmental angina is quite good, this condition can trigger dangerous and potentially fatal cardiac arrhythmias. The type of arrhythmia provoked depends upon which coronary artery is involved. For example, if the right coronary artery is involved, it could cause a heart block, and if the left anterior descending artery is involved it might result in ventricular tachycardia.
Is Prinzmetal angina a provocative test?
Sometimes, however, a cardiac catheterization with “provocative testing” is necessary to make the diagnosis. Because Prinzmetal angina is caused by coronary artery spasm rather than by a fixed blockage in the artery, the catheterization usually shows “normal” coronary arteries. Further, because Prinzmetal angina is not the only kind ...
Can you get Prinzmetal Angina from cocaine?
The more severe consequences of Prinzmetal angina are much more likely to occur in smokers, and in people who abuse cocaine or amphetamines.
Is Prinzmetal angina more common in women than men?
Prinzmetal angina is more common in women than in men. People with this condition are often relatively young, quite healthy, and commonly have very few risk factors for typical heart disease — with the exception of smoking. Smoking is commonly a major factor in provoking angina in people with this condition because tobacco products can cause arterial spasm. The autonomic nervous system may play a role as well.
What is Prinzmetal angina?
Prinzmetal angina (vasospastic angina or variant angina) is a known clinical condition characterized by chest discomfort or pain at rest with transient electrocardiographic changes in the ST segment, and with a prompt response to nitrates. These symptoms occur due to abnormal coronary artery spasm. This activity reviews the evaluation and management of Prinzmetal angina and explains the role of the interprofessional team in improving care for patients with this condition.
What are the risk factors for vasospastic angina?
Typical cardiovascular risk factors have not directly been associated with the presence of vasospastic angina, except for cigarette smoking and inflammatory states determined by high hs-CRP levels. A metabolic disorder such as insulin resistance has also been associated with vasospastic angina.
How long does it take for vasospastic angina to go away?
Overall, 75% of patients can be free of myocardial infarct at 5 years. The factor that might independently determine the free infarct survival includes the presence and severity of pre-existing coronary stenosis, the number of vessels with hyperreactivity or spams, and the use of calcium channel blockers. Half of the patients with angina will have persistent symptoms.
What is a vasospastic angina?
Vasospastic angina, variant angina, or Prinzmetal angina is a known clinical entity characterized by chest pain at rest with transient ischemic electrocardiographic changes in the ST segment, with a prompt response to nitrates. These symptoms are attributed to coronary arteries spasm.[1][2]
How to reduce angina?
Treatment is focused on decreasing episodes of angina and preventing complications like myocardial injury and arrhythmia. Lifestyle modifications should be encouraged, especially smoking cessation. This is one of the critical interventions in reducing the frequency of episodes. Avoiding medications or drugs that can trigger coronary vasospasm, for example, cocaine, marijuana, and ephedrine-based products) is also important. [11][10]
What drugs cause chest pain?
Several drugs such as ephedrine and sumatriptan can cause typical chest pain due to coronary spasm. Recreational drugs like cocaine, amphetamines, alcohol, and marijuana are also possible precipitating factors.
Why should beta blockers be avoided?
The use of beta-blockers, especially those with nonselective adrenoceptor blocking effects, should be avoided because these drugs can aggravate the symptoms.
What are the risk factors for vasospastic angina?
Typical cardiovascular risk factors have not directly been associated with the presence of vasospastic angina, except for cigarette smoking and inflammatory states determined by high high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) levels. A metabolic disorder such as insulin resistance has also been associated with vasospastic angina.
Is calcium channel blocker effective for vasospastic angina?
Calcium antagonist plays an important role in the management of vasospastic angina. It is a first-line treatment due to a vasodilation effect in the coronary vasculature. Calcium antagonist is effective in alleviating symptoms in 90% of patients. Moreover, one study demonstrated that the use of calcium channel blocker therapy was an independent predictor of myocardial infarct-free survival in vasospastic angina patients.
Is Prinzmetal angina good?
In general, the long-term prognosis for Prinzmetal variant angina is good if patients get adequate treatment 6). Overall, 75% of patients can be free of myocardial infarct (heart attack) at 5 years 7). The factor that might independently determine the free infarct survival includes the presence and severity of pre-existing coronary stenosis, the number of vessels with hyperreactivity or spams, and the use of calcium channel blockers. Half of the patients with angina will have persistent symptoms.
When does Prinzmetal angina occur?
Unlike typical angina – which is often triggered by exertion or emotional stress – Prinzmetal’s angina almost always occurs when a person is at rest, usually between midnight and early morning. These attacks can be very painful.
Why does my angina hurt?
Causes of Variant (Prinzmetal) Angina: The pain from variant angina is caused by a spasm in the coronary arteries (which supply blood to the heart muscle). The coronary arteries can spasm as a result of: Exposure to cold weather. Stress.
How long does it take for Prinzmetal to stop working?
After six to 12 months of treatment, doctors may gradually reduce the medication. Prinzmetal's angina is a chronic condition that will need to be followed by your healthcare provider even though the prognosis is generally good. Track your angina symptoms with our Angina Log.
What are the different types of angina?
Prinzmetal angina may also be referred to as: 1 Variant angina 2 Prinzmetal's variant angina 3 Angina inversa
Is Prinzmetal's angina rare?
Angina inversa. Prinzmetal’s angina is rare, representing about two out of 100 cases of angina, and usually occurs in younger patients than those who have other kinds of angina.
What is Prinzmetal variant angina?
The American Heart Association is the nation’s oldest and largest voluntary organization dedicated to fighting heart disease and stroke.
What causes PVA in a patient?
In some cases it may be triggered by alcohol withdrawal, stress, exposure to cold, certain medications, or use of stimulants such as cocaine. [1] [3] The diagnosis of PVA involves findings on an electrocardiogram, evidence of the spasms on angiogram, and relief of sudden symptoms with medicines called nitrates. [2]
What is the pain of a PVA?
Episodes of PVA can be very painful, and may last from several minutes to thirty minutes. [1] [2] [3] In some cases the pain may spread from the chest to the head, shoulder, or arm. [3] The pain associated with PVA is caused by a spasm in the arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle ( coronary arteries ). This results in an obstruction of blood flow. [1] [2] In some people, persistent spasms increase the risk for serious complications such as a life-threatening arrhythmia or heart attack. [2]
How long does angina last?
The main symptom of Prinzmetal's variant angina is recurring episodes of chest pain (angina) that usually occur when a person is at rest, during bedtime hours (around midnight to 8am). Some people report feeling "discomfort" rather than "pain." In some people, pain may spread to the neck, jaw, shoulder, or arm. Other sensations during episodes may include tightness or pressure in the chest, "heart burn," nausea, sweating, dizziness, and palpitations. Episodes tend to last around 5 to 15 minutes (longer in some cases), and tend to be similar to each other.
What is the diagnosis of PVA?
The diagnosis of PVA involves findings on an electrocardiogram, evidence of the spasms on angiogram, and relief of sudden symptoms with medicines called nitrates. [2]
Does smoking cause PVA?
For people with PVA who smoke, quitting smoking can lead to a significant decrease in the frequency of episodes. [2] . While most people with PVA do not experience serious complications, it is a chronic condition that needs to be monitored over time. [1]
What is Prinzmetal's angina?
Causes. Treatment. Prognosis. Prinzmetal’s angina is a form of chest pain, pressure, or tightness (angina) caused by spasms in the arteries that supply blood to the heart. It is a form of unstable angina, meaning that it occurs at rest, often without a predictable pattern. This is in contrast to stable angina, in ...
Why does Prinzmetal cause chest pain?
The chest pain of Prinzmetal’sangina is caused by coronary artery spasm, an abnormal or involuntary constriction of the muscle in a coronary artery. This spasm makes the diameter of the artery smaller, restricting the supply of blood and oxygen to the heart, causing chest pain. In rare cases if the spasm is not.
Why does Prinzmetal pain occur?
The pain usually occurs between midnight and approximately 8:00 AM. Prinzmetal’s angina may be brought on by hyperventilation, exposure to cold, or extreme emotional stress. Prinzmetal’sangina is named after the researcher who first noted that coronary artery spasms were to blame. It is also called variant angina because of the unusual pattern ...
Why is it important to stop smoking with Prinzmetal?
It is especially important to stop smoking because smoking increases the likelihood of coronary artery spasms. 5 By lowering your risk factors, you will reduce your chances of developing atherosclerosis. In addition, people diagnosed with Prinzmetal’s angina should avoid exposure to cold and high stress situations since these can trigger spasms.
How old is the average Prinzmetal patient?
People with Prinzmetal’sangina are generally younger than those with stable angina; the average Prinzmetal’s angina patient is between 51 and 57 years old. They also have fewer risk factors for heart disease with the exception of smoking, which is the most significant risk factor for coronary artery spasm.
What is the best medicine for chest pain?
If you continue to experience episodes of chest pain, then a different class of calcium channel blocker or a long-acting nitrate may be given. Nitroglycerin is used when you are experiencing a spasm to stop it, thereby alleviating pain; it is not used as a preventive medication.
What is Prinzmetal used for?
Prinzmetal’sangina is treated with medications, specifically nitroglycerin (NTG), long-acting nitrates, and calcium channel blockers, all of which widen or open the blood vessels and improve blood and oxygen flow to the heart muscle. Calcium channel blockers are generally prescribed first.
What Is Prinzmetal Angina?
Prinzmetal Angina also known by the name of Coronary Artery Spasm is a medical condition in which there is temporary spasm of the coronary arteries causing pain and discomfort. This condition is usually seen in people under the age of 50. These spasms can be extremely mild to very severe. If the spasms last for more than 15 minutes then it can cause some damage to the heart or may even cause a heart attack.
How Is Prinzmetal Angina Treated?
Majority of the symptoms of Prinzmetal Angina can be relieved by taking nitrates and calcium-channel blockers. These medications dilate and relax the arteries and restore normal flow of the blood to the heart. These medications also are helpful in preventing frequent episodes of Prinzmetal Angina. Studies also suggest that statins have also shown to be effective in relieving symptoms of Prinzmetal Angina. Statins are also helpful in preventing buildup of plaques. Lifestyle modification is the key to prevent episodes of Prinzmetal Angina with abstaining from smoking and drinking alcohol or using recreational drugs.
What Is Angina?
Angina is the name given to discomfort and pain resulting due to some heart muscle not receiving enough blood supply that is required for it to function. Angina is normally caused due to coronary heart disease or CHD. This condition arises due to the arteries becoming blocked with plaque. This plaque may start to slowly build and over time cause the arteries to become so narrow that it may affect the blood supply to the heart. Angina is said to occur when the heart gets stressed and needs to work more than usual for the body to function normally. This happens during extreme physical activity or severe emotional response. Angina is very rarely caused by coronary artery spasms.
How Can I Reduce My Risk Of Prinzmetal Angina?
The best way to reduce the risk of having Prinzmetal Angina is by having a healthy lifestyle. This can be done by the following:
What Is The Difference Between Angina Caused By Coronary Heart Disease And Coronary Artery Spasm?
Individuals who have angina due to coronary heart disease will have pain with activities or extreme emotion which will go away by resting or taking an anginal medication like nitroglycerine. Individuals whose pain is caused due to coronary artery spasms will have pain first thing in the morning or while at rest instead of when doing physical activity.
What causes angina in the heart?
When you climb stairs, exercise or walk, your heart demands more blood, but narrowed arteries slow down blood flow. Besides physical activity, other factors such as emotional stress, cold temperatures, heavy meals and smoking also can narrow arteries and trigger angina.
Why is my angina unstable?
Unstable angina can also be caused by blood clots that block or partially block your heart's blood vessels. Unstable angina worsens and isn't relieved by rest or your usual medications. If the blood flow doesn't improve, your heart is starved of oxygen and a heart attack occurs.
What is the pain in the chest called?
Overview. Angina is a type of chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart. Angina (an-JIE-nuh or AN-juh-nuh) is a symptom of coronary artery disease. Angina, also called angina pectoris, is often described as squeezing, pressure, heaviness, tightness or pain in your chest. Some people with angina symptoms say angina feels like ...
How does stress affect your heart?
Stress. Stress can increase your risk of angina and heart attacks. Too much stress, as well as anger, also can raise your blood pressure. Surges of hormones produced during stress can narrow your arteries and worsen angina.
What is the risk of heart attacks and angina?
Cholesterol is a major part of the deposits that can narrow arteries throughout your body, including those that supply your heart. A high level of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, also known as "bad" cholesterol, increases your risk of angina and heart attacks. A high level of triglycerides, a type of blood fat related to your diet, also is unhealthy.
What are the characteristics of unstable angina?
Characteristics of unstable angina (a medical emergency) Occurs even at rest. Is a change in your usual pattern of angina. Is unexpected. Is usually more severe and lasts longer than stable angina, maybe 30 minutes or longer. May not disappear with rest or use of angina medication. Might signal a heart attack.
Can angina be different in women?
Angina in women can be different than men. American Heart Association. http://www.heart.org/HEARTORG/Conditions/HeartAttack/WarningSignsofaHeartAttack/Angina-in-Women-Can-Be-Different-Than-Men_UCM_448902_Article.jsp#.WgKDTXZrxEZ. Accessed Feb. 10, 2020.